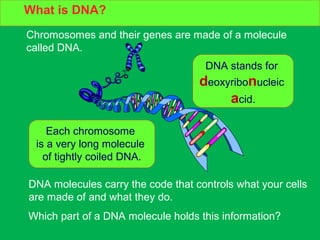
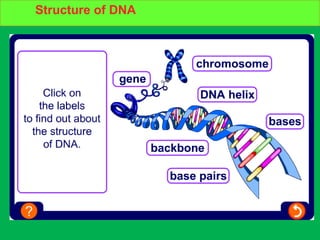
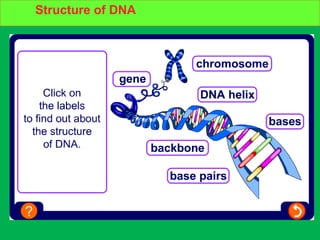
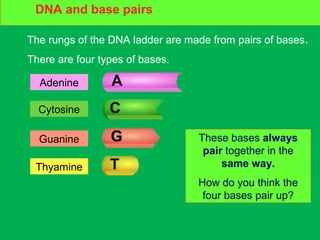
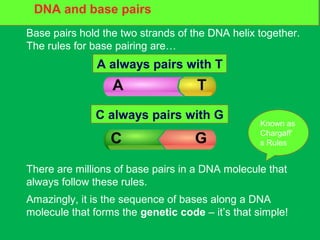
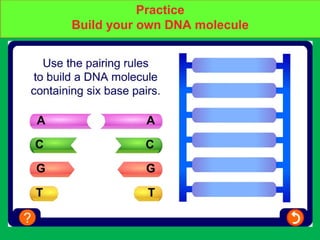
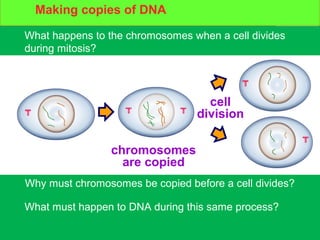
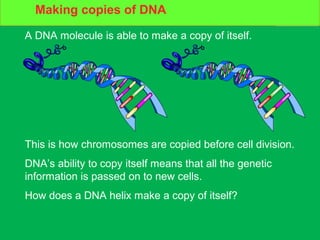
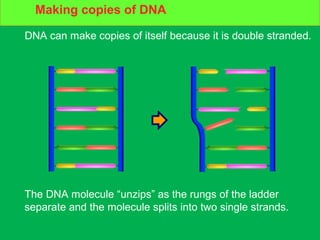
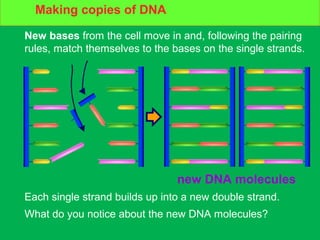
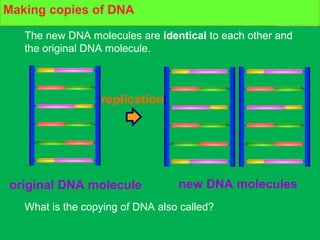
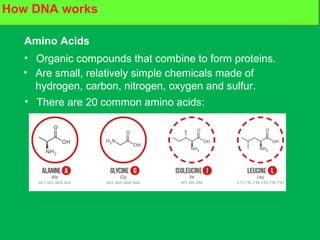
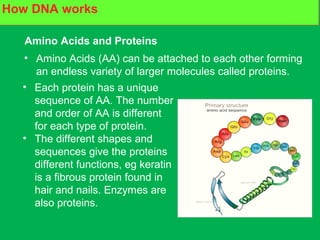
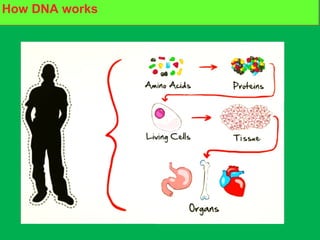
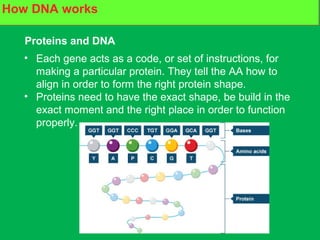
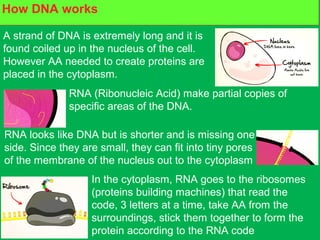
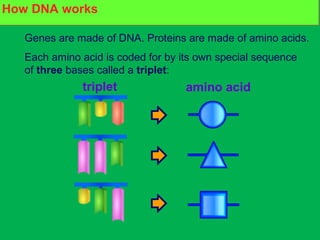
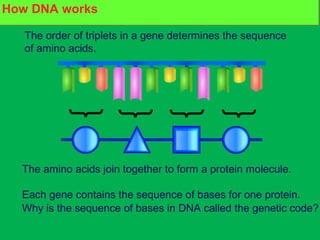
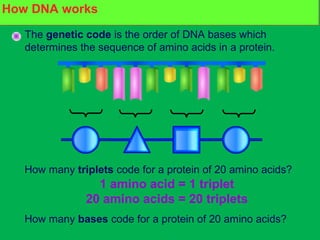
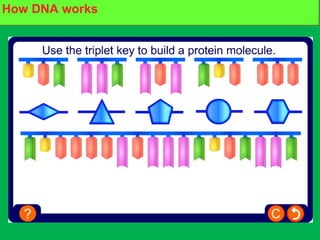
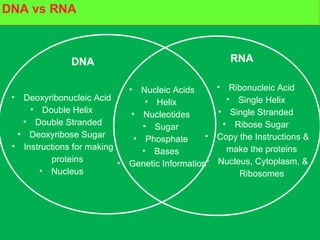
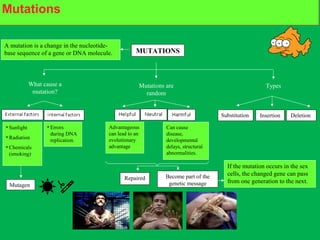
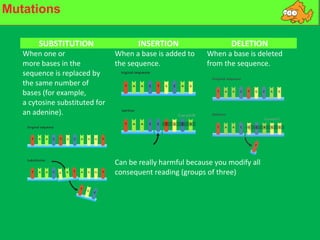
Genes and DNA molecules carry the genetic code that controls what cells are made of and what they do. DNA is made up of a double helix structure with base pairs that always pair together in the same way - A pairs with T and C pairs with G. DNA can make copies of itself through a process called replication where the DNA helix unzips and each single strand builds a new double strand, allowing genetic information to be passed on to new cells.