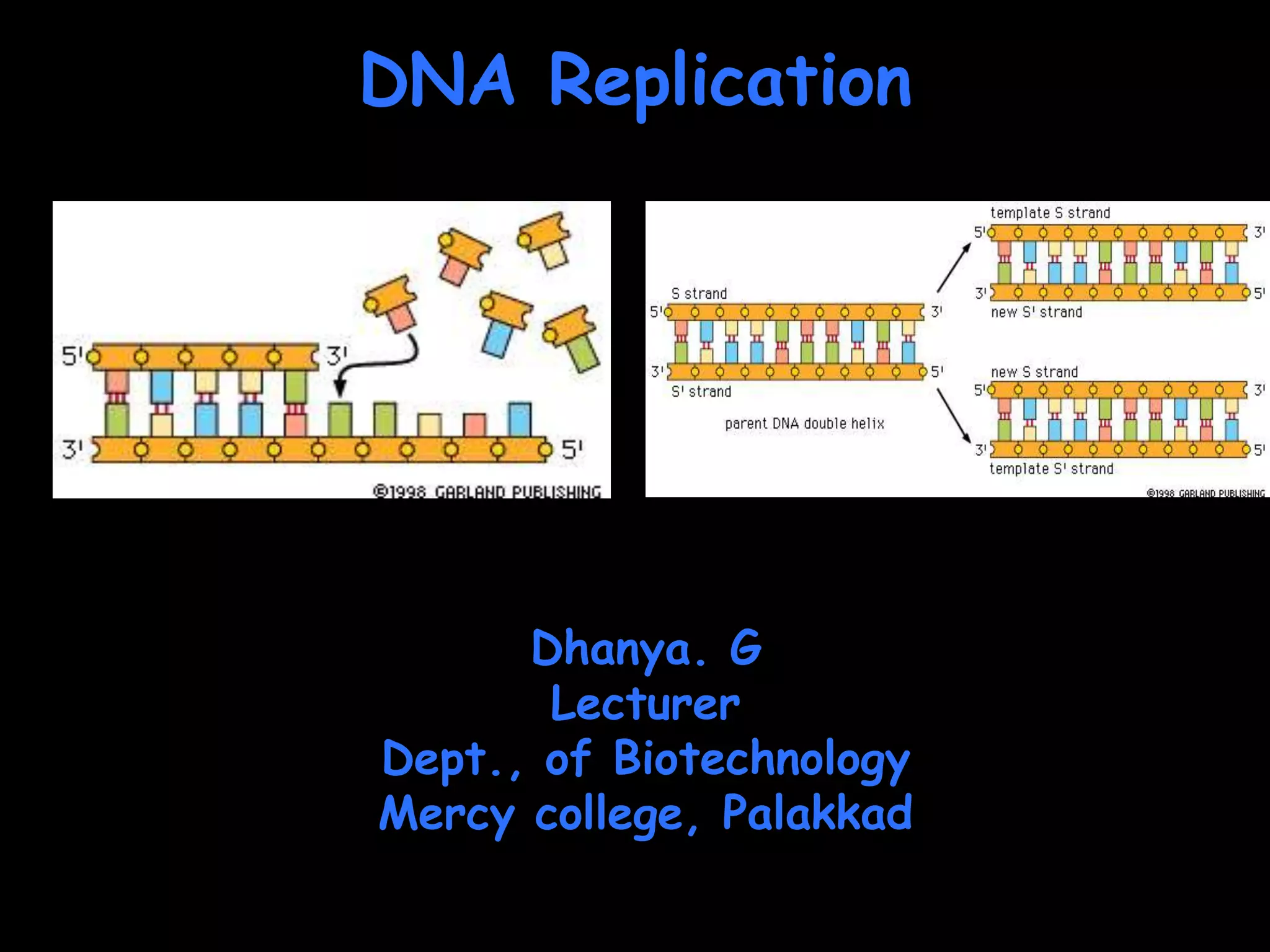
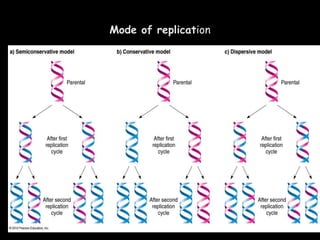
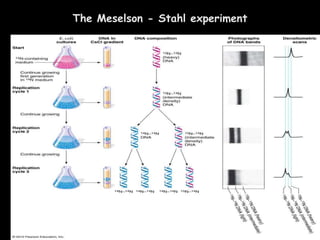
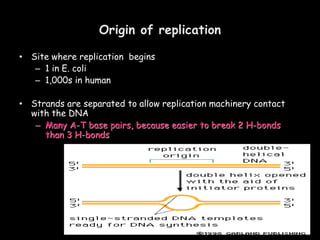
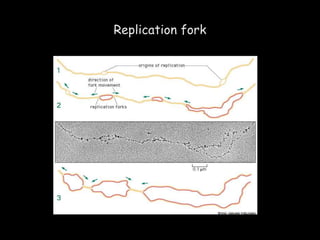
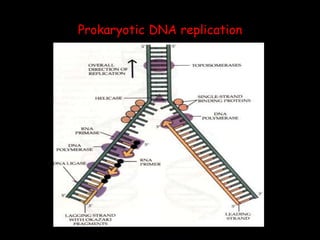
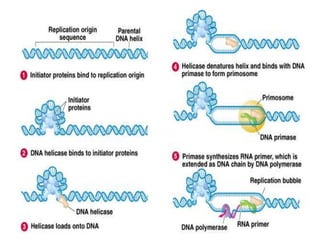
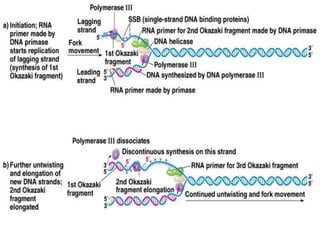
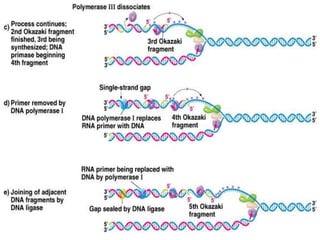
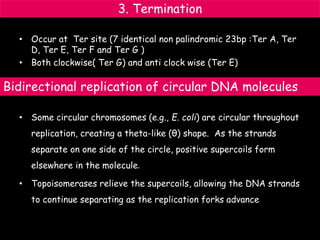
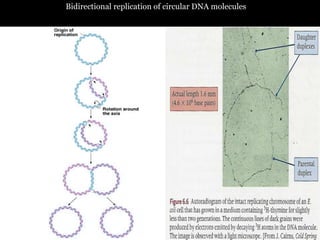
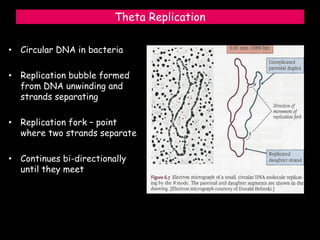
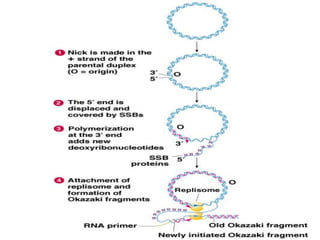
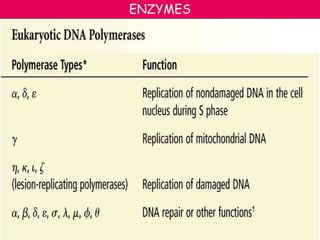
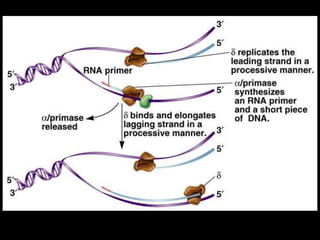
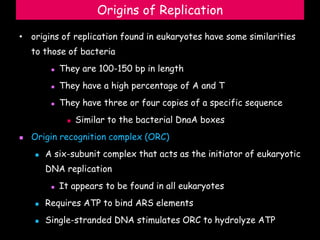
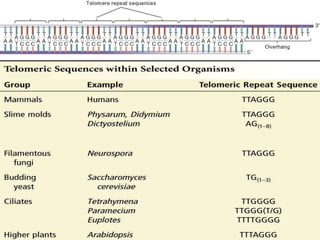
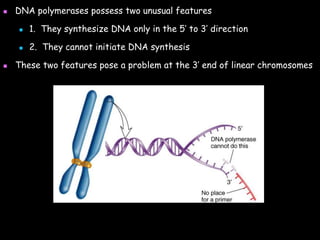
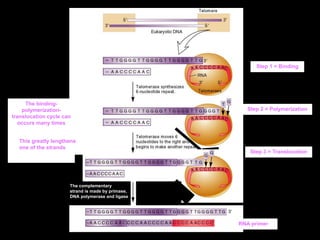
DNA replication is a complex process that involves unwinding of the DNA double helix, synthesis of new strands that are complementary to the original strands, and enzymes such as DNA polymerase and helicase. There are multiple origins of replication in eukaryotes that allow bidirectional replication from many starting points along DNA molecules. Enzymes involved include DNA polymerase alpha that works with primase to initiate DNA synthesis, and DNA polymerases delta and epsilon that carry out leading and lagging strand elongation. Telomeres prevent shortening of chromosomes with each round of replication through the action of telomerase.