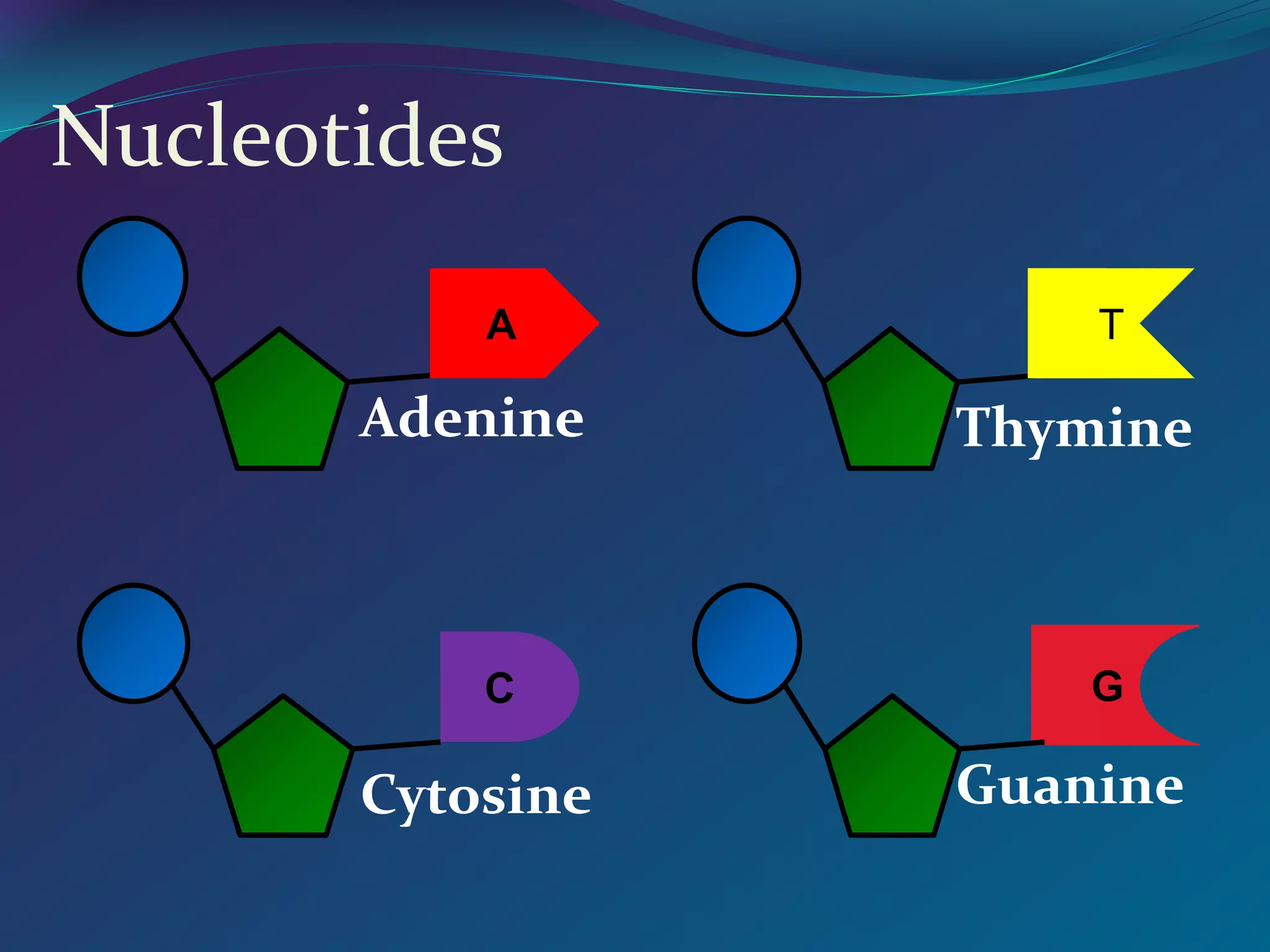
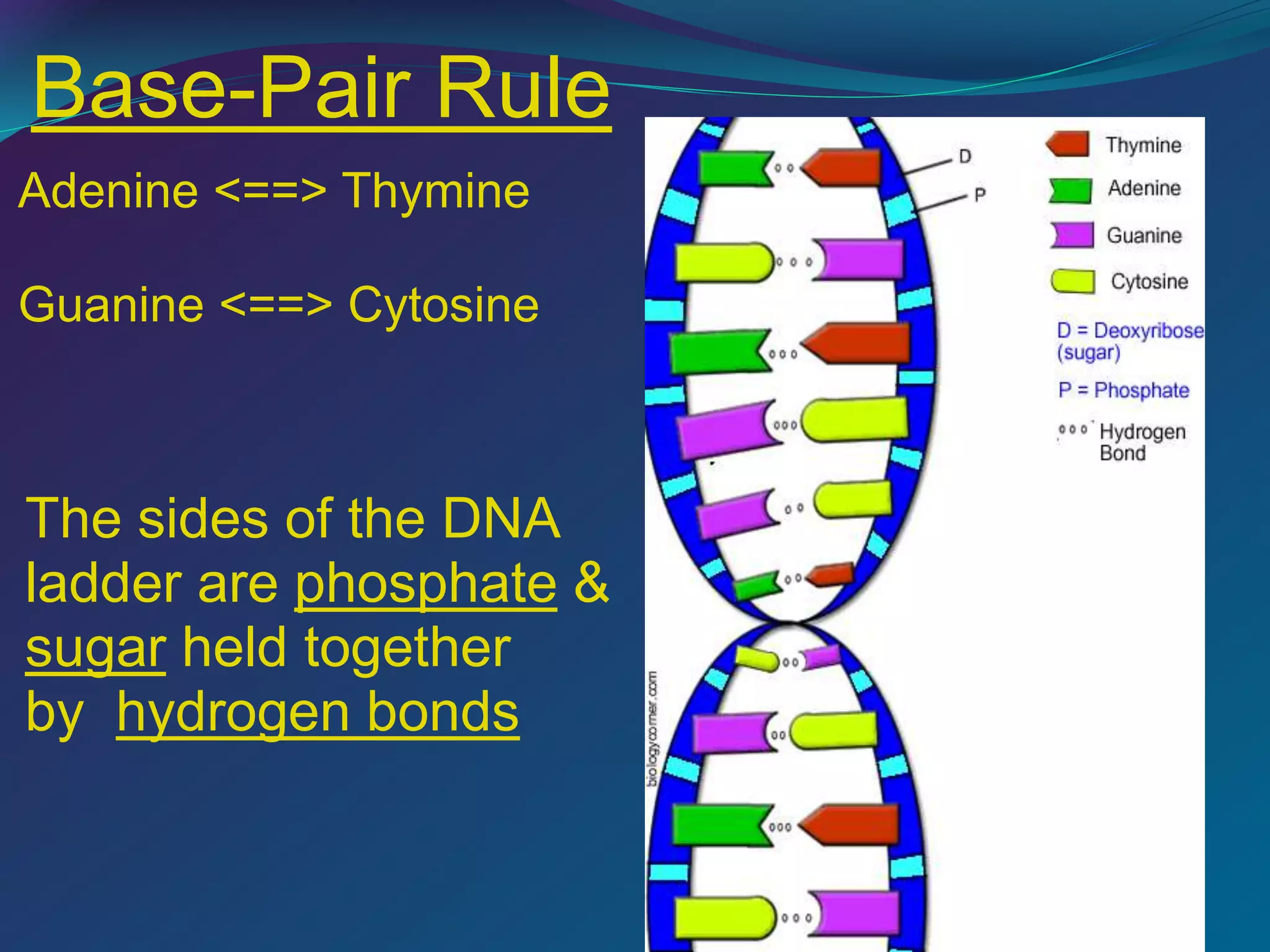
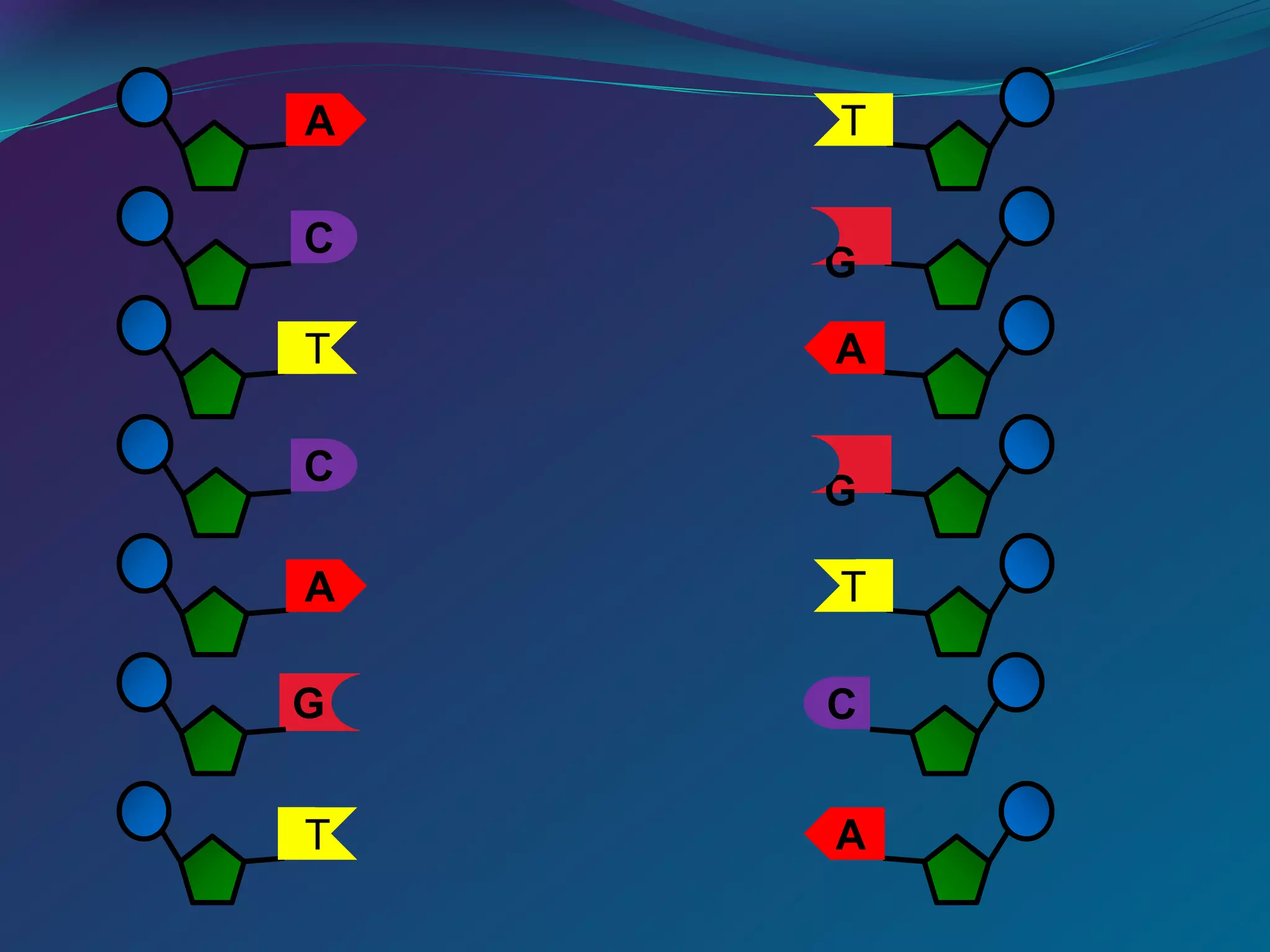
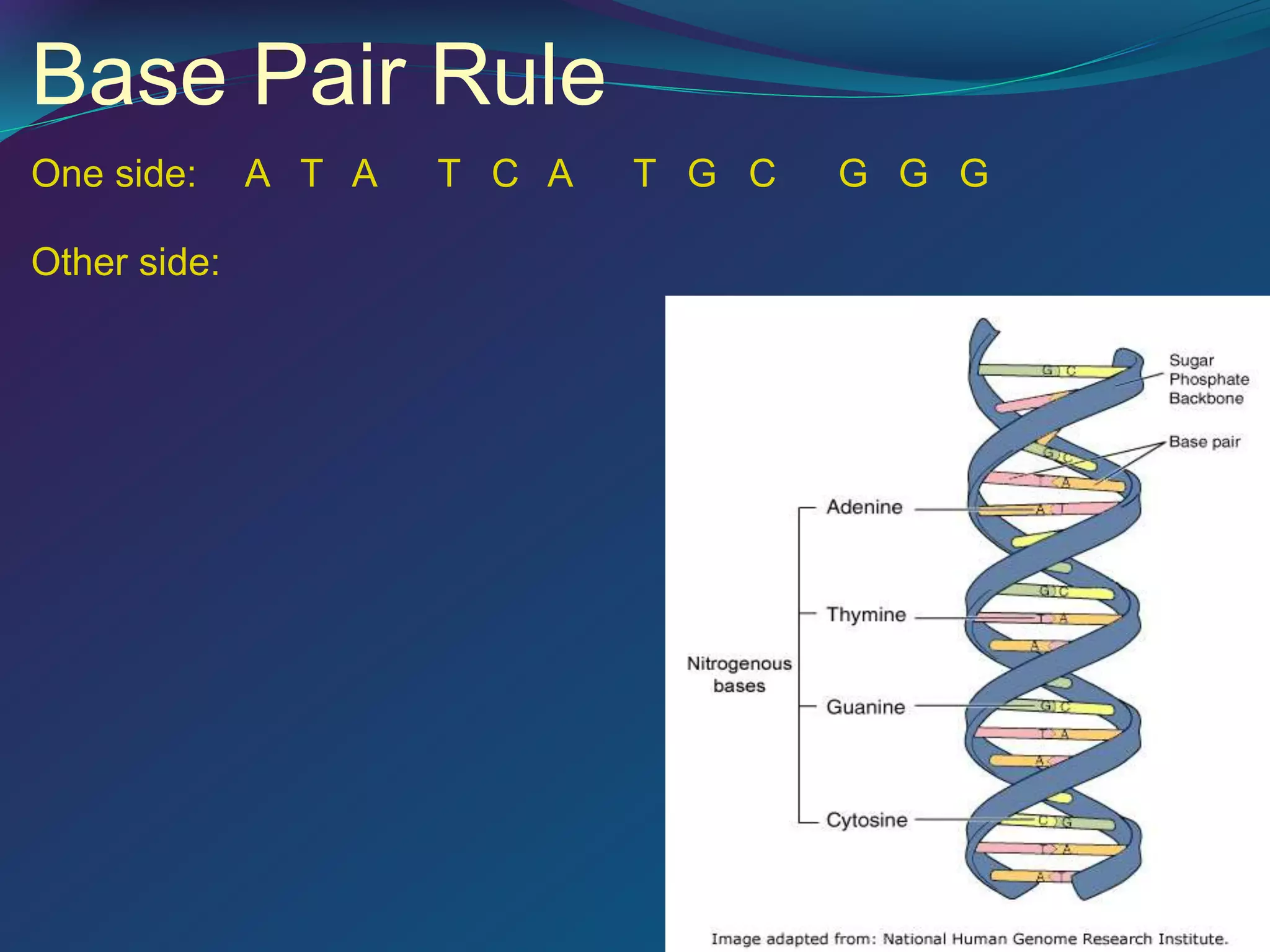
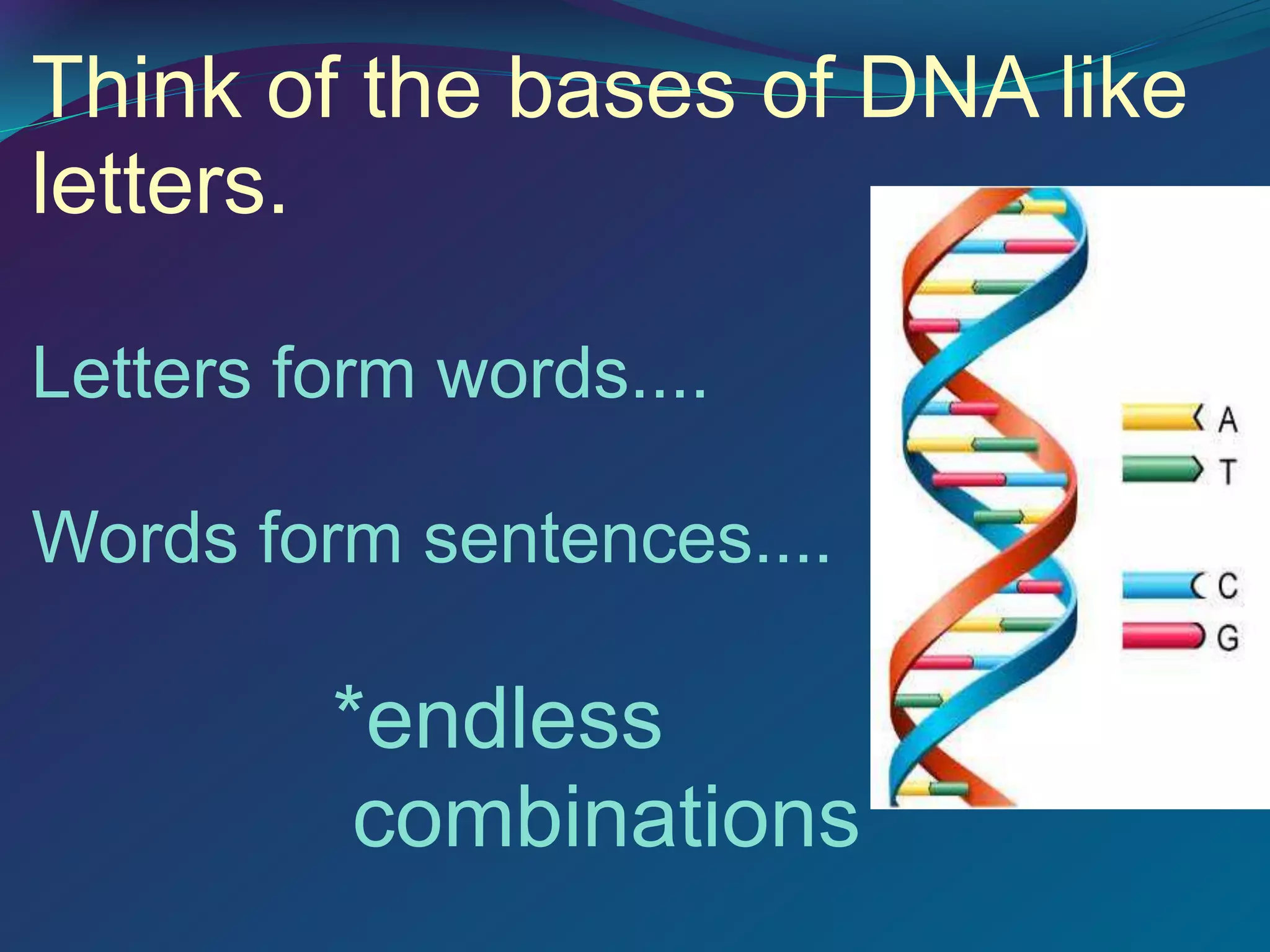
DNA is made up of millions of nucleotides that form a double helix structure. Each nucleotide consists of a phosphate, sugar, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine. The bases bond together in a specific pairing - adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine. This complementary base pairing allows the sequence of bases on one strand to determine the sequence on the other strand. Genes are sections of DNA that code for proteins, with the sequence of bases in a gene dictating the specific protein produced.