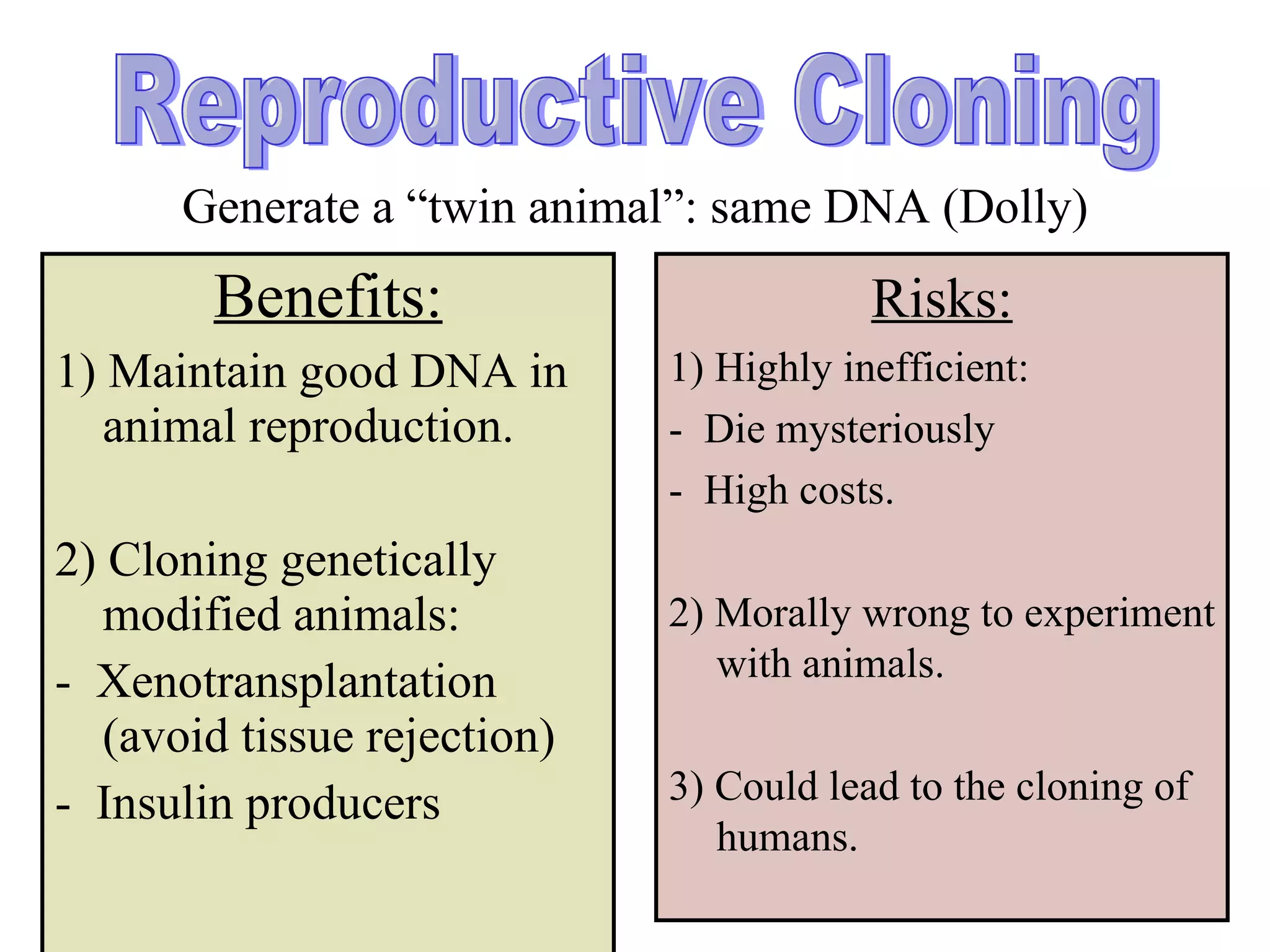
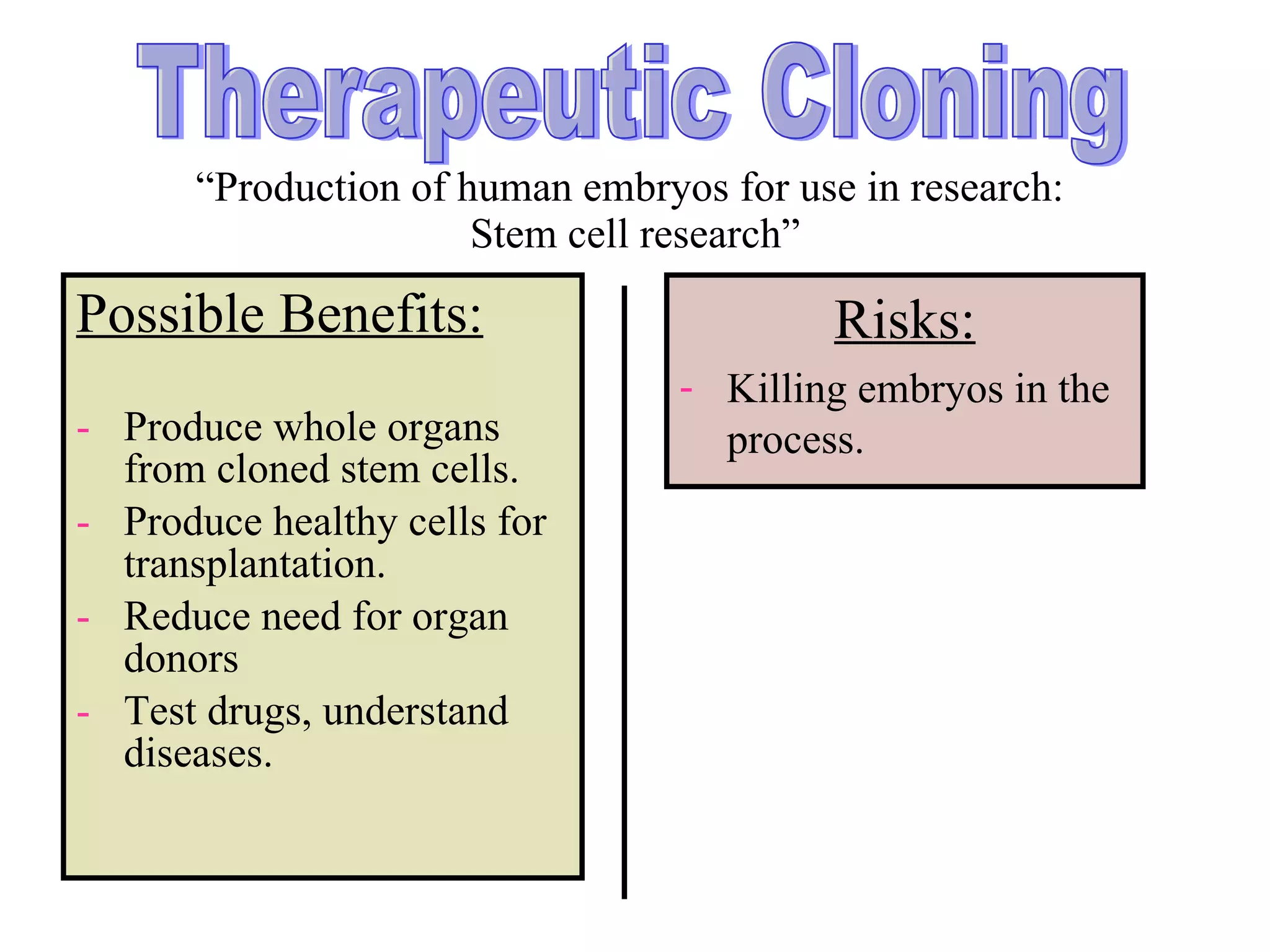
There are three main types of cloning: 1) DNA cloning which clones genes for uses like protein production and vaccine development, 2) reproductive cloning which produces genetically identical animals but risks are high inefficiency and potential harm, and 3) therapeutic cloning which produces stem cells for research on treating diseases but risks include killing embryos.