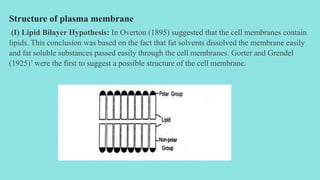
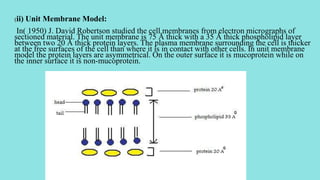
The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable membrane that surrounds the cell. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The fluid mosaic model from 1972 describes the plasma membrane as a fluid bilayer with integral proteins embedded within it, peripheral proteins attached to its surface, and lipid-anchored proteins. The plasma membrane regulates what enters and exits the cell through diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion using channel proteins, and active transport using carrier proteins that require ATP. Endocytosis and exocytosis allow bulk transport across the membrane through vesicles.