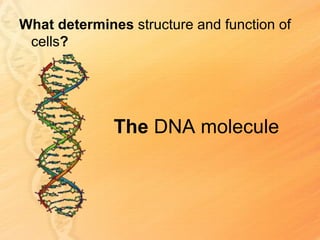
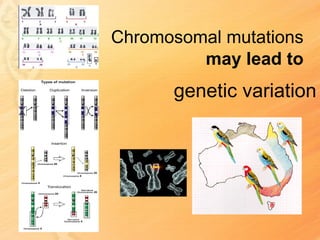
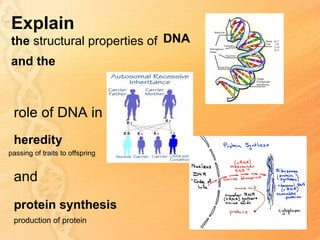
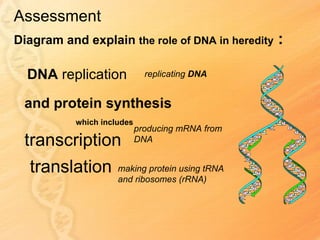
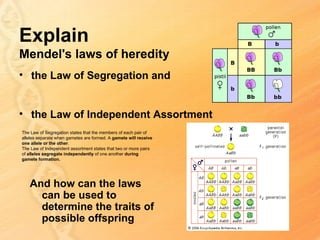
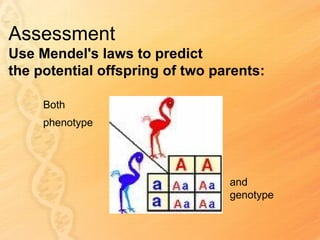
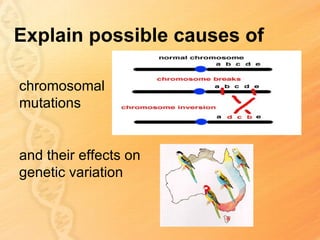
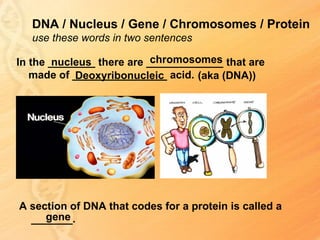
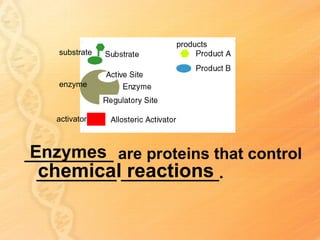
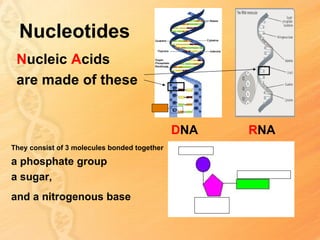
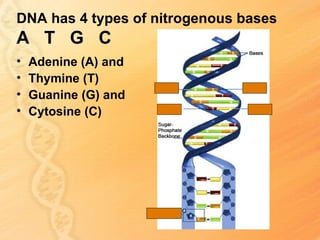
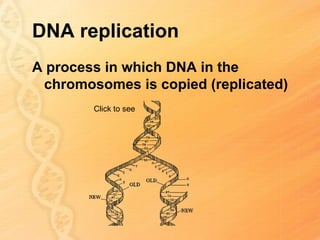
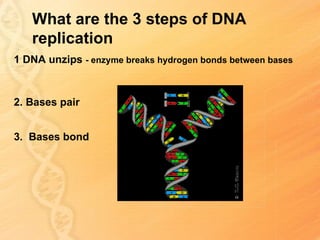
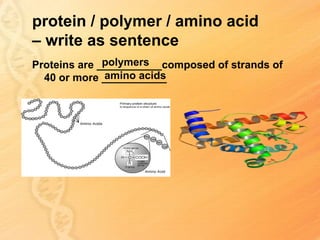
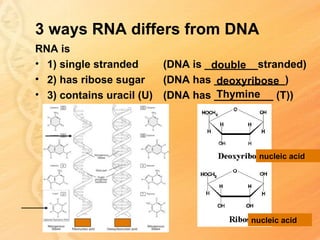
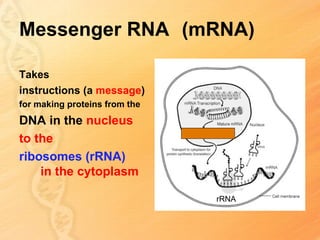
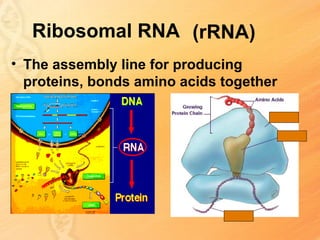
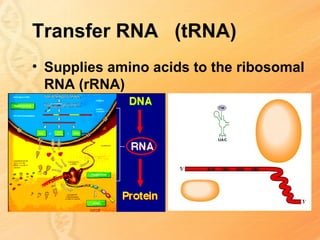
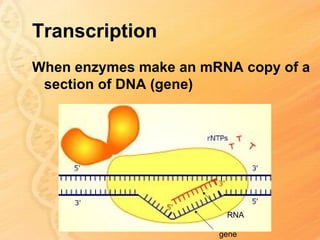
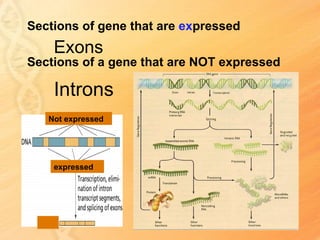
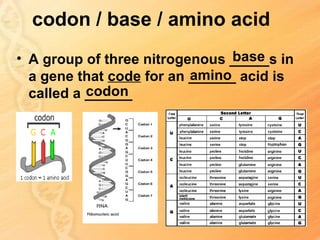
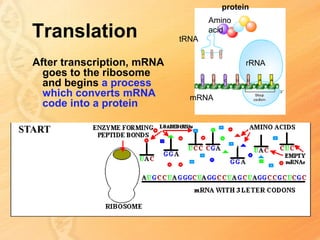
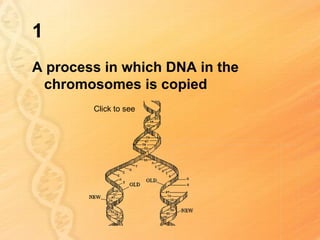
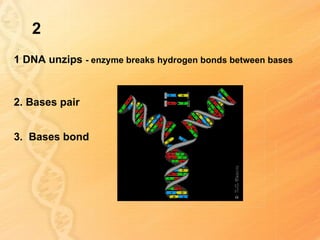
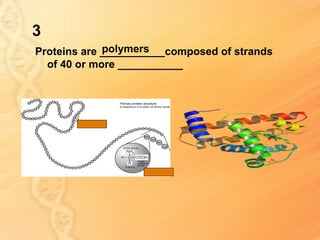
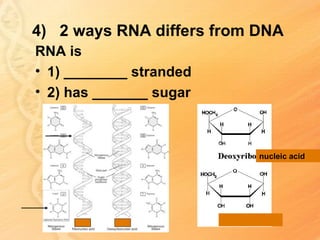
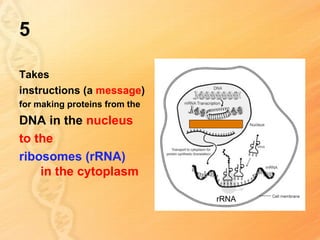
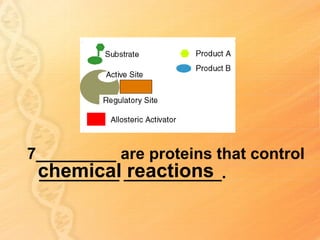
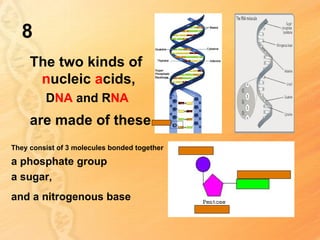
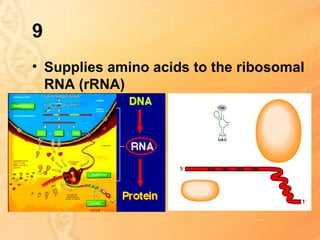
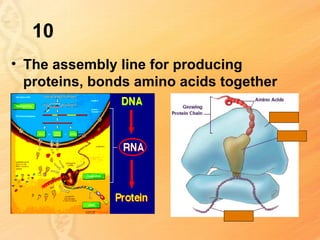
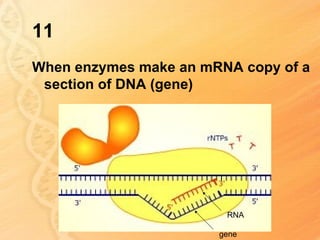
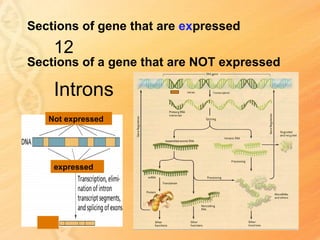
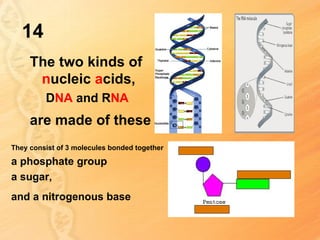
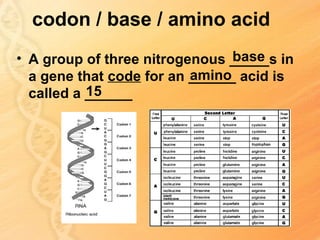
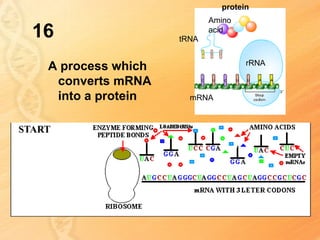
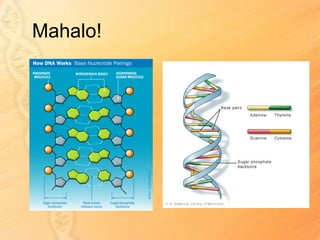
This document provides information about biology topics covered in the second semester, including genetics and evolution. It discusses the structure and function of DNA, how DNA carries genetic information from parents to offspring, and its role in heredity and protein synthesis. It covers Mendel's laws of heredity and how they can be used to determine offspring traits. It also explains chromosomal mutations and genetic variation. The document outlines the process of DNA replication and the steps of transcription and translation in which DNA is copied and transcribed to mRNA and then translated to proteins with the help of tRNA and rRNA.