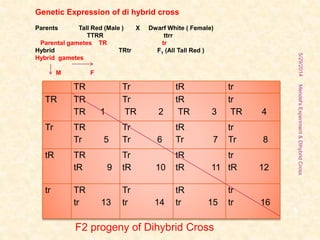
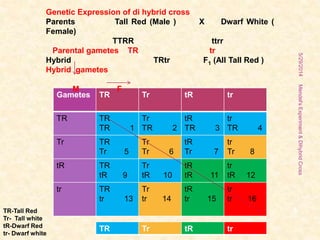
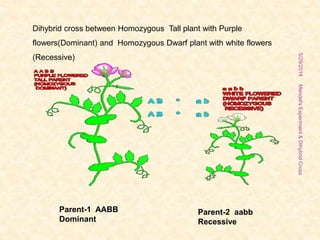
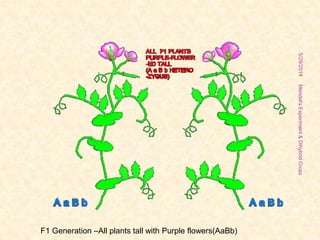
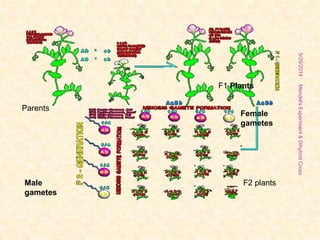
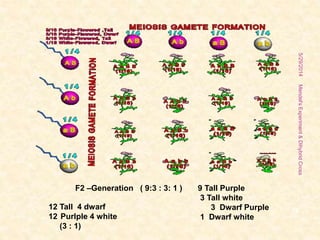
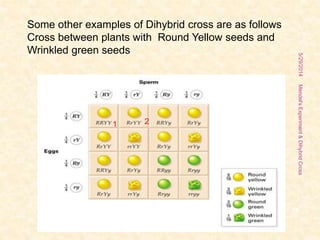
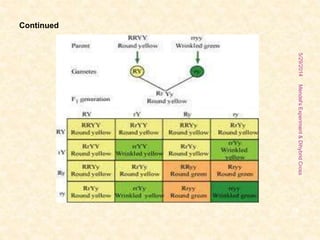
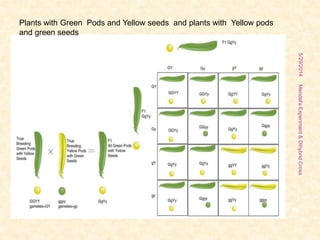
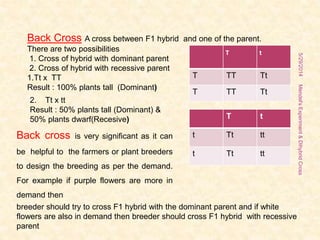
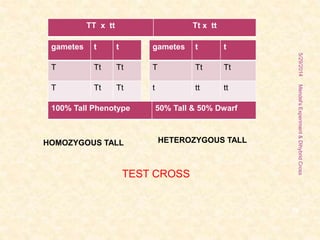
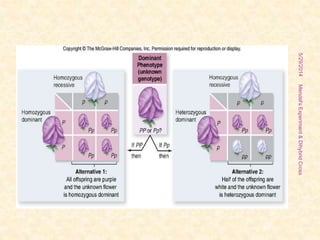
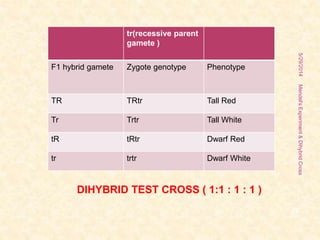
The document outlines Gregor Mendel's experiments on hybridization, specifically focusing on dihybrid crosses and their significance in understanding inheritance patterns. Mendel's findings led to the formulation of the law of independent assortment, which states that different traits are inherited independently. The document also discusses the methodologies, ratios obtained from crosses, and the concepts of back crosses and test crosses.