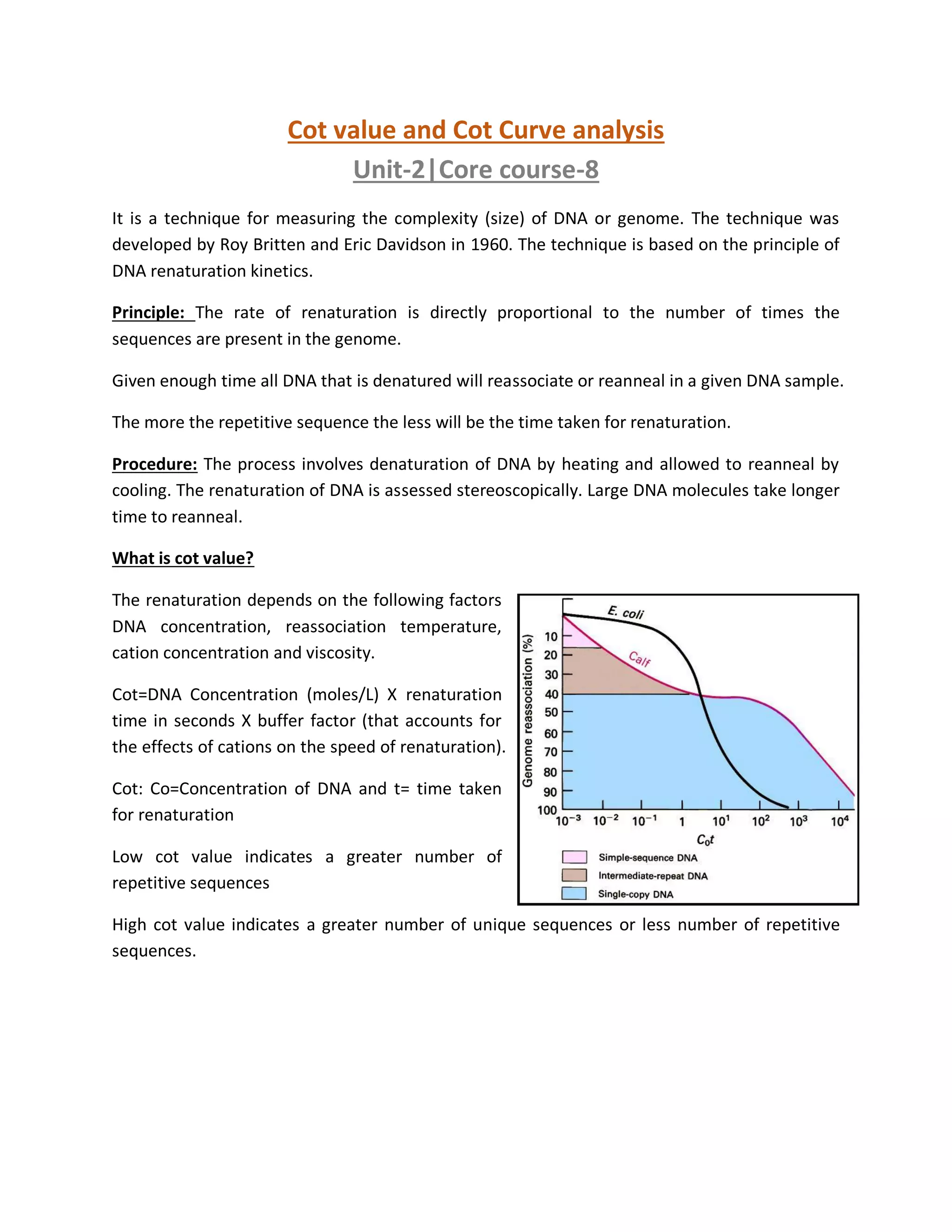
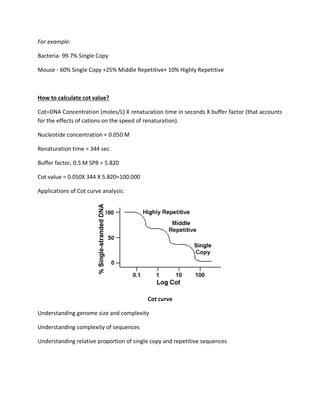
Cot value and Cot Curve analysis is a technique for measuring DNA complexity based on renaturation kinetics. DNA is denatured and allowed to reanneal, with larger DNA taking longer. Cot value accounts for DNA concentration, time, and buffer effects, representing repetitive sequences - lower Cot means more repeats. Examples show bacteria have nearly all single-copy DNA, while mouse has varying proportions of single-copy, middle repetitive, and highly repetitive sequences. Cot curve analysis provides information on genome size, complexity, and proportions of sequence types.