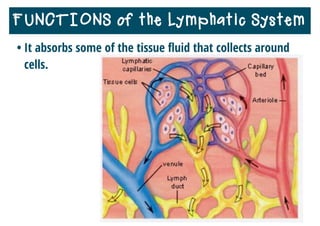
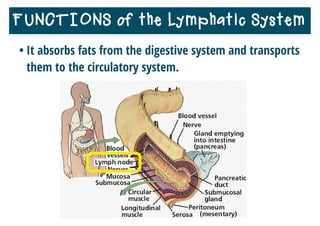
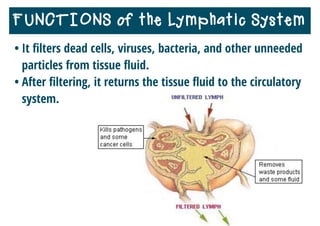
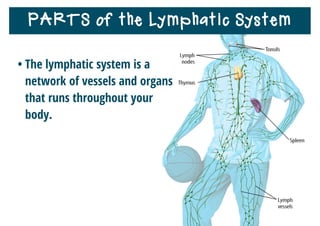
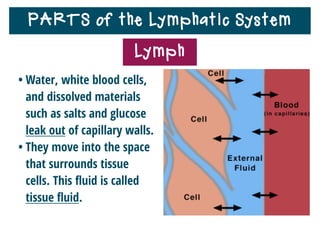
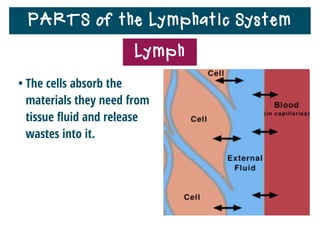
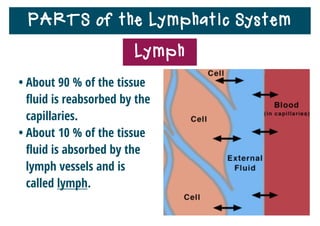
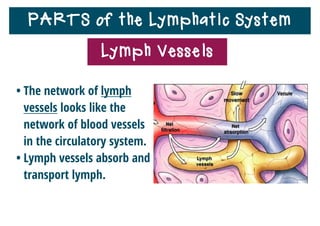
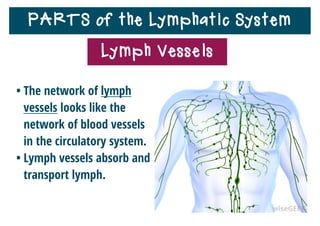
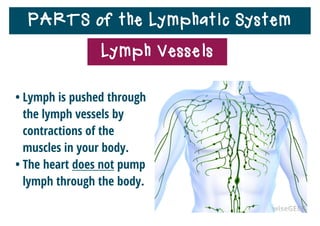
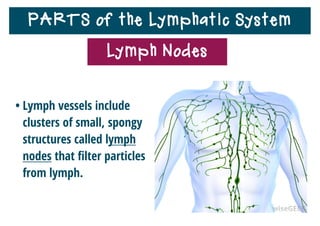
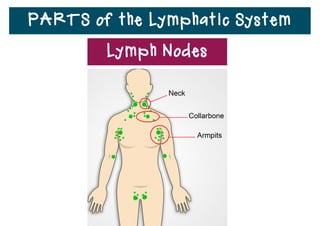
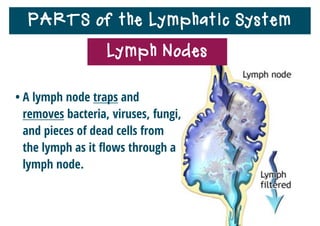
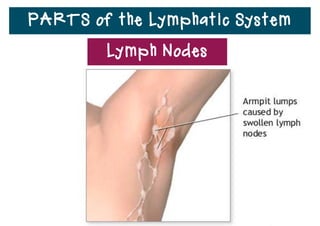
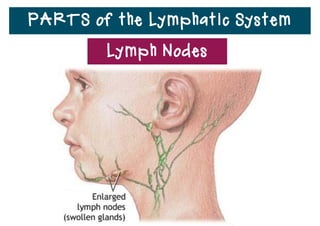
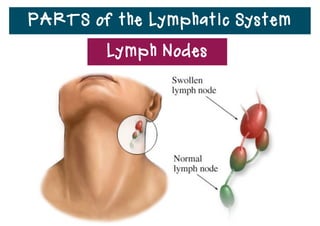
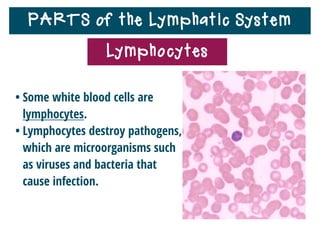
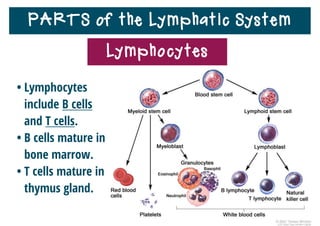
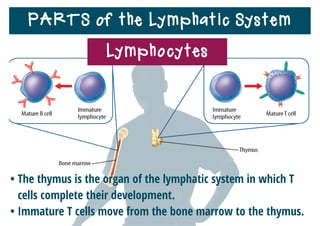
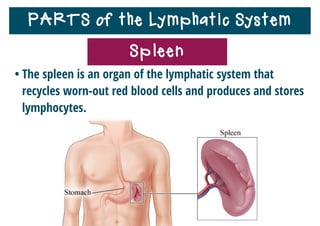
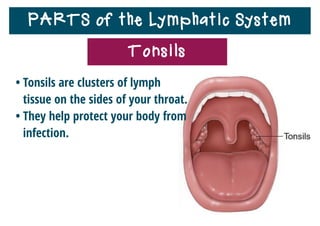
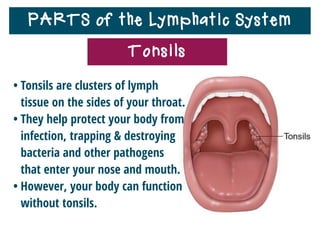
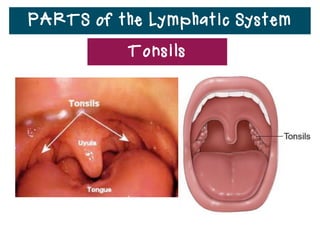
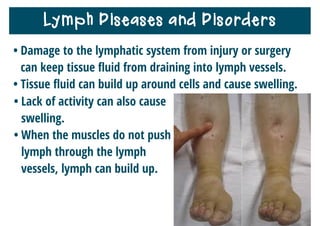
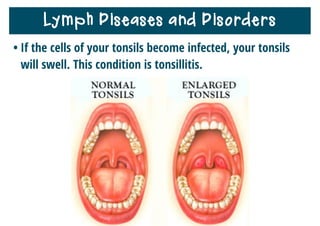
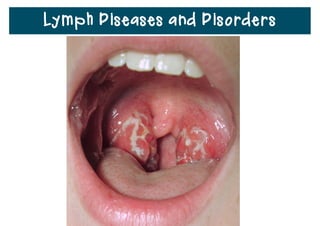
The lymphatic system helps destroy microorganisms, absorbs tissue fluid and transports it back to the bloodstream, and helps fight illnesses and infections. It is composed of lymph vessels, lymph nodes, lymphocytes like B and T cells, the spleen, thymus gland, tonsils, and bone marrow. Together these parts work to filter lymph, produce white blood cells, and defend the body against pathogens.