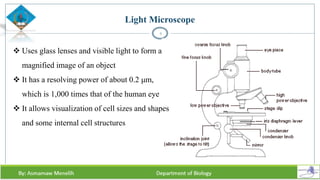
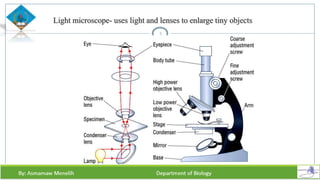
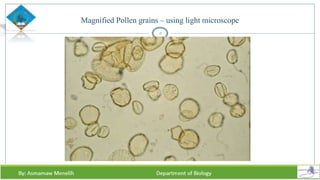
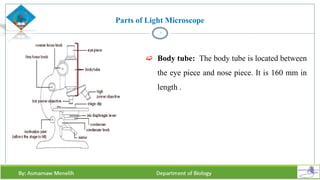
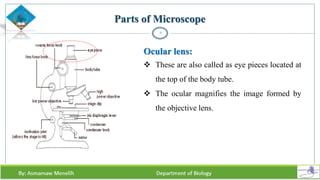
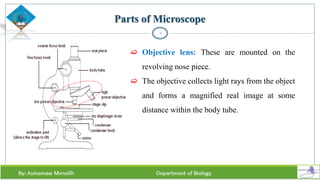
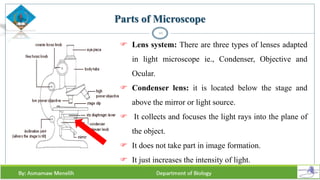
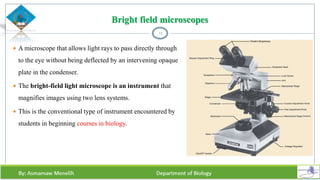
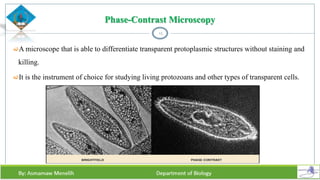
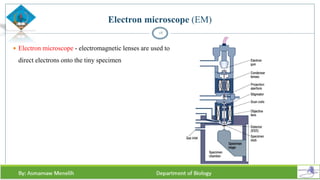
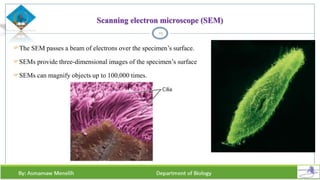
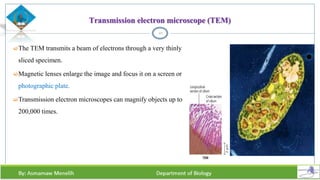
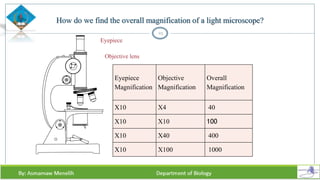
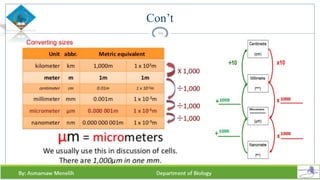
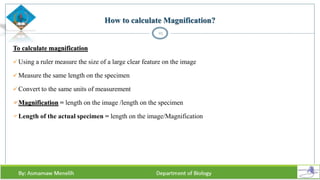
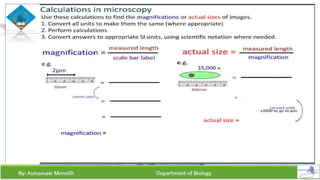
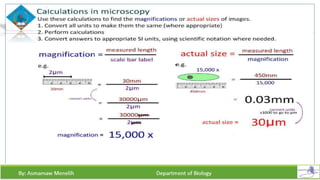
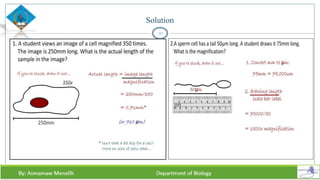
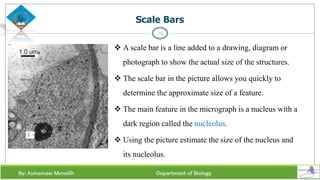
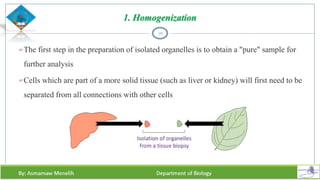
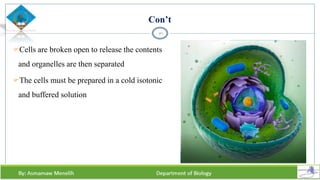
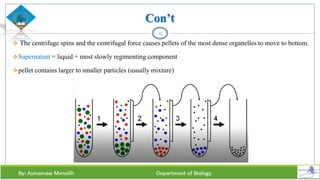
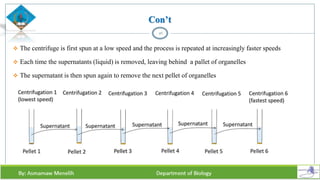
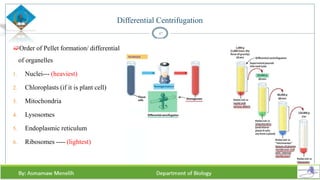
Chapter two discusses methods for studying cells, focusing on microscopy techniques that enhance the visibility of cellular structures. It covers light and electron microscopes, including their types, magnification capabilities, and resolution details, along with cell fractionation methods for isolating organelles. The chapter aims to provide students with foundational knowledge in microscopy to assist in their understanding of cellular biology.