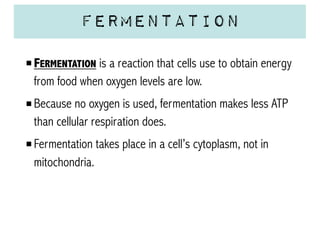
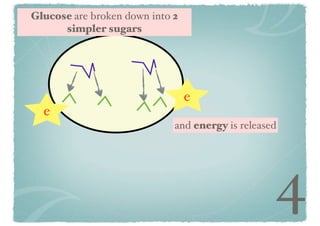
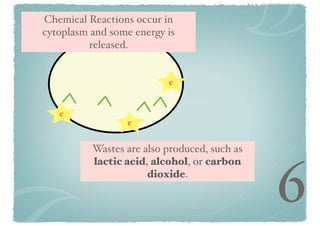
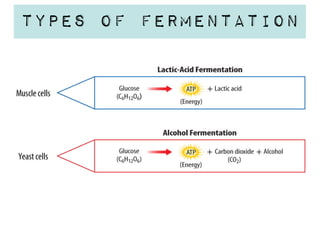
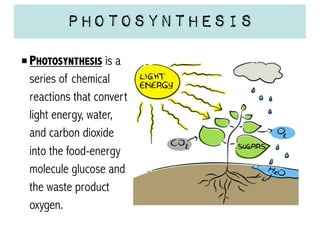
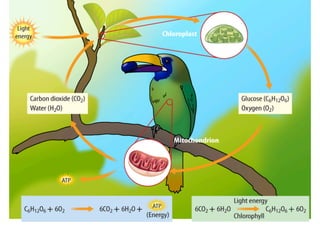
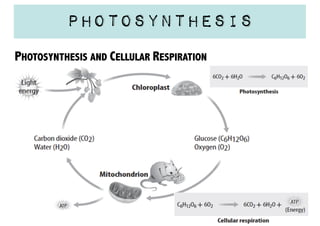
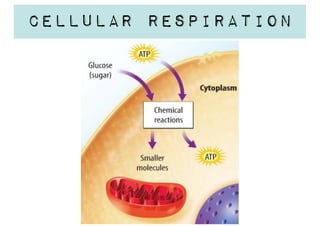
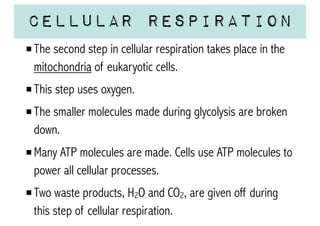
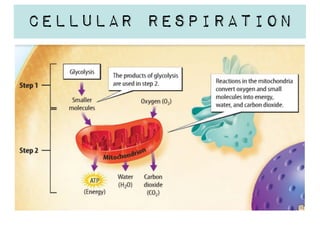
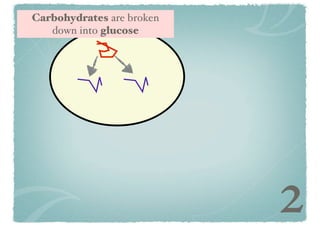
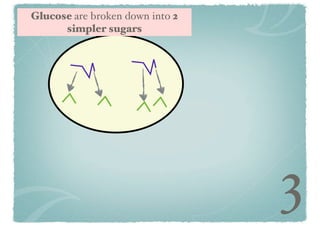
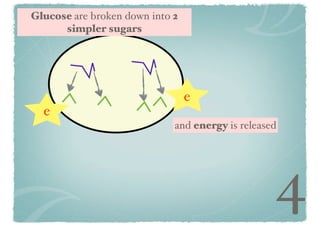
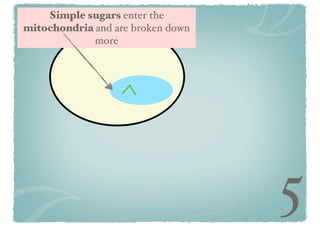
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that convert energy from food into a usable form called ATP. It takes place in two steps - glycolysis in the cytoplasm breaks down glucose, producing some ATP and precursor molecules, while the second step in mitochondria uses oxygen to break down these precursors and produce much more ATP. Fermentation is an alternative pathway used without oxygen to produce less ATP. Photosynthesis converts light energy, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen through reactions in chloroplasts.


![Oxygen is used
Energy is released
Carbon dioxide and water are produced and released as wastes.
energy + CO2 + H2O
]
+ O2
wastes
products
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-131129042914-phpapp02/85/Cells-and-Energy-12-320.jpg)