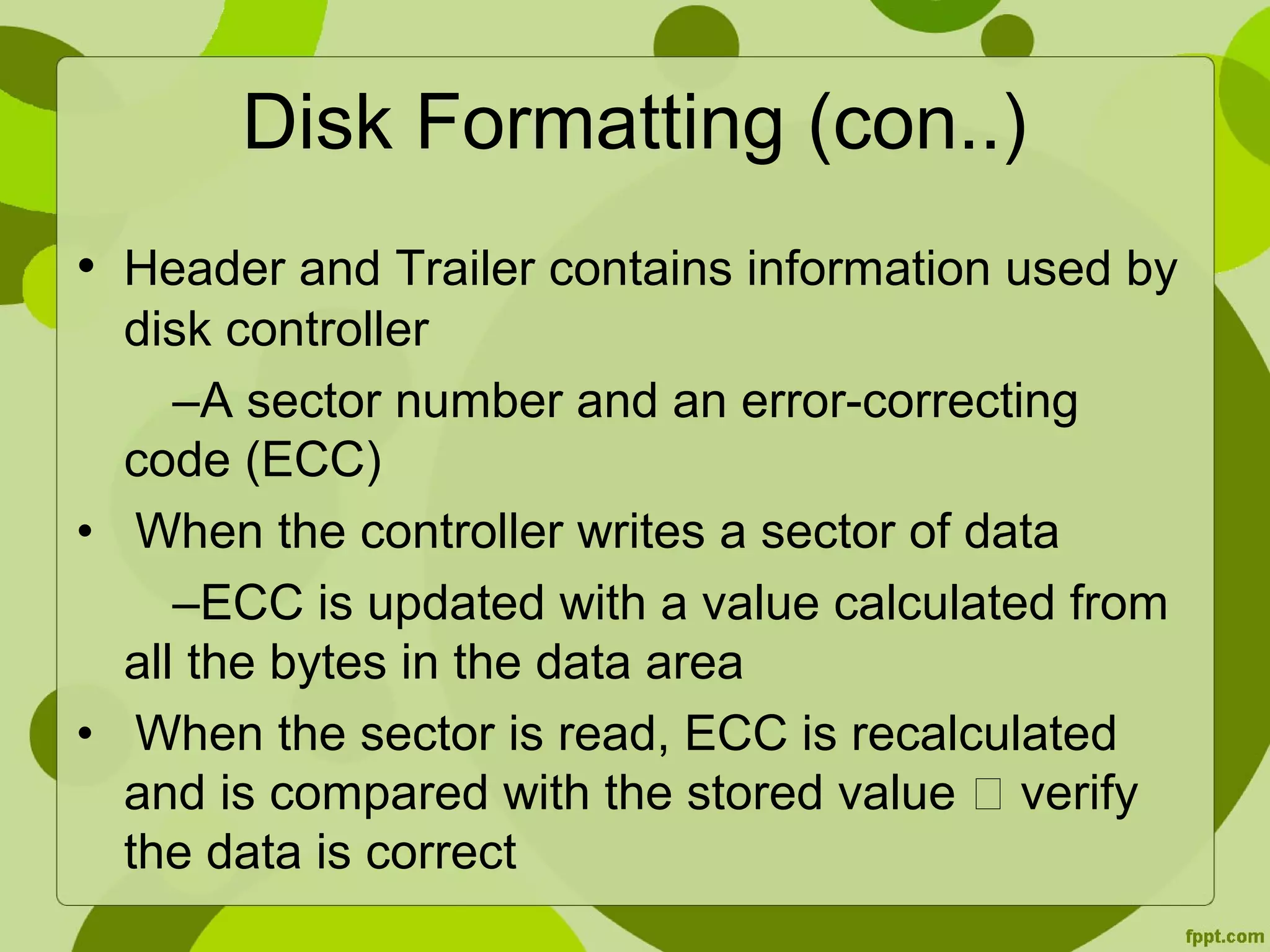
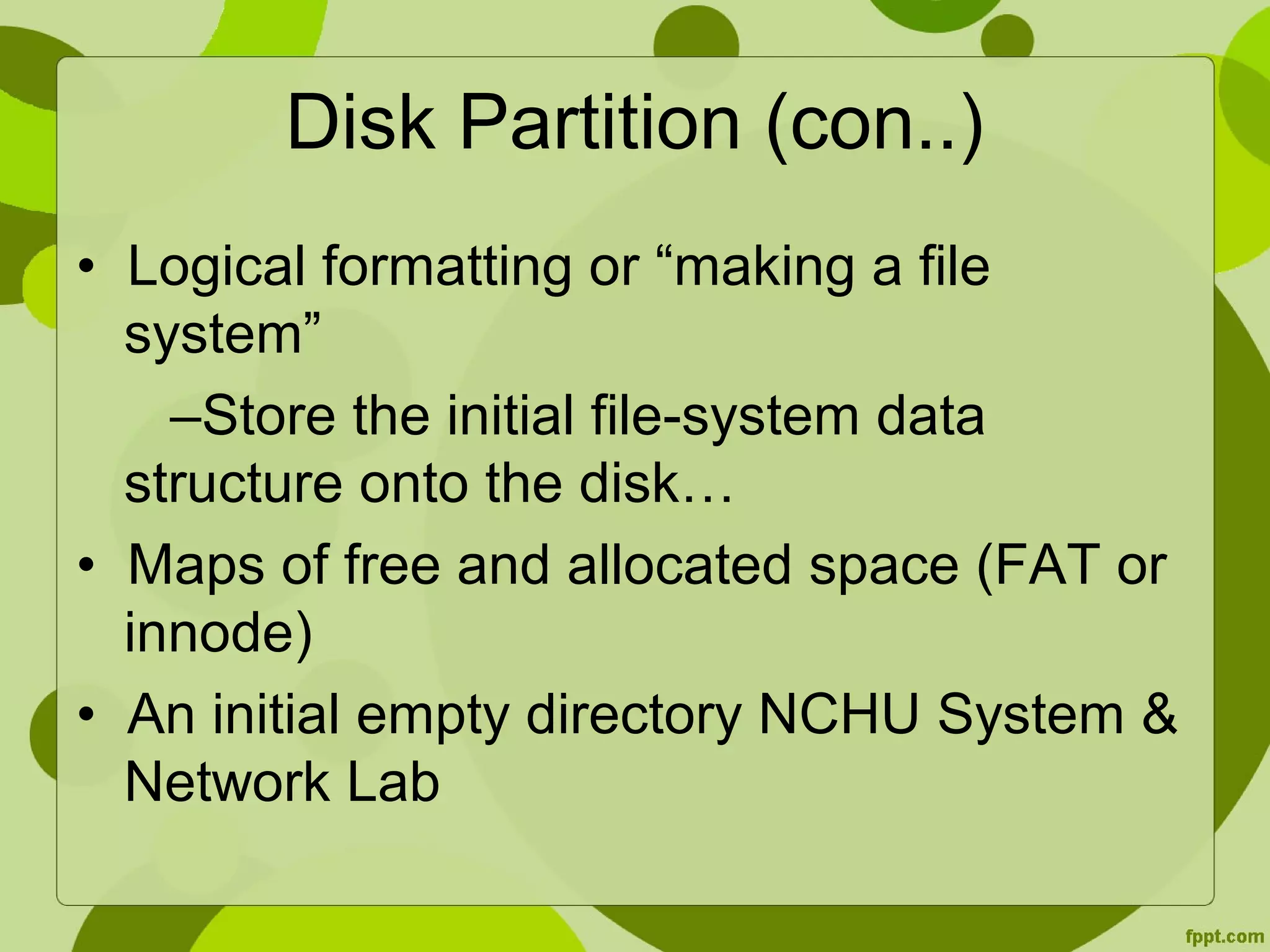
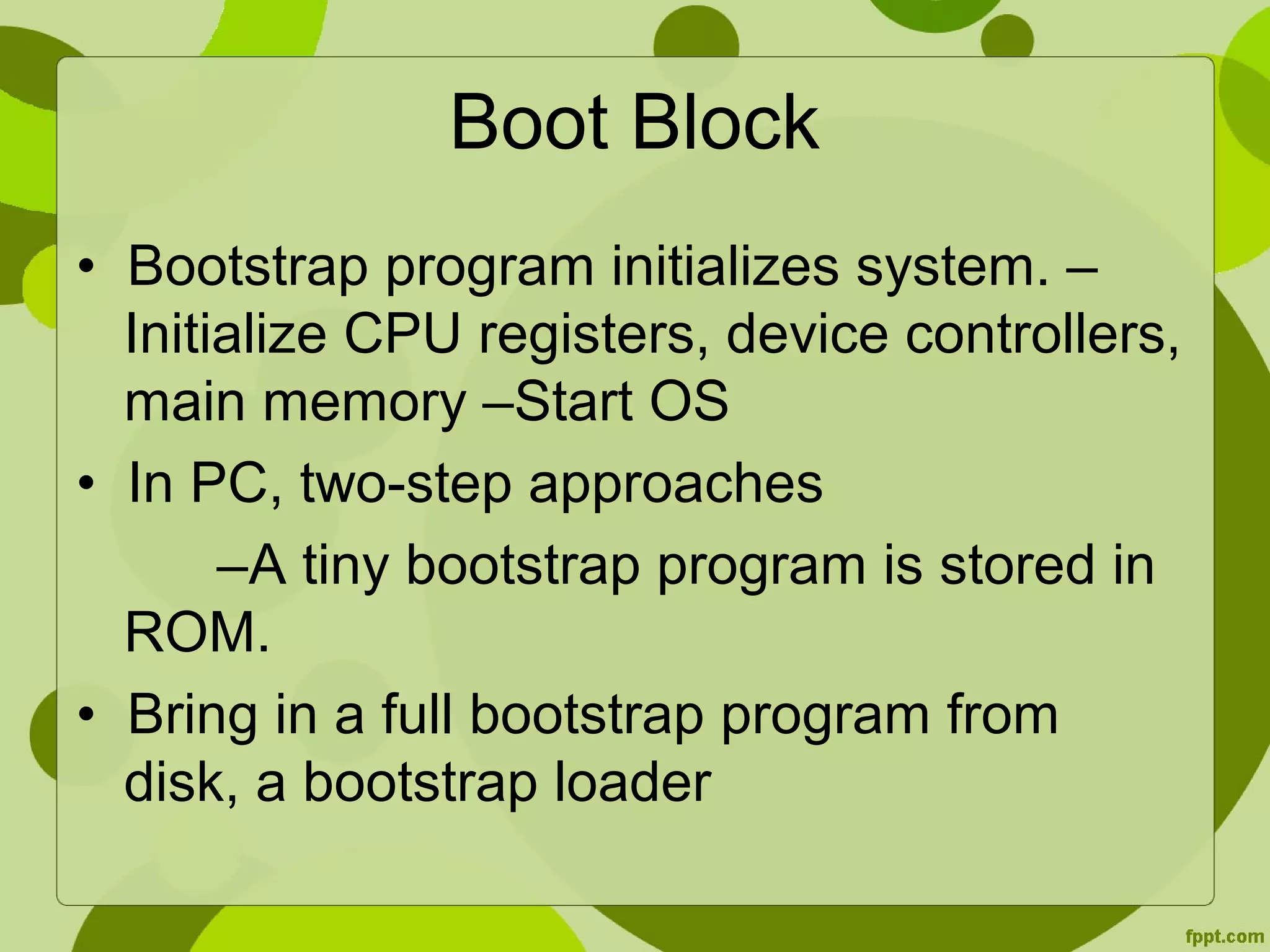
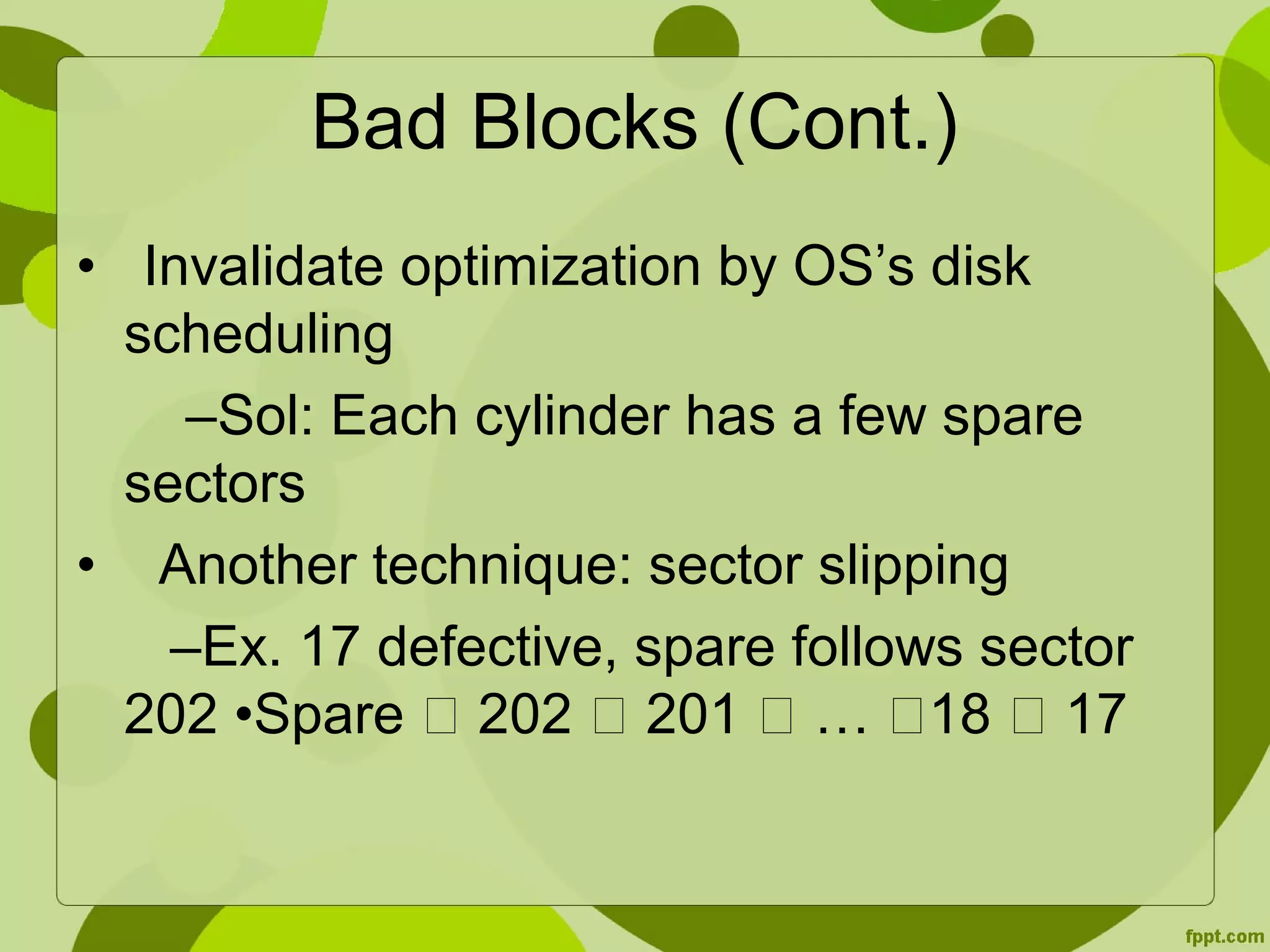
This document discusses disk formatting and partitioning. It explains that low-level formatting divides a disk into sectors that can be read and written to by adding headers, data, and trailers. Logical formatting then creates a file system by adding data structures to map free and allocated space. Disks can also be used as raw disks without a file system for things like swap space. Boot blocks contain bootstrap programs to initialize the system and load the operating system from a fixed location on the boot disk. Disk controllers can manage bad blocks by marking them or replacing them with spare sectors.