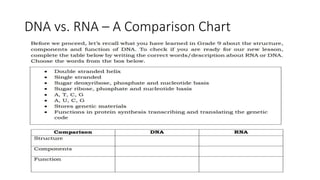
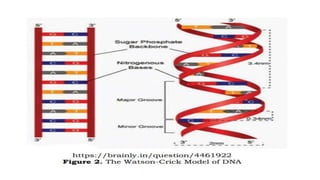
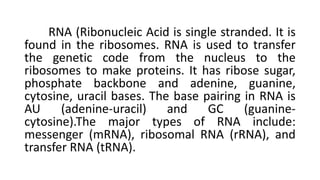
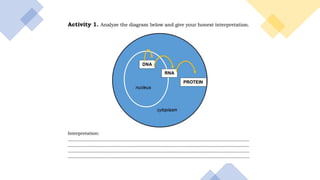
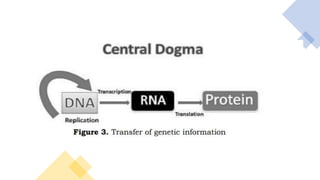
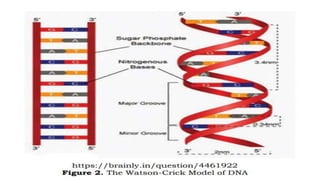
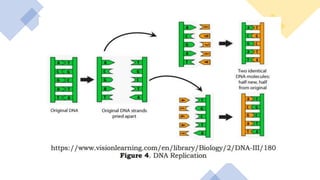
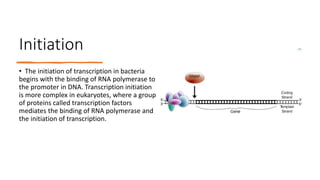
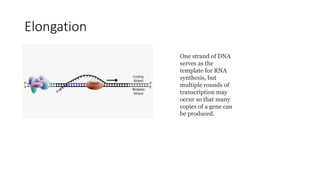
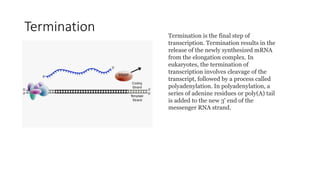
Protein synthesis involves transcription and translation. During transcription, DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA) in the nucleus. The mRNA carries the genetic code from DNA to the cytoplasm for translation. Translation is the process by which the mRNA genetic code is used to produce a specific amino acid sequence or protein with the help of transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomes. The central dogma of molecular biology states that genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to protein.