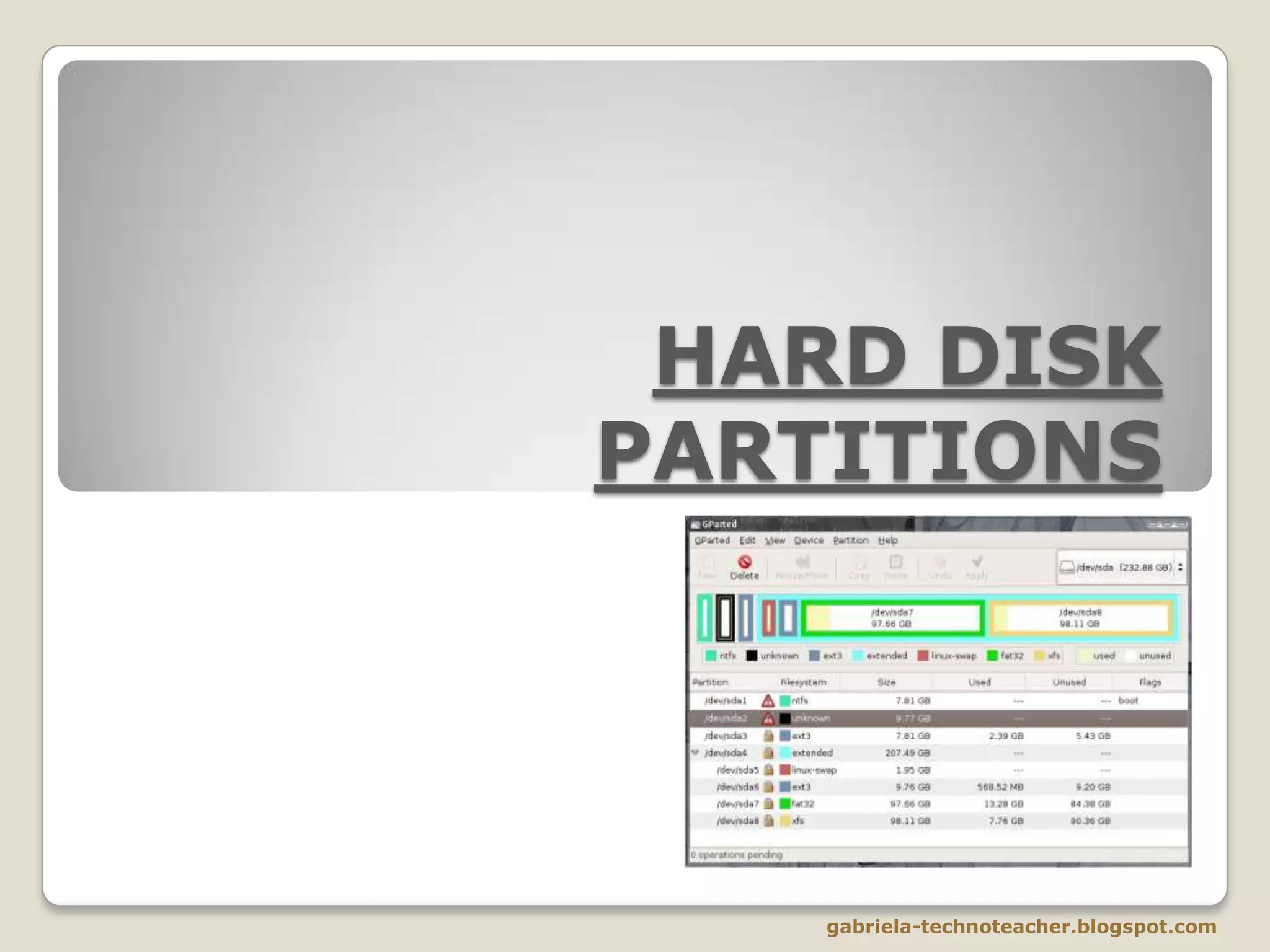
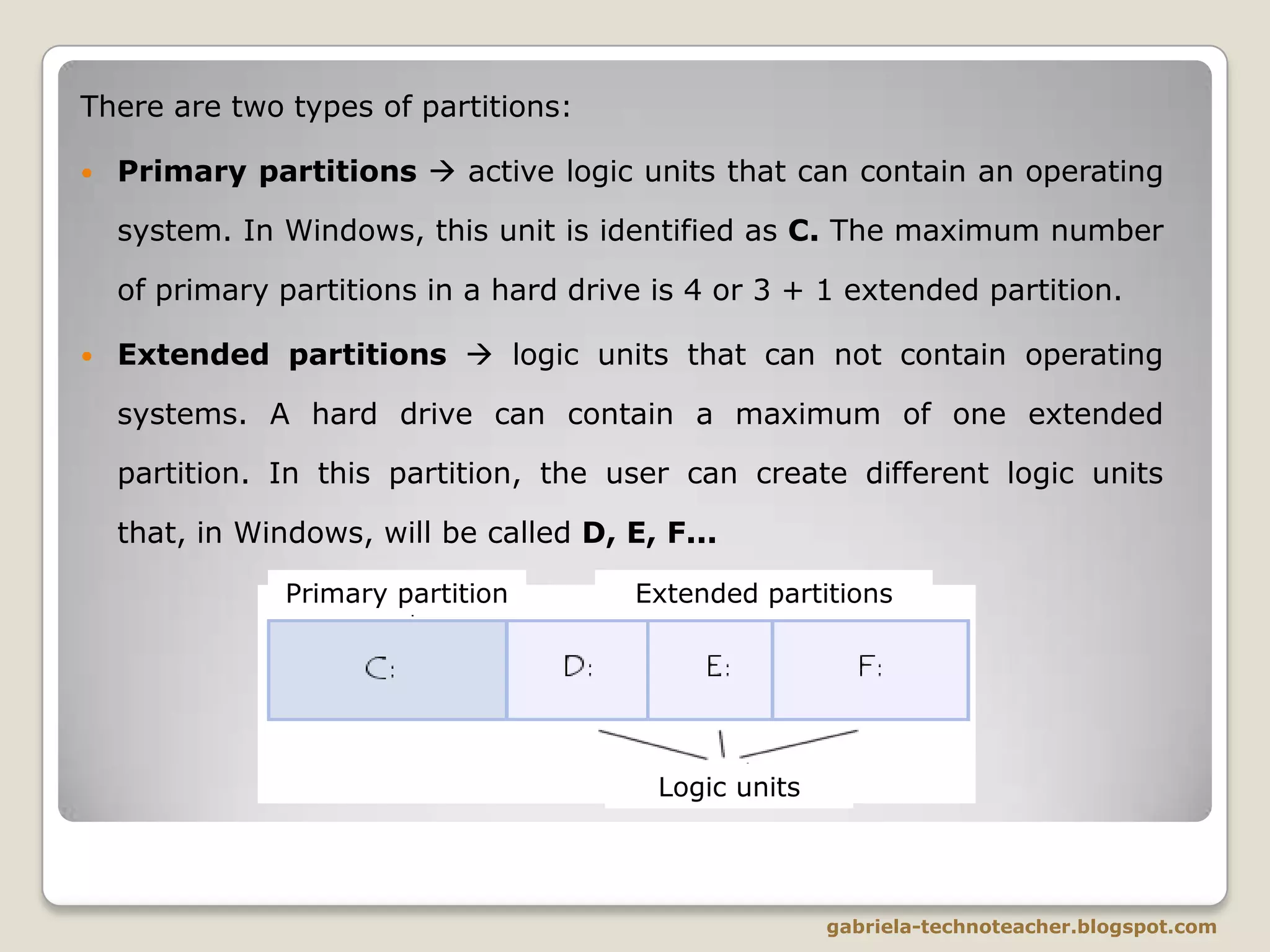
The document discusses the logical structure and partitioning of hard disks. It explains that the hard disk can be divided into logical partitions beyond its physical structure. This allows an operating system to access different sections of the hard disk as separate drives. There are two types of partitions - primary partitions that can directly contain an operating system, and extended partitions that allow creating additional logical drives beyond the 4 primary limit. Partitioning provides benefits like organizing data from multiple users, installing multiple operating systems, improving storage efficiency, and increasing data security through backups.