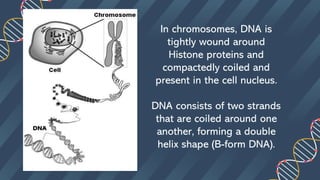
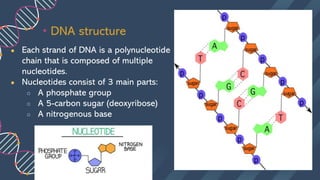
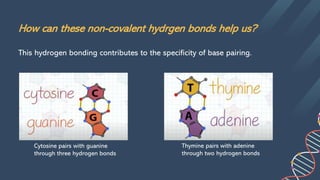
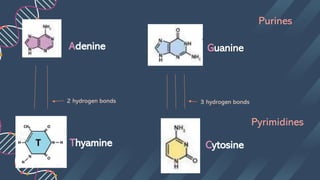
The document describes the structure of DNA. DNA consists of two strands coiled around each other in a double helix shape. Each strand is composed of nucleotides, which contain a phosphate group, 5-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), and a nitrogenous base. The bases on each strand bond with their complementary bases on the other strand through hydrogen bonds, with cytosine bonding to guanine via three hydrogen bonds and thymine bonding to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. This hydrogen bonding contributes to the specificity of base pairing in DNA.