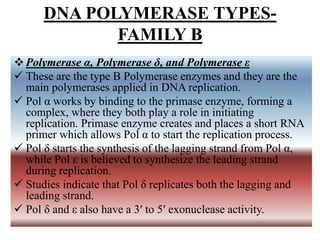
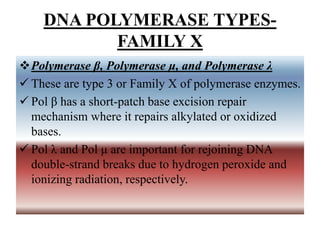
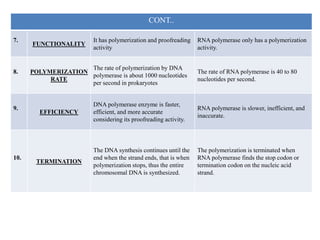
The document outlines the roles and functions of DNA and RNA polymerases, focusing on the mechanisms of DNA replication and repair carried out by various types of DNA polymerases, including their discovery and application in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Different families of DNA polymerases (A, B, X, and Y) are discussed, highlighting their specific functions and interactions, particularly in eukaryotic cells where five distinct polymerases are identified. The document also compares DNA polymerases with RNA polymerases, detailing their mechanisms, efficiency, and requirements for initiation.