Embed presentation
Downloaded 15 times


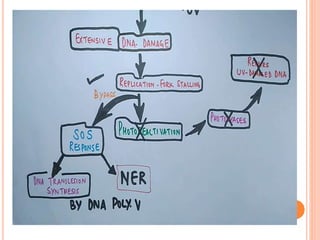

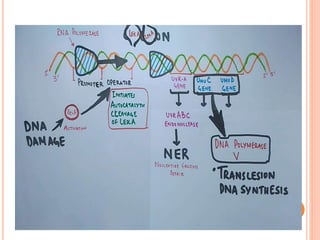
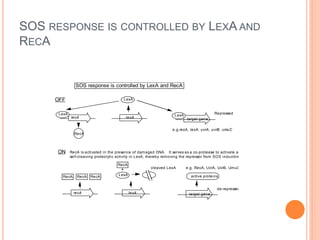

The SOS repair mechanism enables bacterial cells to respond to overwhelming DNA damage, particularly from UV light, by activating a systematic repair response involving over 30 genes. Key proteins in this process include RecA and LexA, which regulate the expression of genes involved in DNA repair, such as UvrA, UvrB, and UmuC. The mechanism ensures that cellular repair occurs prior to cell division, although it can be error-prone due to the activation of bypass mechanisms.





