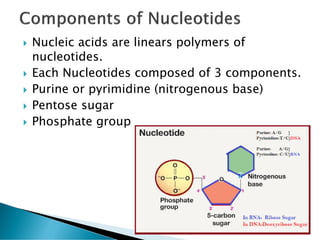
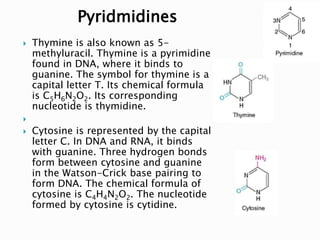
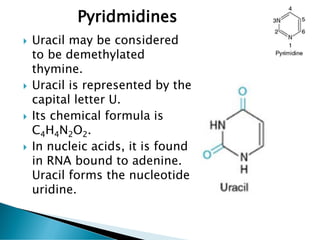
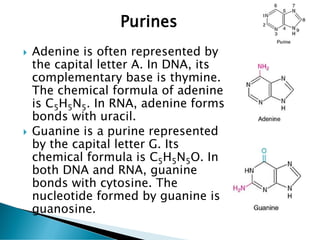
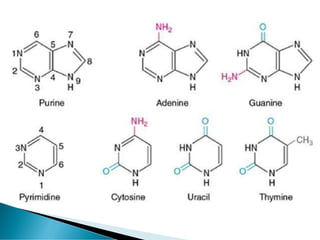
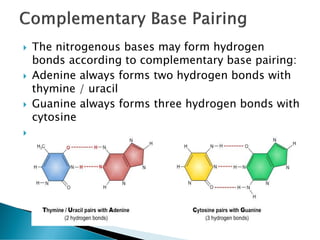
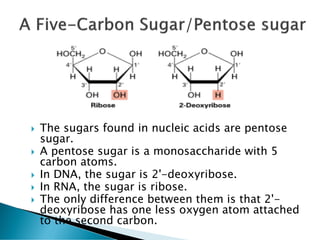
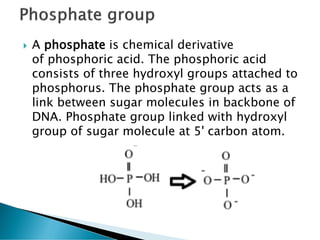
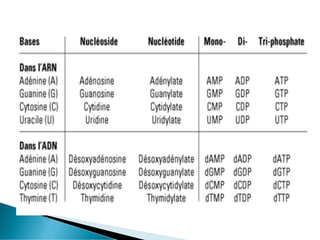
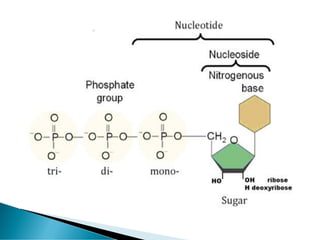
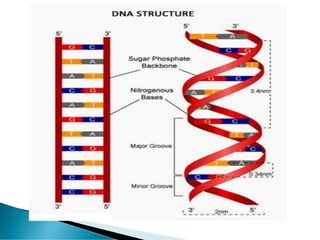
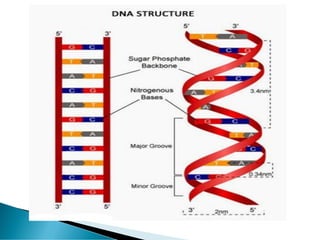
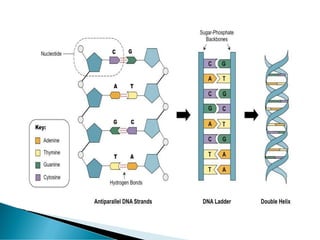
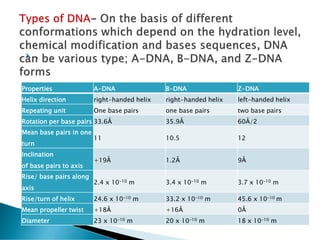
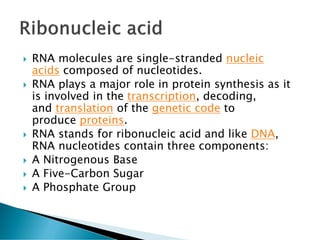
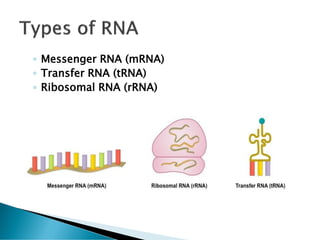
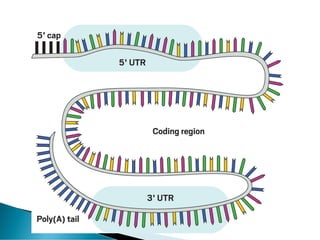
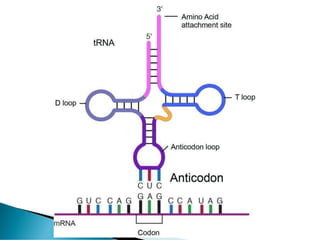
Nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, are linear polymers of nucleotides composed of nitrogenous bases, pentose sugars, and phosphate groups. DNA consists of paired bases (adenine-thymine and guanine-cytosine) forming a double helix structure, while RNA is single-stranded and plays a key role in protein synthesis via mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. The document outlines the chemical structure of nucleotides, the mechanisms of base pairing, and the functions of various types of RNA in genetic coding and protein production.