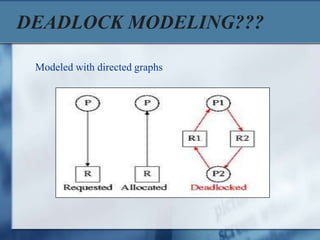
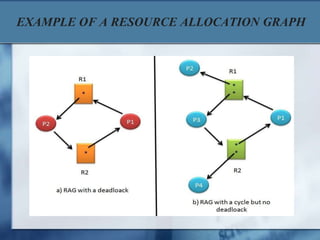
This document discusses deadlocks in operating systems. It defines a deadlock as a set of blocked processes that are each holding a resource and waiting for a resource held by another process. Four conditions must be met for a deadlock to occur: mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption, and circular wait. Deadlocks can be modeled using directed resource allocation graphs. Methods for handling deadlocks include prevention, avoidance, detection, and recovery.