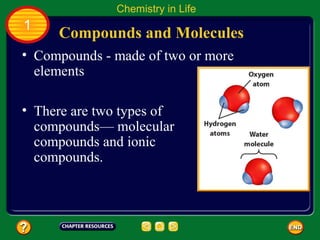
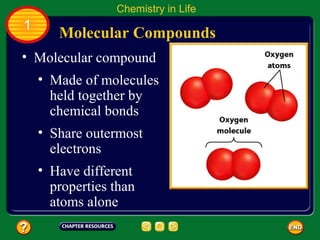
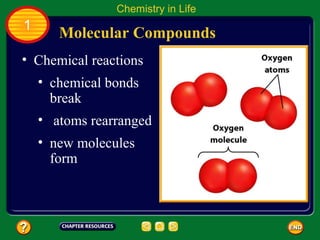
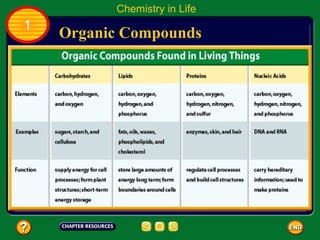
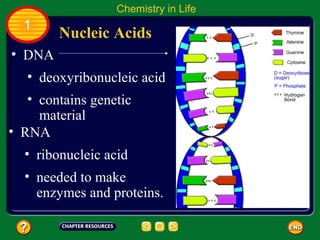
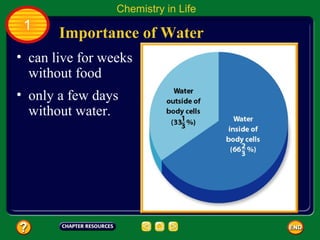
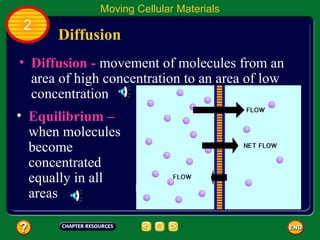
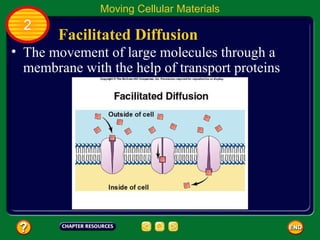
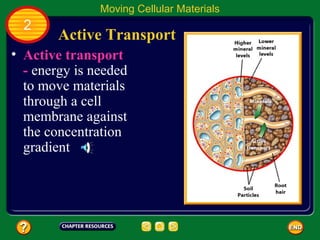
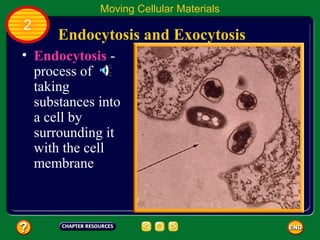
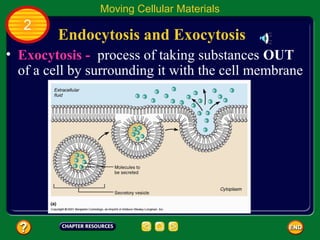
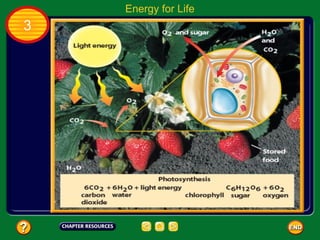
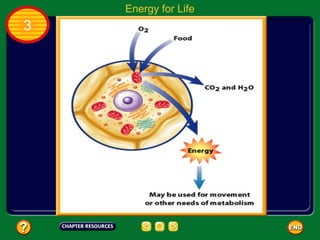
This document contains an outline of sections from a chapter on cell processes. The sections include: Chemistry of Life, Moving Cellular Materials, and Energy for Life. Chemistry of Life covers topics like matter, atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures, organic compounds, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and water. Moving Cellular Materials discusses passive transport mechanisms like diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion as well as active transport and endocytosis/exocytosis. Energy for Life addresses metabolism, photosynthesis, cellular respiration, fermentation, and the breakdown and storage of carbohydrates.