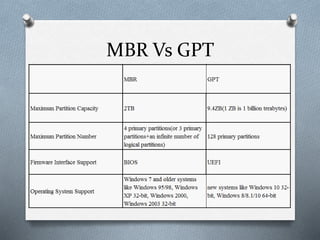
A partition divides a hard drive into logical sections for storing files and installing operating systems. There are three types of partitions: primary, extended, and logical. A primary partition can host an operating system, while an extended partition contains logical drives. The master boot record (MBR) stores information on partition locations and boots the system, but is limited to 4 primary partitions under 2.2TB each. The GUID partition table (GPT) replaces MBR and supports over 18 exabytes per partition. GPT uses a protective MBR for compatibility with older systems.