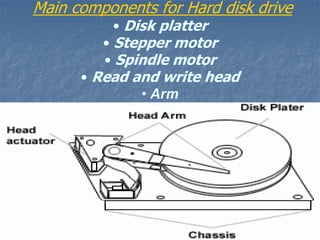
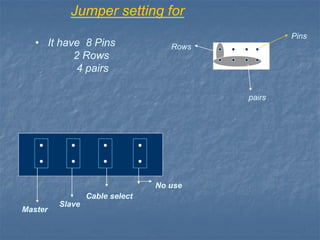
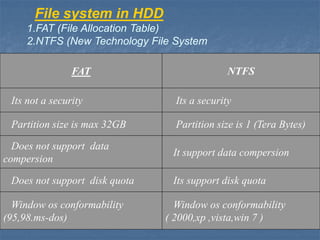
Hard disk drives are secondary storage devices that store data magnetically on spinning platters. They contain disks coated with magnetic material, read/write heads to access data, and motors to spin disks and position heads. Data is organized on disks in concentric tracks divided into sectors. Common interfaces are IDE, SATA, and SCSI, with SATA now most common. Hard disk capacity is measured in bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, and terabytes depending on size.