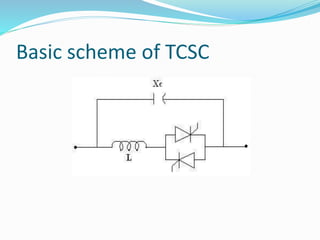
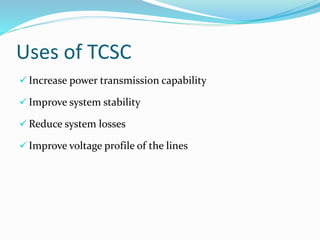
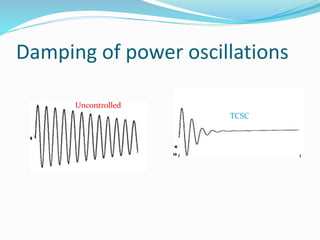
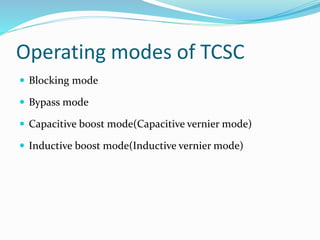
The document discusses Thyristor Controlled Series Compensation (TCSC), a FACTS device that uses thyristors to control the capacitive reactance of transmission lines. TCSC can enhance power flow, limit fault current, improve stability and transients. It introduces benefits like mitigating subsynchronous resonance risks, damping power oscillations, and improving post-contingency stability. TCSC operates in modes like blocking, bypass, capacitive boost and inductive boost to accurately regulate power flow and damp oscillations while increasing transmission capacity and stability.