This document summarizes DNA and RNA polymerases. It discusses:
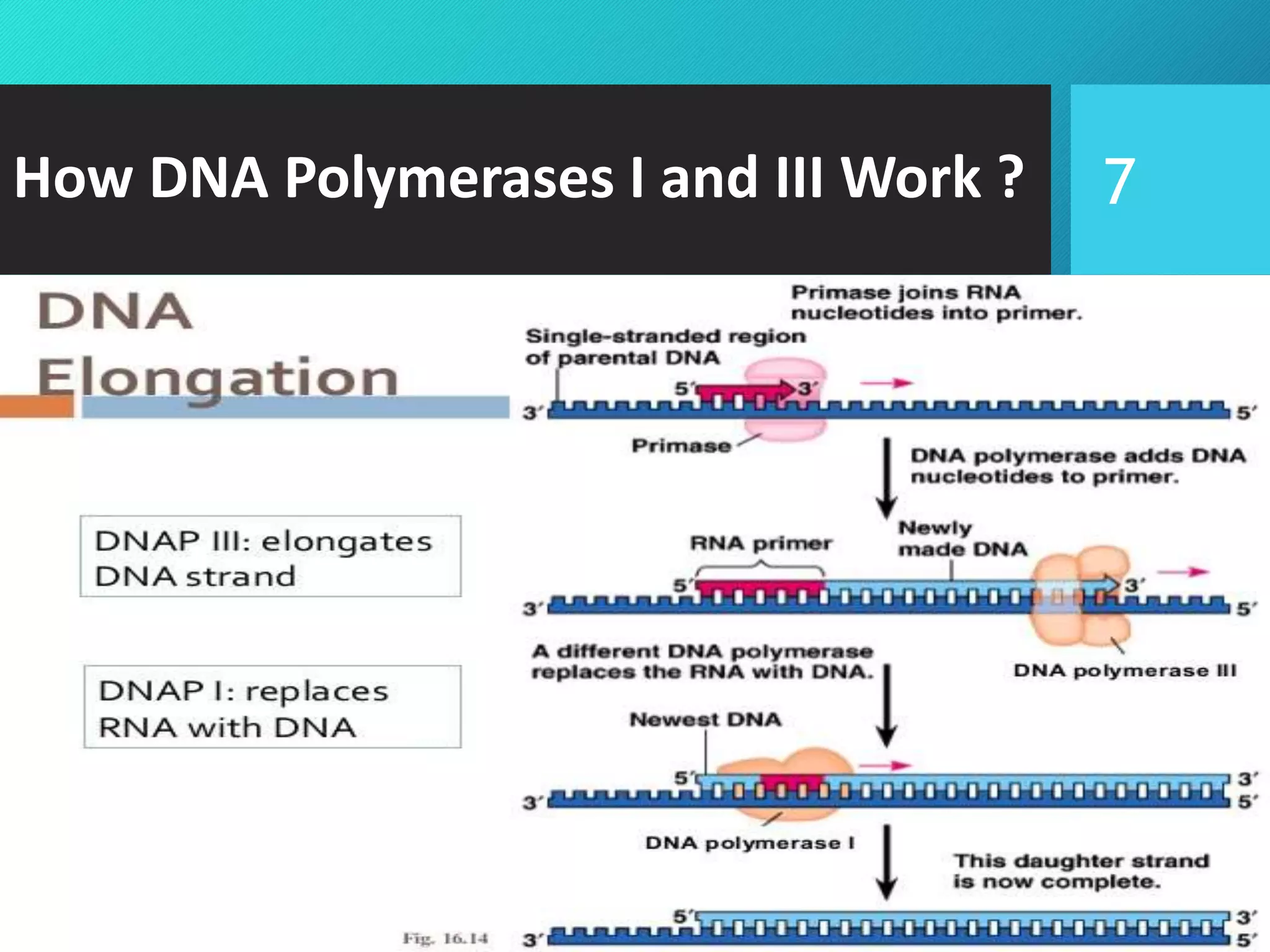
- The three main types of prokaryotic DNA polymerases (DNA polymerase I, II, and III), what they are responsible for, and how they work.
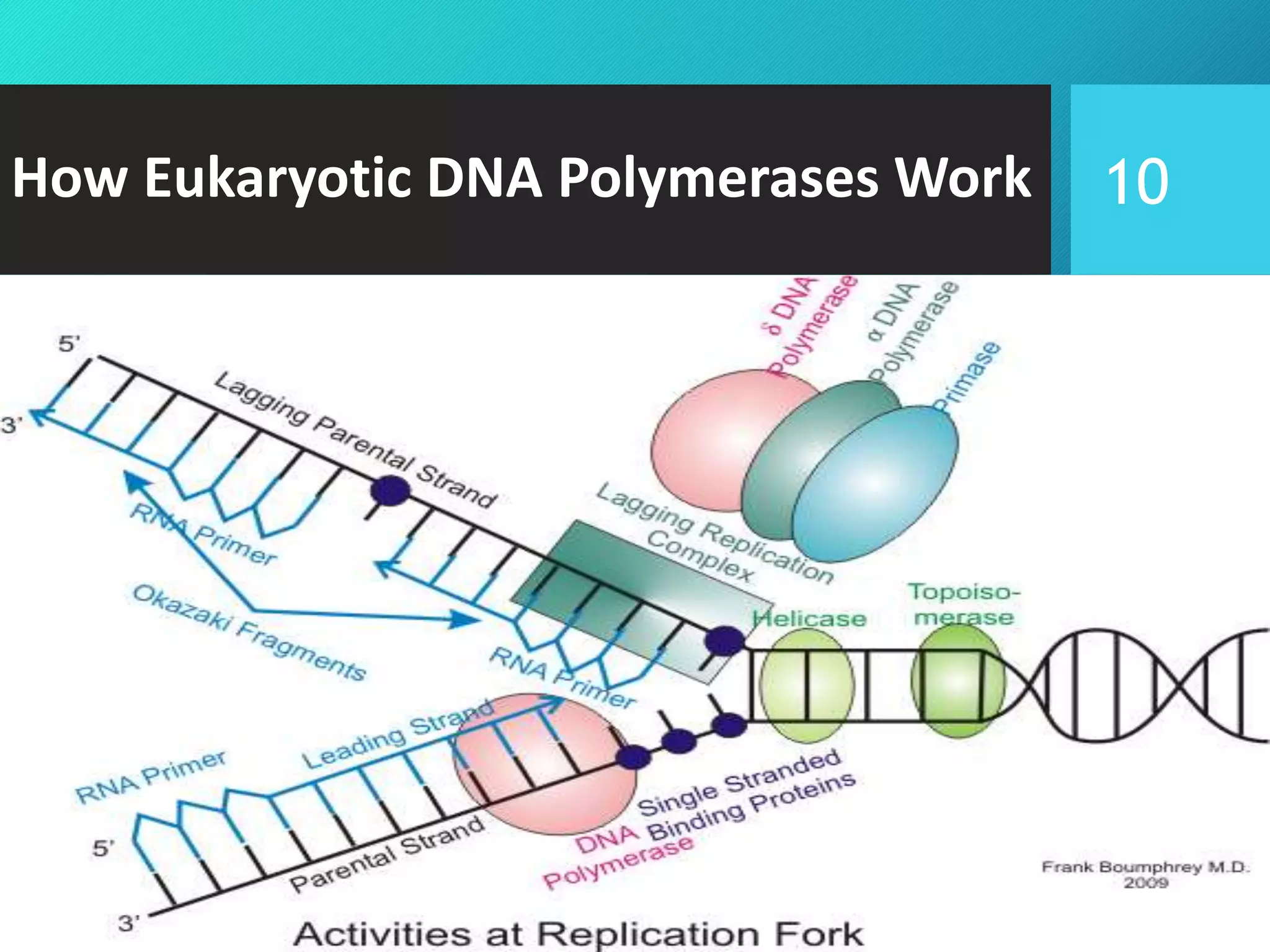
- The main eukaryotic DNA polymerases (DNA polymerase α, β, γ, δ, and ε), what they are responsible for, and how they work.
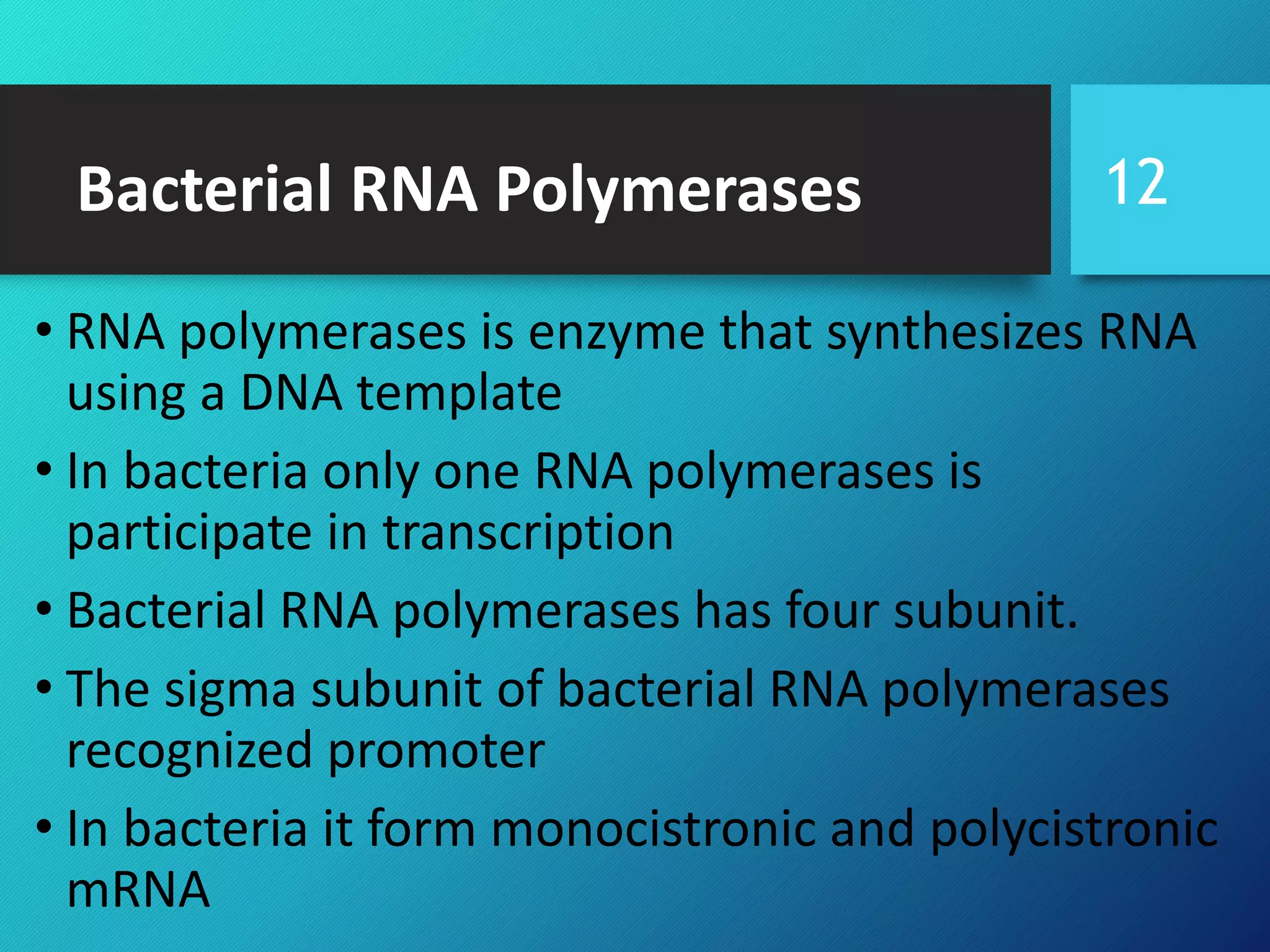
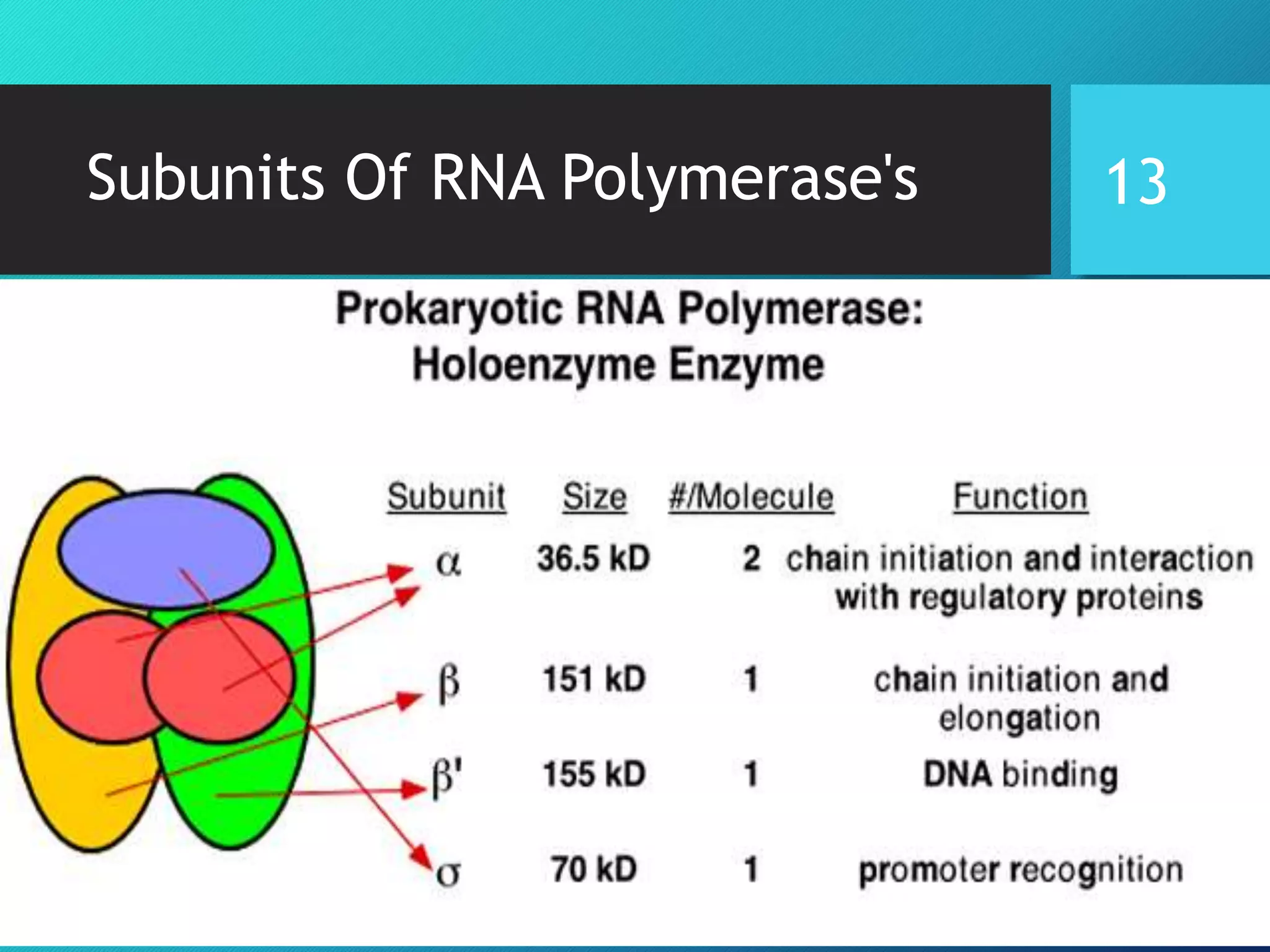
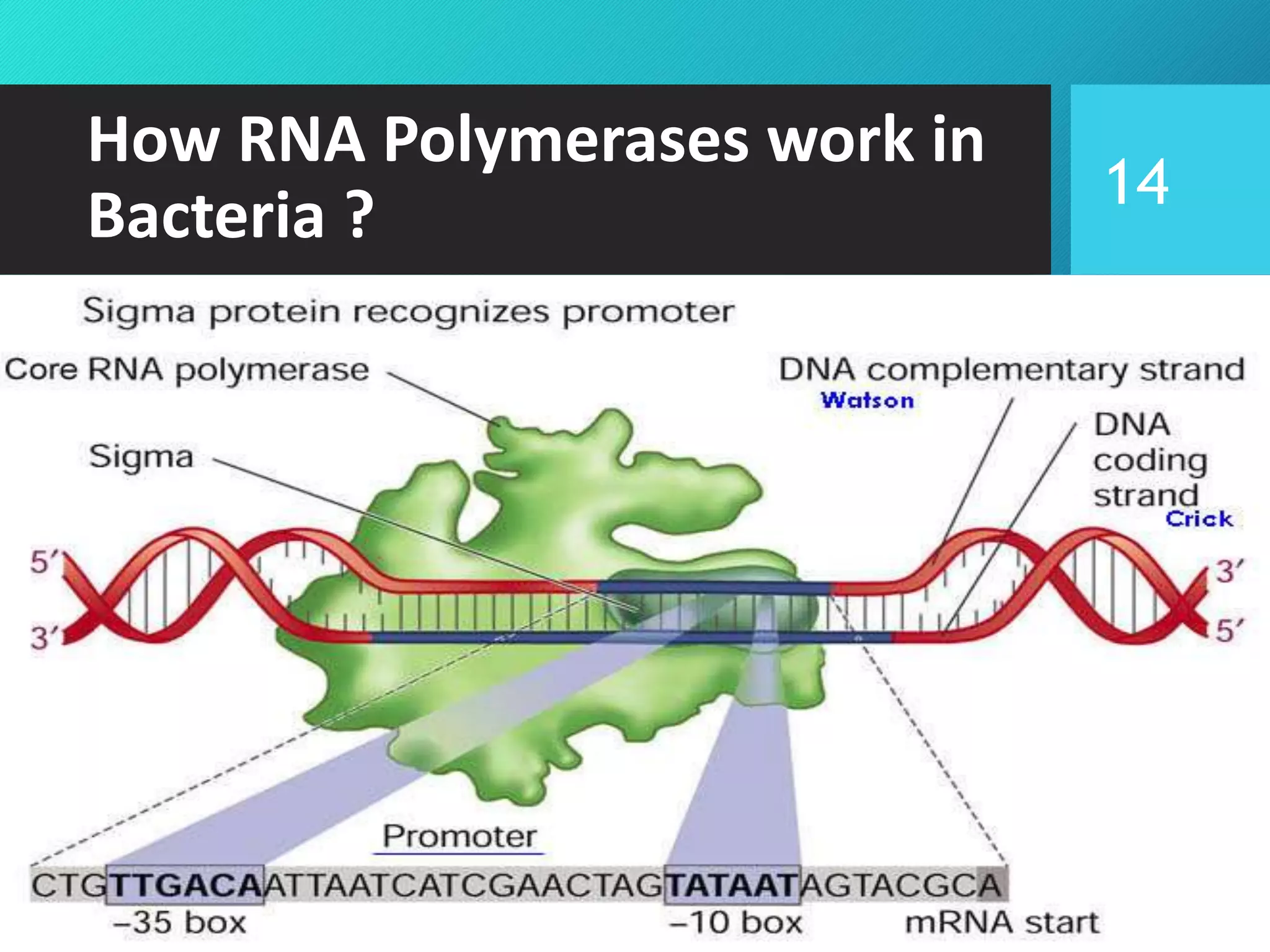
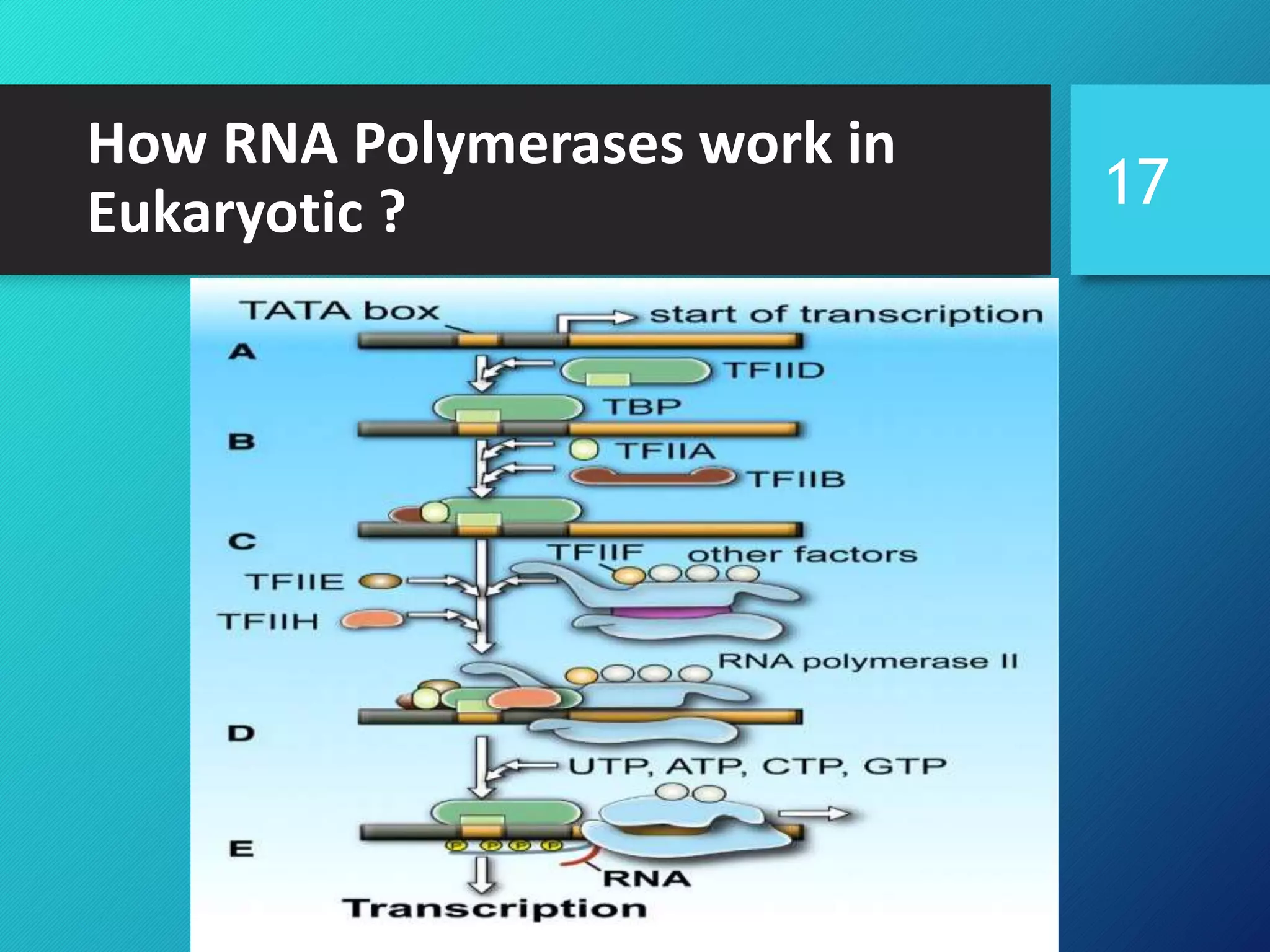
- RNA polymerase, the main types in bacteria and eukaryotes, their subunits, and how they work to transcribe DNA into RNA through the process of transcription.