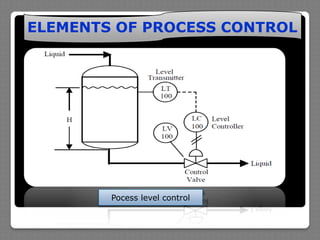
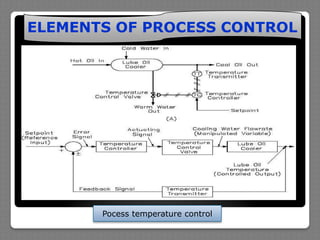
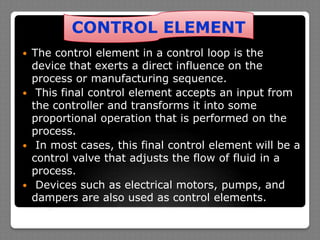
The document describes the basic elements of process control systems, including measurement, evaluation, and control elements. It provides examples of using a level transmitter, level controller, and control valve to regulate liquid level in a tank. It also discusses using temperature sensors and controllers to regulate process temperature. Block diagrams are presented to illustrate how these elements work together in a control loop. The purposes of open loop and closed loop control systems are also overviewed.