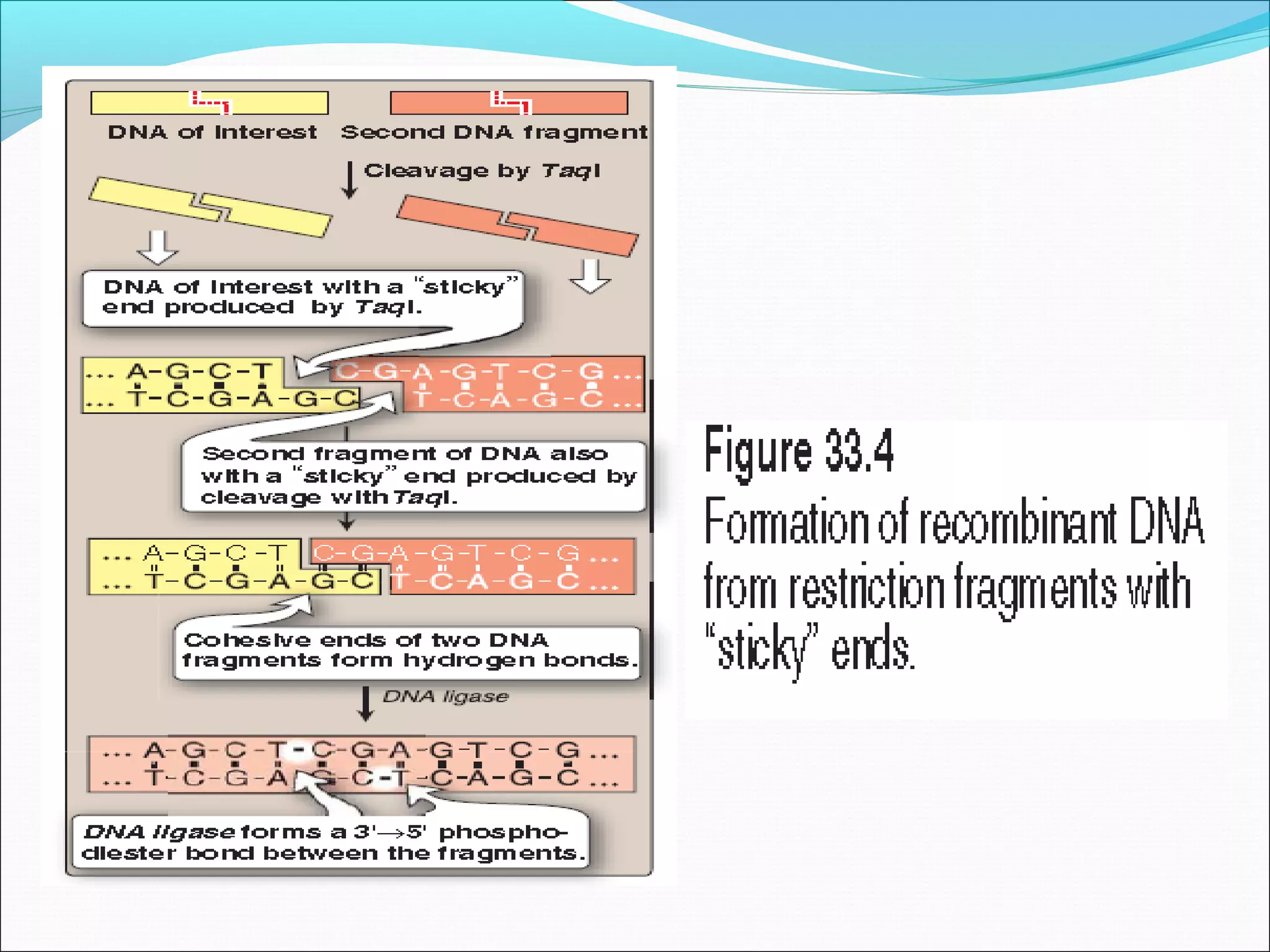
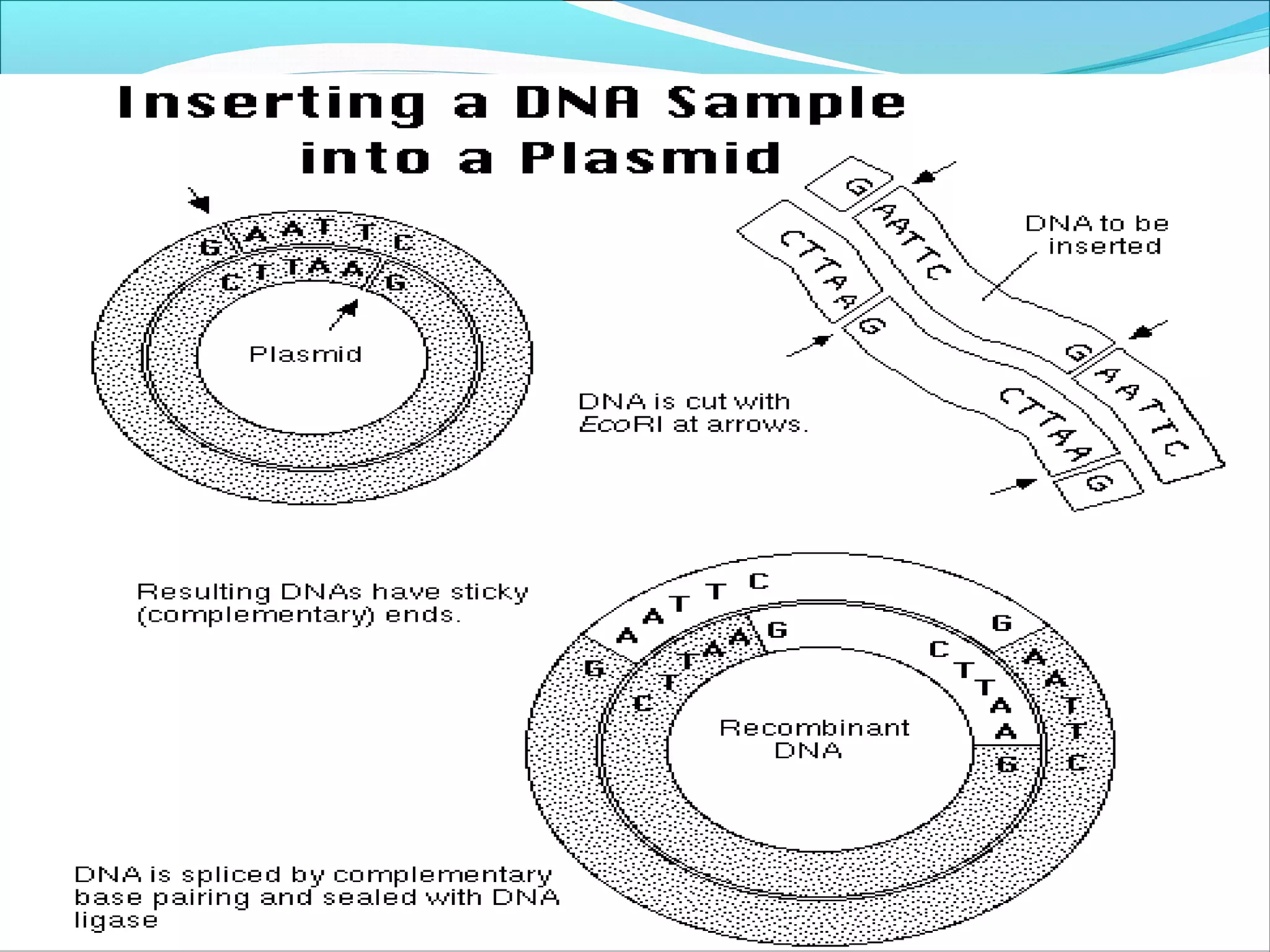
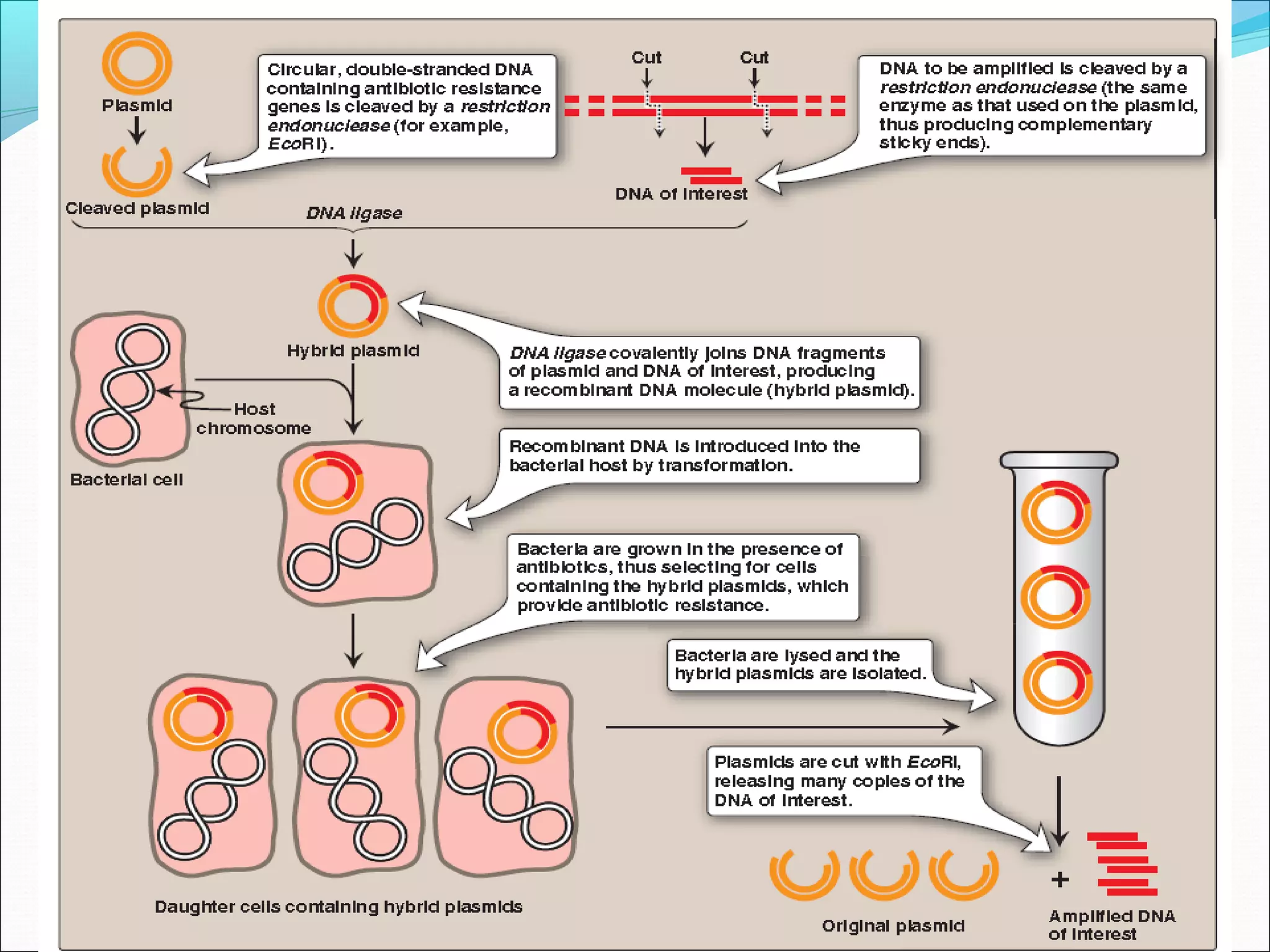
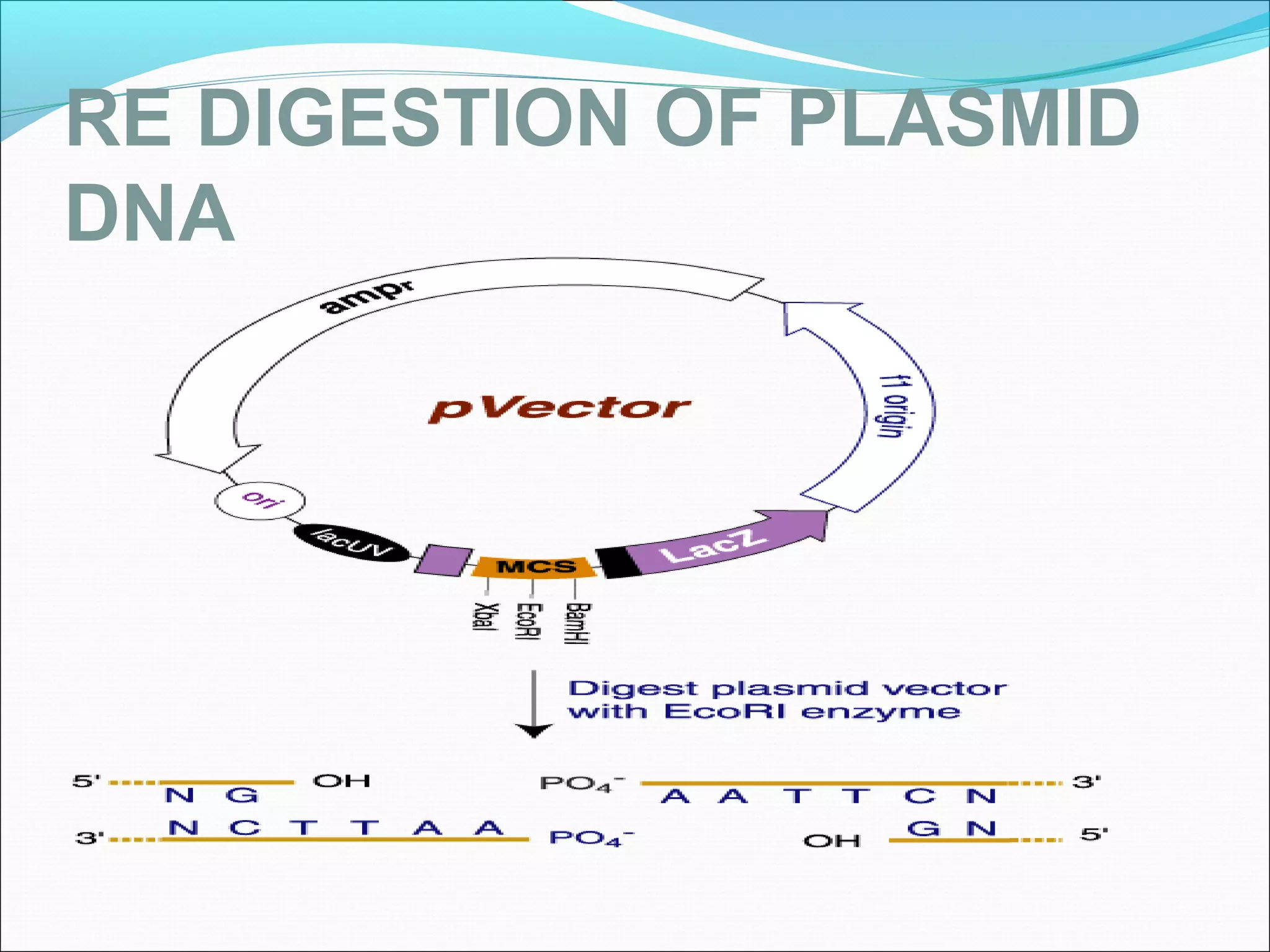
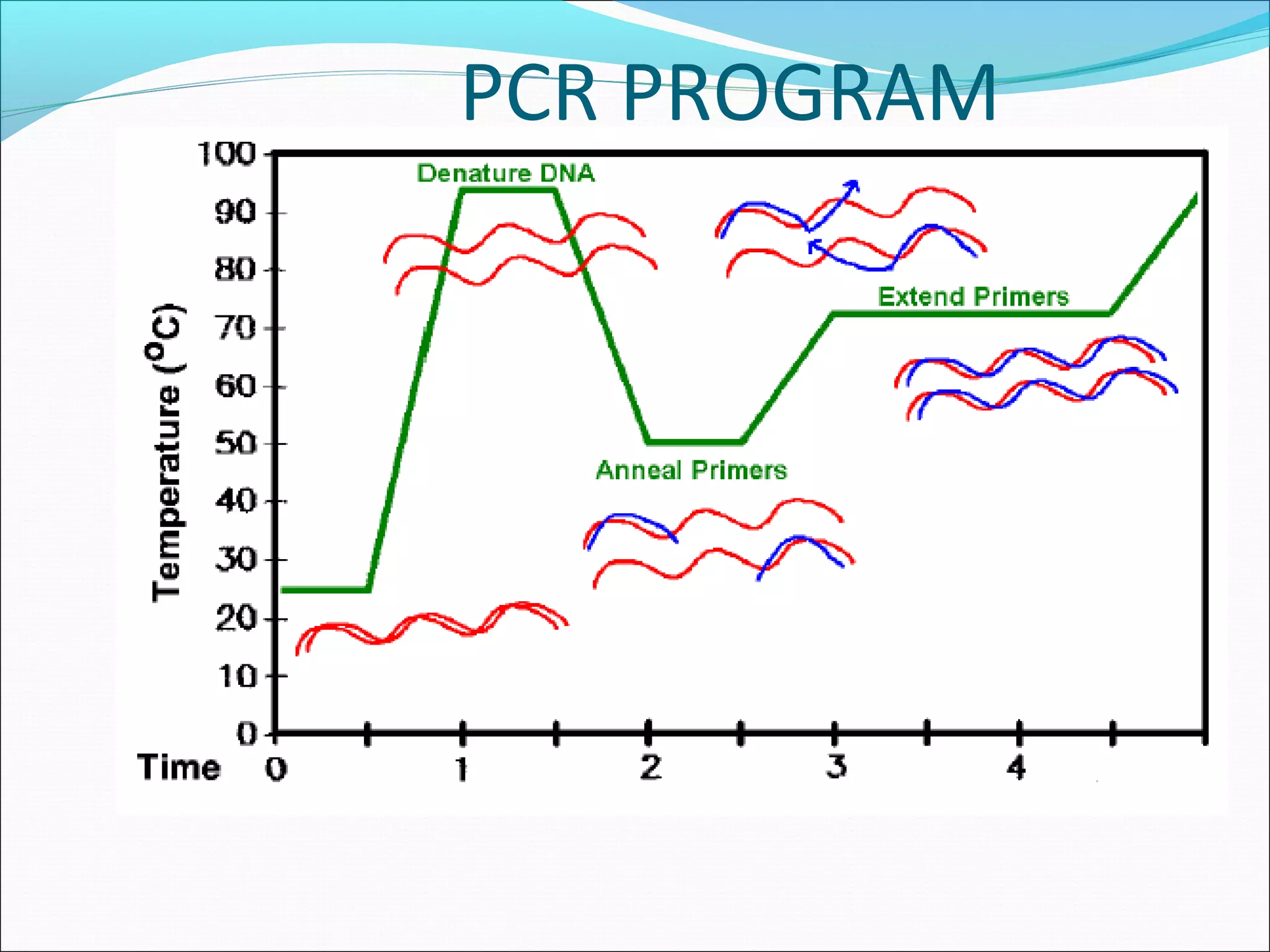
Recombinant DNA technology allows DNA from different species to be isolated, cut, spliced together, and replicated. This creates new "recombinant" DNA molecules. Key steps include using restriction enzymes to cut DNA into fragments, inserting fragments into cloning vectors like plasmids, and transforming host cells to replicate the recombinant DNA. PCR is also used to amplify specific DNA sequences. Recombinant DNA technology has many applications, including producing human proteins, diagnosing genetic diseases, and detecting bacteria and viruses.