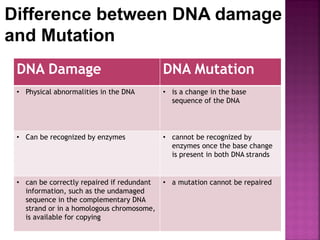
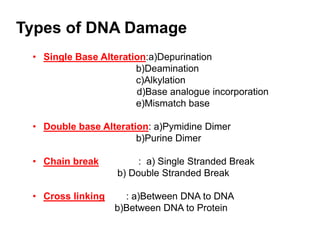
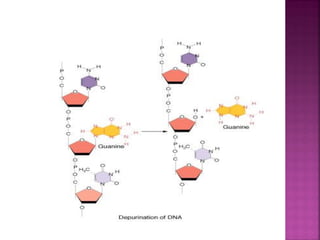
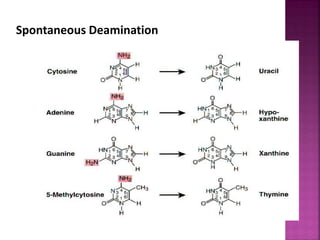
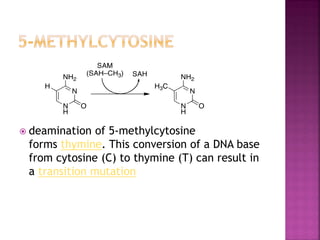
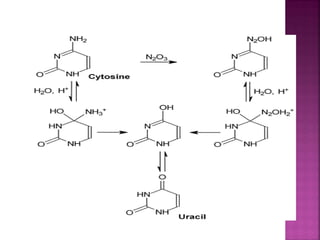
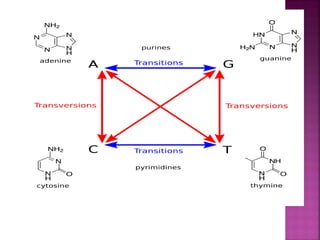
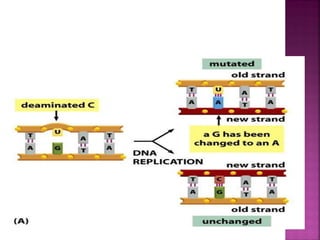
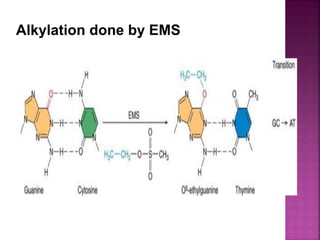
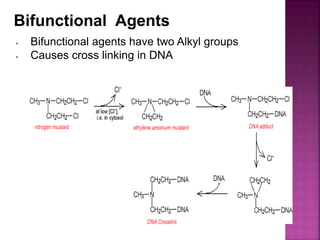
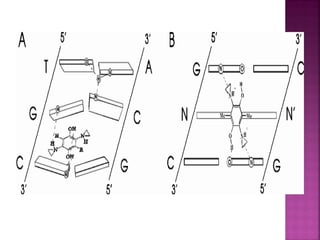
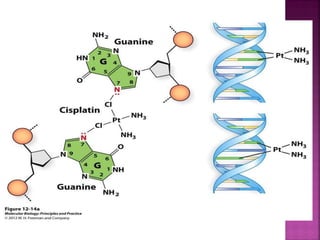
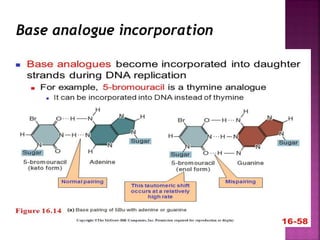
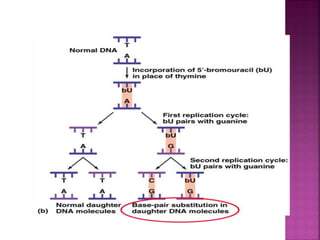
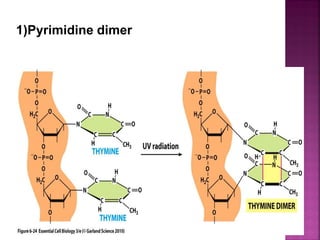
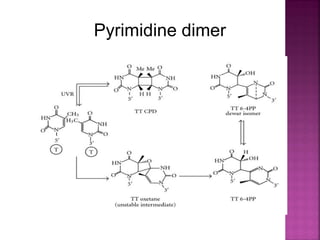
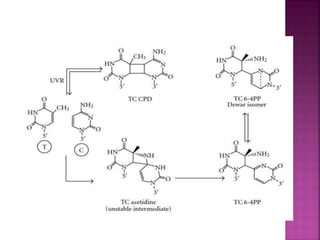
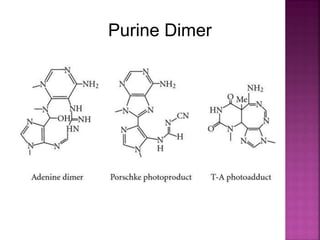
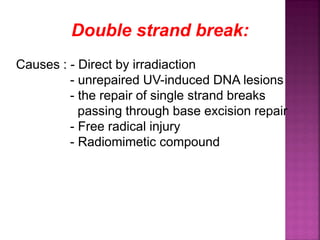
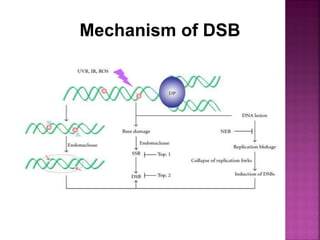
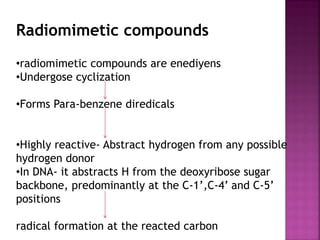
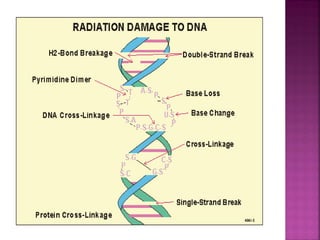
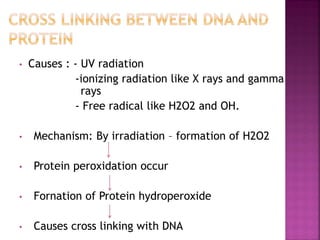
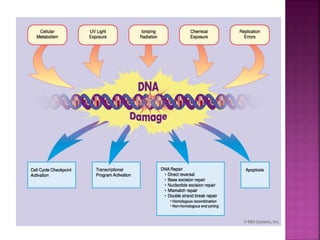
DNA can be damaged through various means, including single base alterations, double base alterations, chain breaks, and cross-linking. Single base alterations include depurination, deamination, alkylation, base analogue incorporation, and mismatch bases. Double base alterations include pyrimidine dimers and purine dimers caused by UV radiation. Chain breaks include single and double stranded breaks caused by irradiation and free radicals. Cross-linking can occur between DNA and DNA or DNA and proteins due to UV radiation, ionizing radiation, and free radicals. Unrepaired damage can lead to mutations if incorrectly repaired during replication.