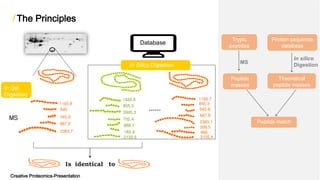
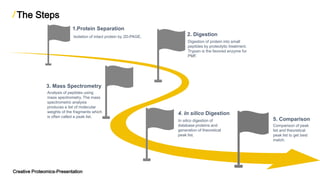
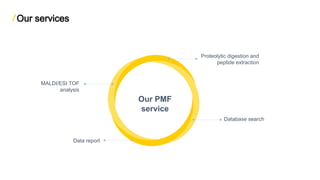
The document discusses peptide mass fingerprinting (PMF), a high-throughput protein identification technique developed in 1993, utilizing mass spectrometers like MALDI-TOF and ESI-TOF. It outlines the method's steps, including protein separation, digestion, mass spectrometry analysis, in silico digestion, and peak list comparison. While PMF is easy to perform and faster than traditional peptide sequencing, it has limitations, such as requiring known protein sequences in the database and potential issues with post-translational modifications.