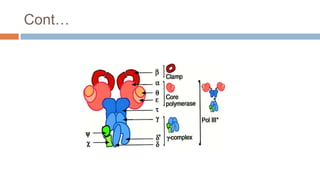
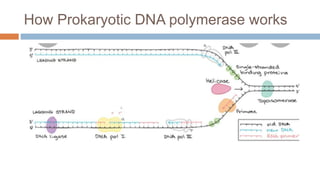
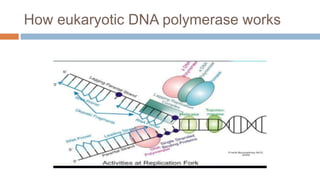
DNA polymerases are essential enzymes responsible for synthesizing and repairing DNA in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, first identified by Arthur Kornberg in 1956. Various types of DNA polymerases have distinct roles, such as DNA polymerase I involved in repair and DNA polymerase III, the main enzyme for replication in E. coli. Their primary functions include DNA replication, repair, and proofreading to maintain genomic integrity.