Embed presentation
Downloaded 418 times












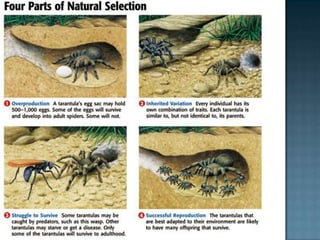



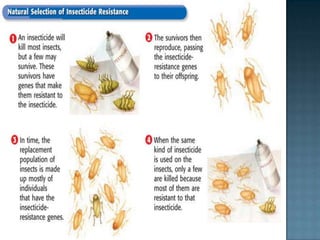

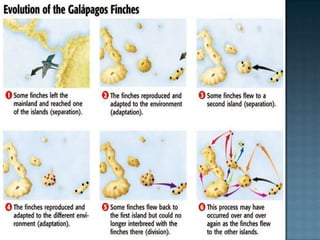










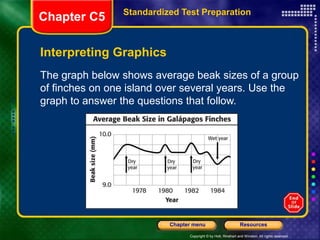
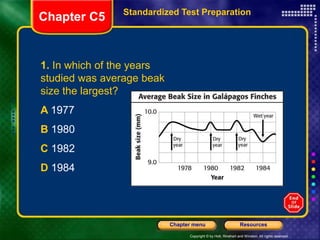
















The document discusses several key topics related to evolution and natural selection: - It defines what a species is and explains that adaptations help organisms survive and reproduce. - It notes that scientists observe species changing over time through the process of evolution as populations gradually change. - Fossils found in rock layers provide evidence of past life and allow scientists to construct a timeline of life known as the fossil record. - It discusses Charles Darwin's voyage on the HMS Beagle where he made observations of finch beak variations on the Galapagos Islands that influenced his theory of evolution by natural selection.














































