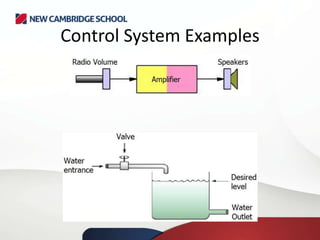
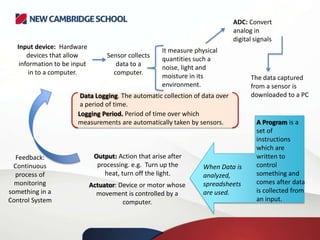
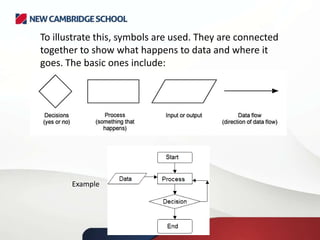
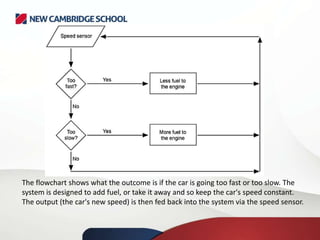
A control system typically comprises a computer or microprocessor that handles data from sensors and sends signals to output devices. An interface box converts signals between the sensors and the processor. A control system manages and regulates the behavior of other systems using input and output devices. Sensors collect data as input, which is processed by a computer program and can result in actuators controlling output devices based on the feedback received.