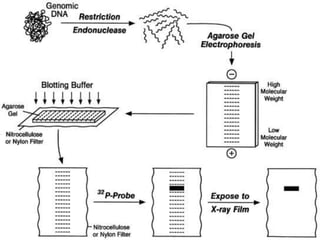
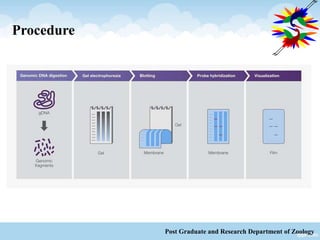
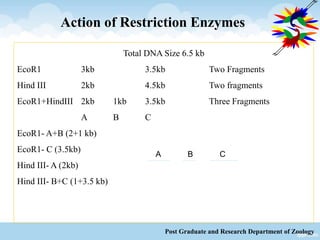
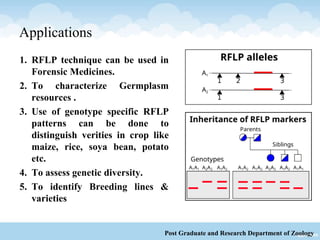
This document discusses Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP), a genetic marker technique. RFLP involves digesting genomic DNA with restriction enzymes, separating the fragments via gel electrophoresis, transferring the fragments to a membrane, and detecting variations in fragment lengths between individuals. The key steps are isolating DNA from samples, restriction enzyme digestion of the DNA, electrophoresis to separate fragments, Southern blotting to transfer DNA to a membrane, and autoradiography to detect polymorphisms. RFLP has advantages like using reliable genotypic characteristics and being co-dominant, but also disadvantages like being time-consuming and multi-step. RFLP can be applied to mapping chromosomes, assessing genetic diversity, and distinguishing