This document provides an overview of control systems engineering. It discusses:
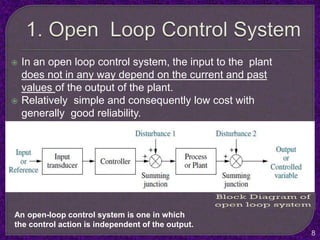
- The basics of control theory including open and closed loop control systems.
- Examples of control systems in real life including manual vs automatic control of a car.
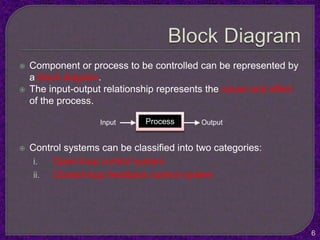
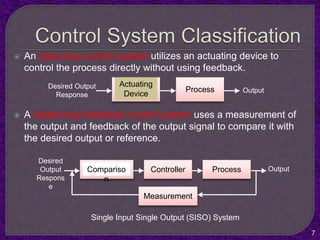
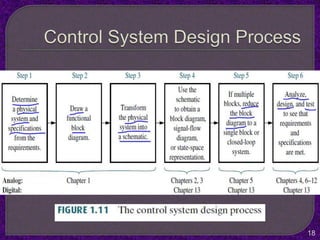
- Classification of control systems as open loop or closed loop and the processes of each.
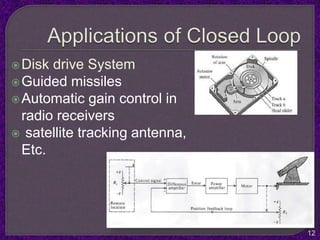
- Applications of control systems including temperature regulation and motor speed control.
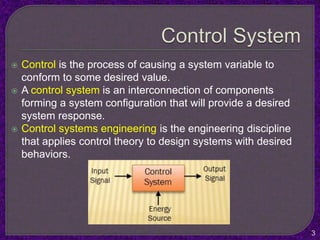
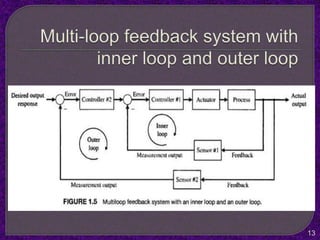
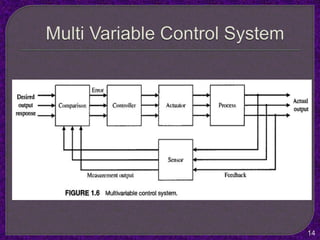
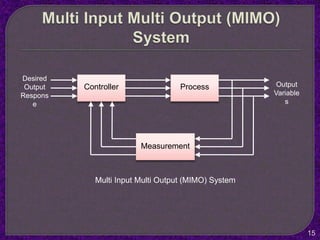
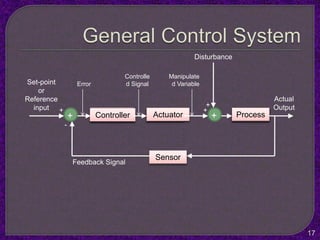
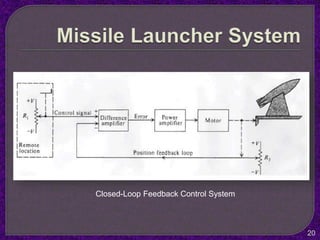
- The purpose of control systems is to cause a system variable to conform to a desired value through feedback.