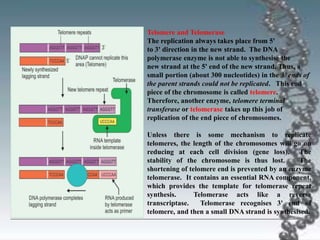
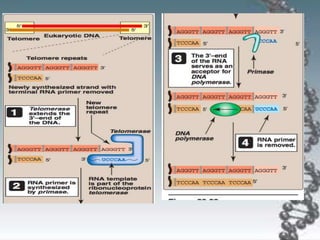
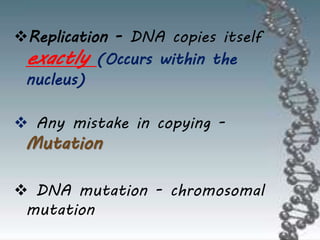
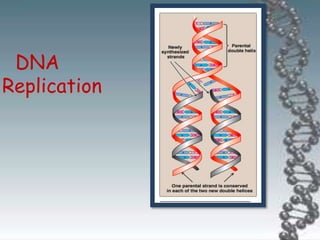
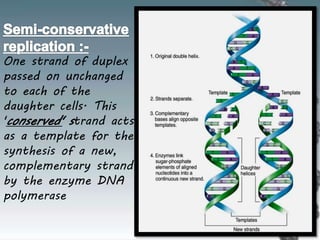
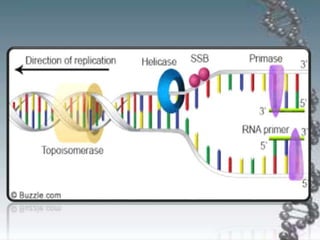
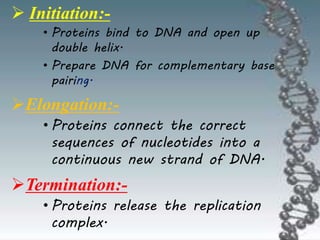
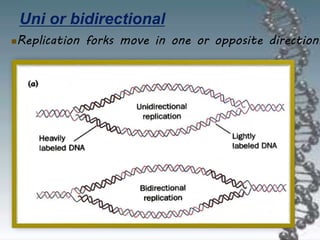
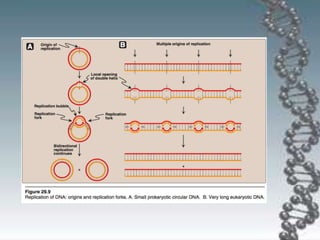
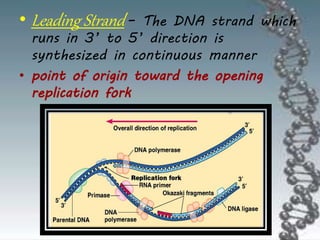
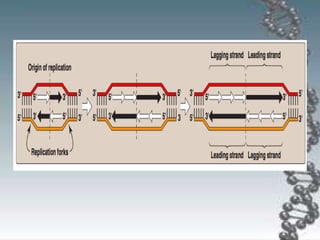
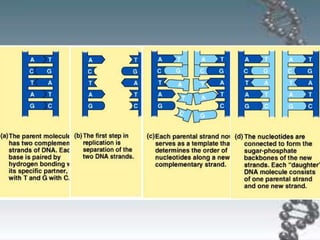
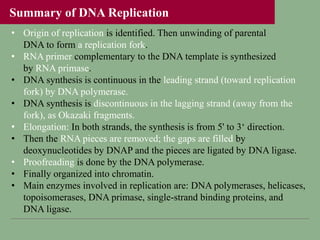
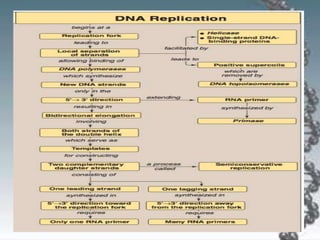
- DNA replication involves DNA copying itself exactly through a semi-conservative process that begins at the origin of replication and proceeds bidirectionally.
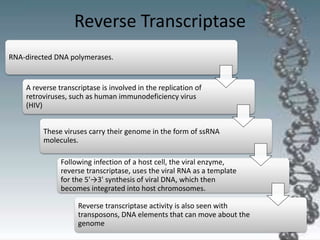
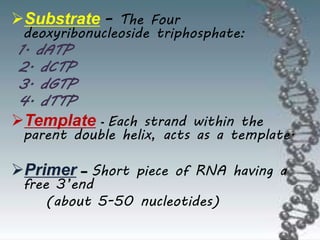
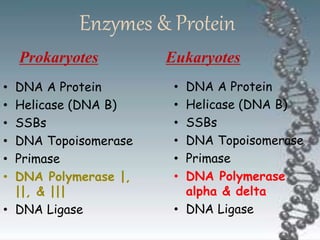
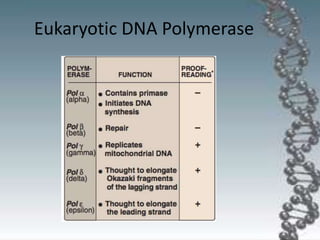
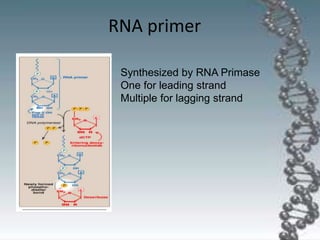
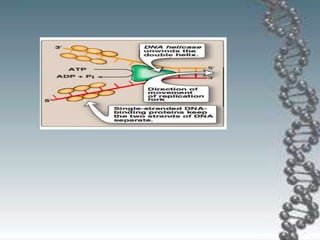
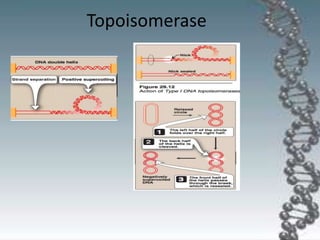
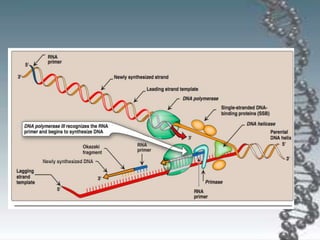
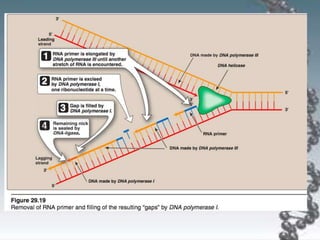
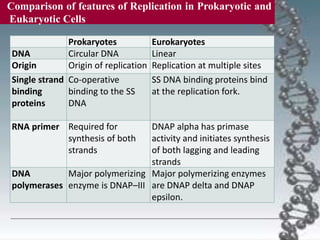
- The key enzymes involved are DNA helicase, topoisomerases, primase, DNA polymerase, and DNA ligase. DNA polymerase synthesizes new strands in the 5' to 3' direction using existing strands as templates.
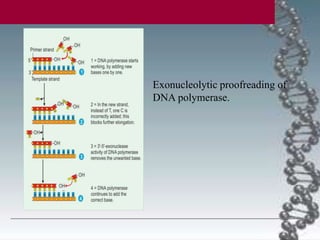
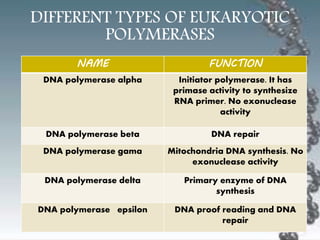
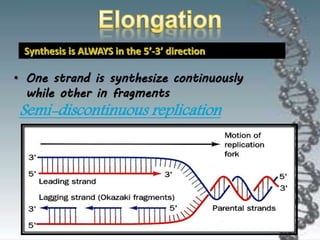
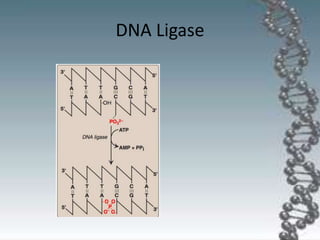
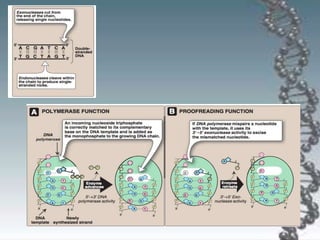
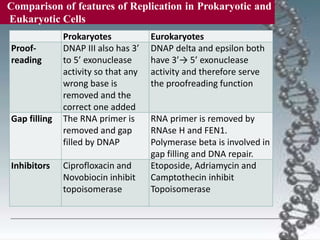
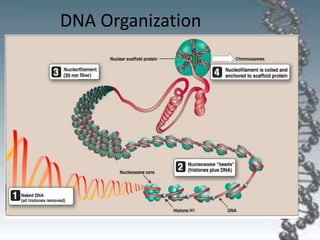
- In eukaryotes, replication of the lagging strand occurs through discontinuous Okazaki fragments that are later ligated together. DNA polymerase also has a proofreading function.
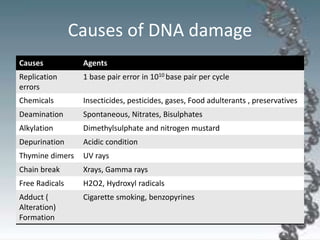
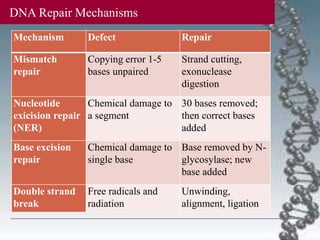
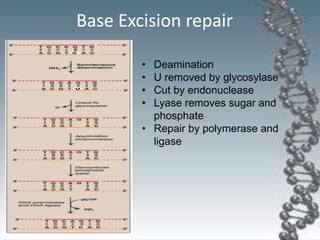
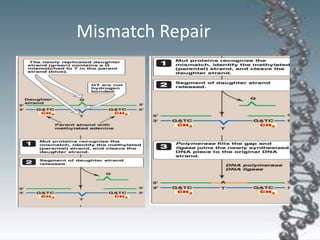
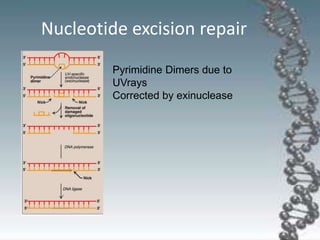
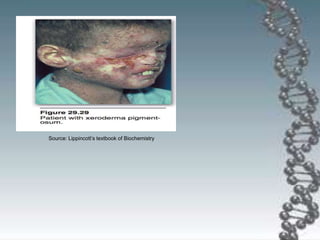
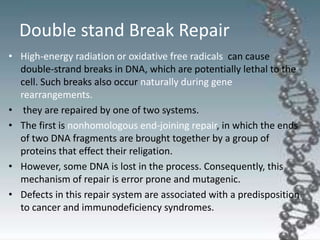
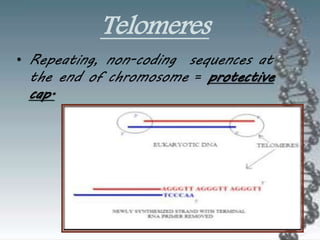
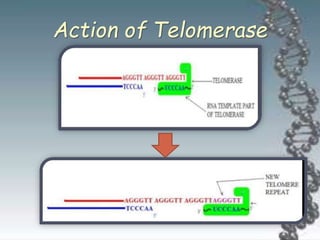
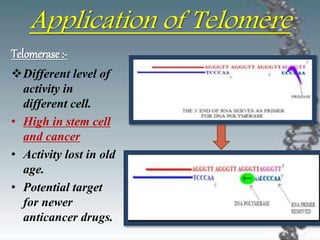
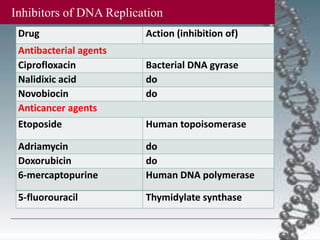
- DNA damage can occur from chemicals, radiation, and replication errors but cells have multiple repair mechanisms like base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, and









![DNA POLYMERASE -I
- Polymerization activity-5’-3’
- Exonuclease activity [proof reading
activity] -3’-5’ (also in 5’-3’)
-RNA dependent DNA polymerization
activity
- Replace RNA primer and add DNA
DNA POLYMERASE -II
- Polymerization activity -5’-3’
- Exonuclease activity -3’-5’
Backup enzyme- mostly in repair](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnareplicationpptr-200410100719/85/Dna-replication-MBBS-17-320.jpg)











![• Oxidation of bases (e.g. 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine).
• Alkylation (methylation) of bases, such as 7-methyl guanosine,
1-methyl adenine, 6-methyl guanine.
• Hydrolysis of bases, such as deamination, depurination, and
depyrimidination.
• Adduct formation, e.g. benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide causes dG adduct.
• Mismatch of bases, due to errors in DNA replication.
• Monoadduct damage cause by change in single nitrogenous base of DNA.
• Ultraviolet-B (UV-B) light causes cross-linking between adjacent cytosine
and thymine bases creating pyrimidine dimers. This is a direct damage.
• Ultraviolet-A light creates mostly free radicals, causing indirect DNA
damages.
• Ionizing radiation such as gamma-rays may induce irreparable DNA damage.
• Elevated temperature causes depurination (loss of purine bases from the
DNA backbone) and single strand breaks.
• Chemicals such as aromatic hydrocarbons cause DNA adducts.
Types of Damage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnareplicationpptr-200410100719/85/Dna-replication-MBBS-53-320.jpg)