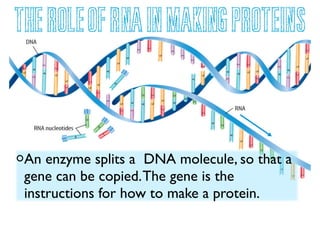
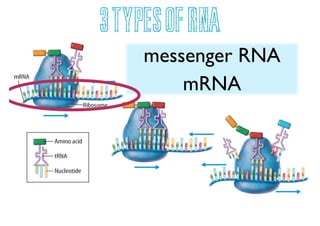
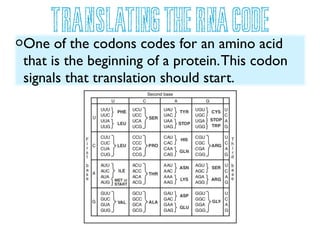
DNA contains genes that provide instructions for making proteins. DNA has a double helix structure with two strands coiled around each other. Each strand contains repeating sequences of nucleotides with one of four nitrogen bases (A, T, C, G). RNA is similar but single-stranded and helps carry instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the cell's protein-making machinery. Mutations can occur during DNA replication, resulting in changes to genes that may cause genetic disorders or beneficial trait variations.