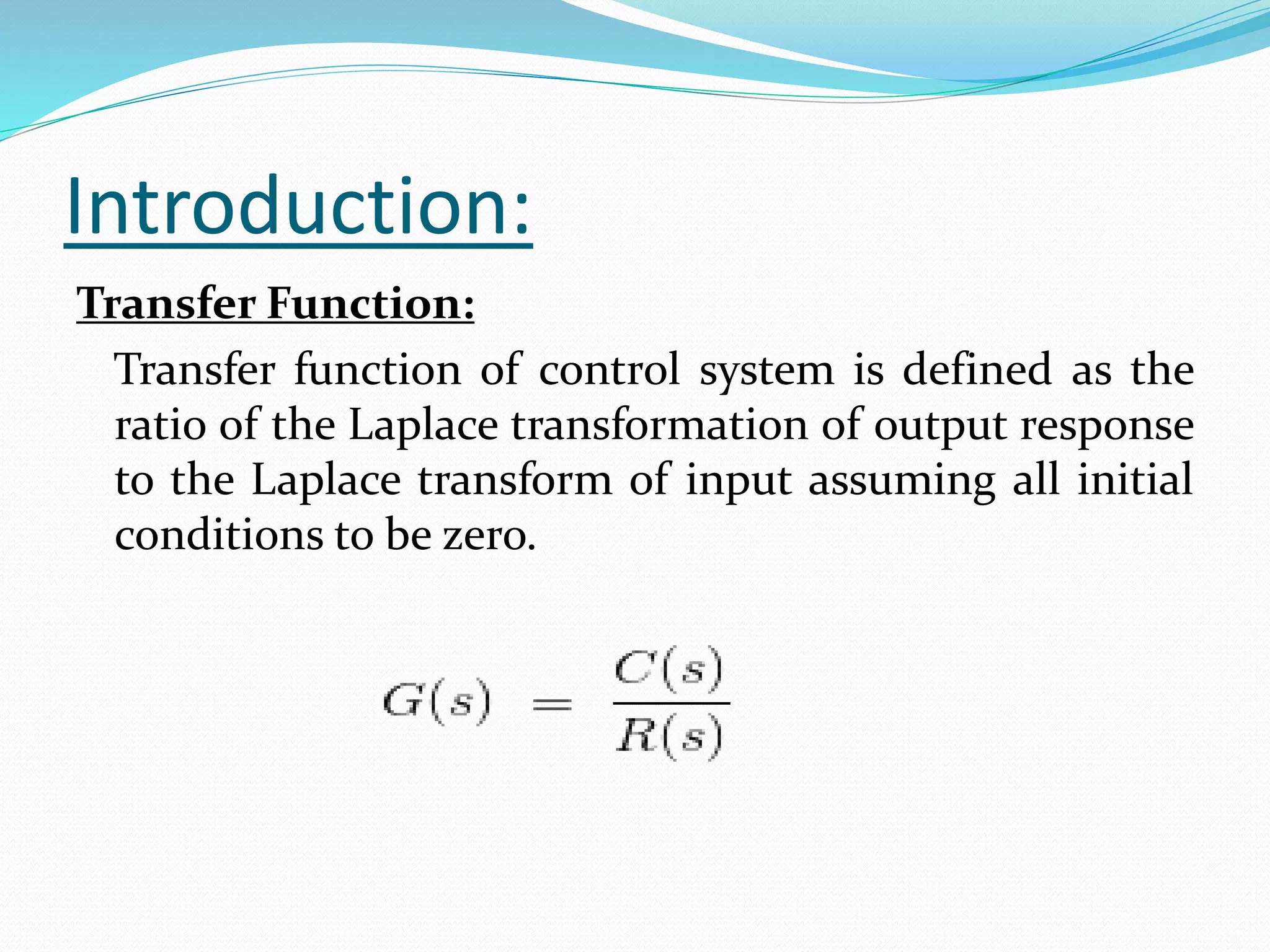
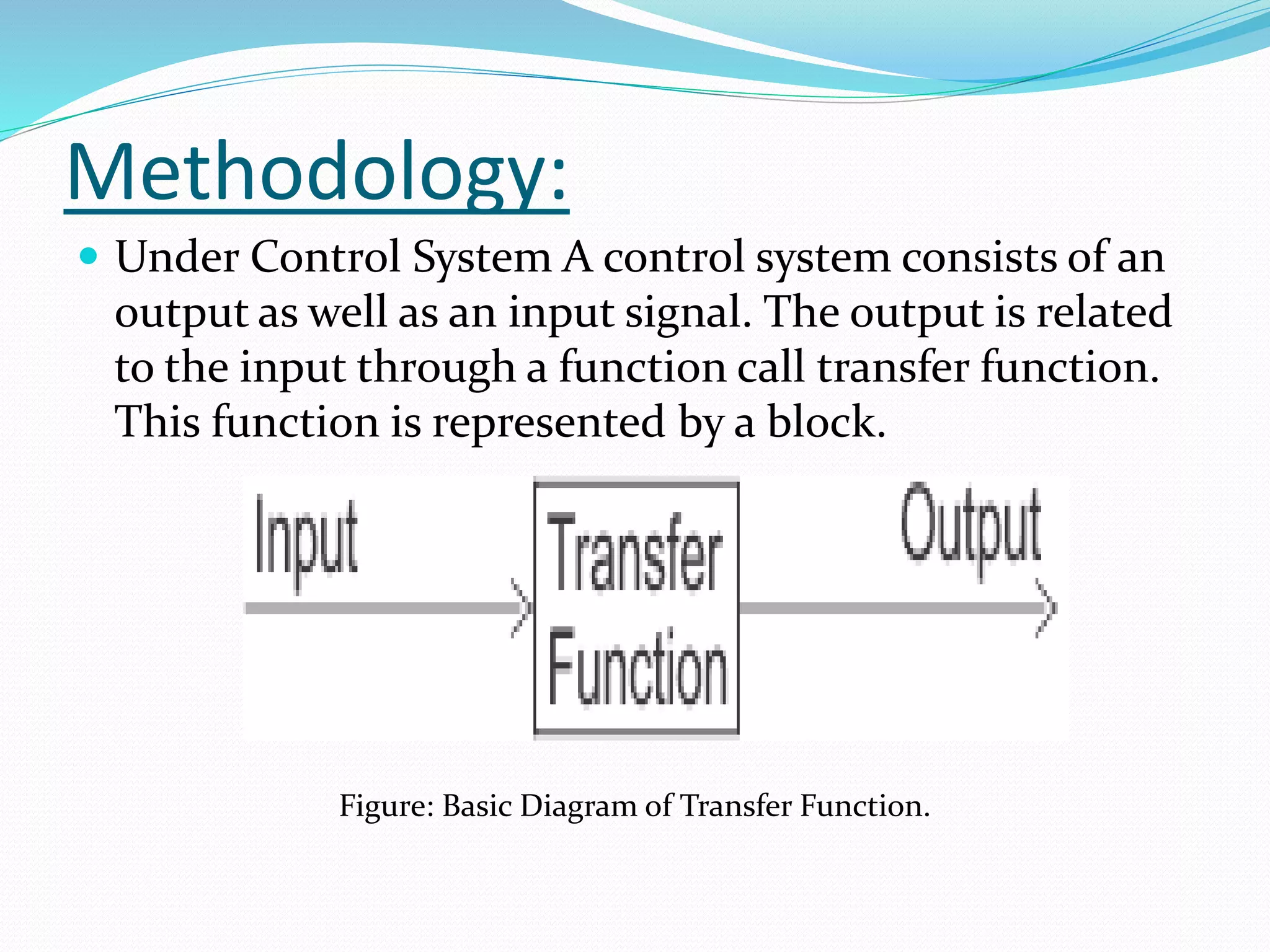
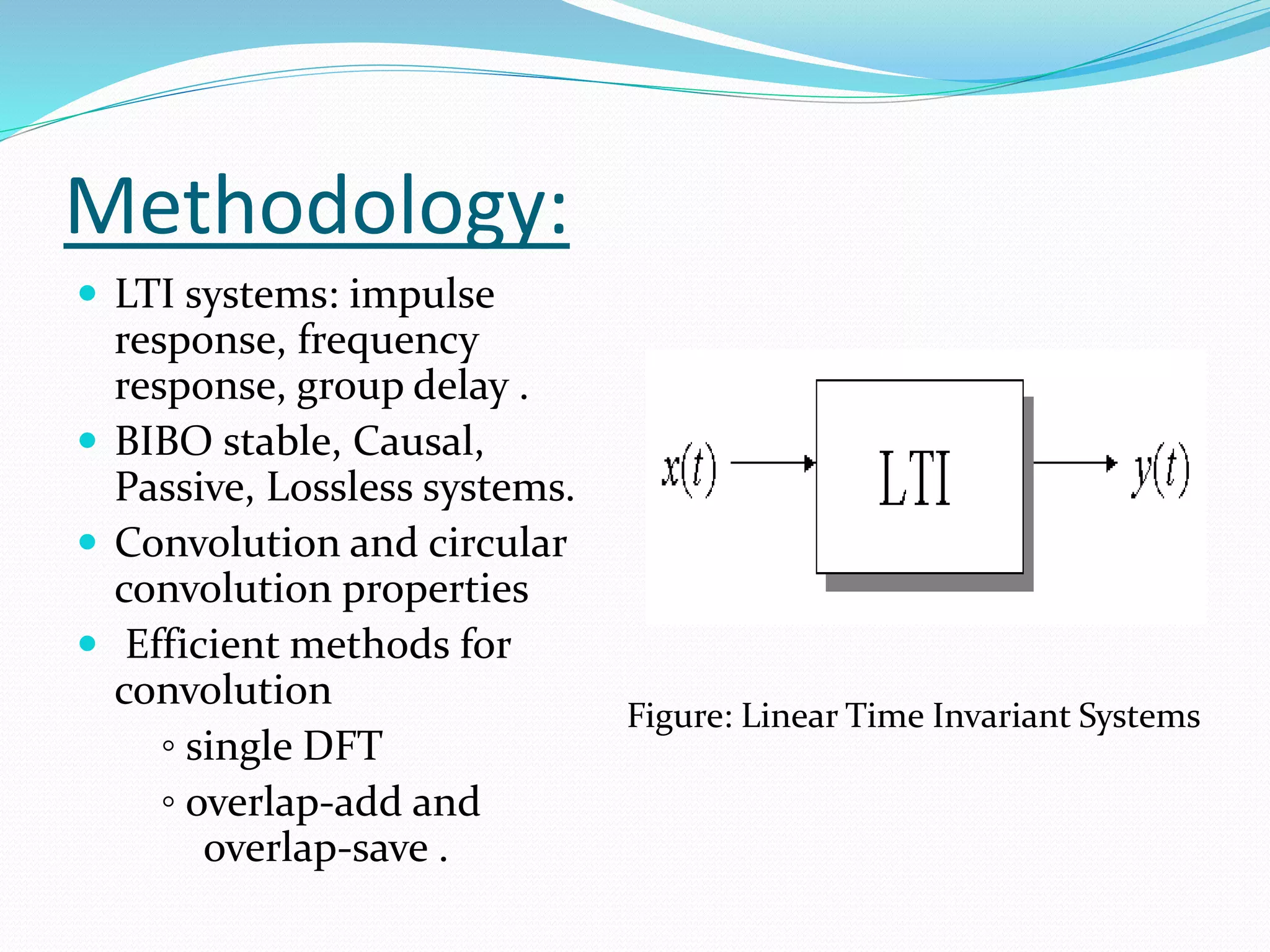
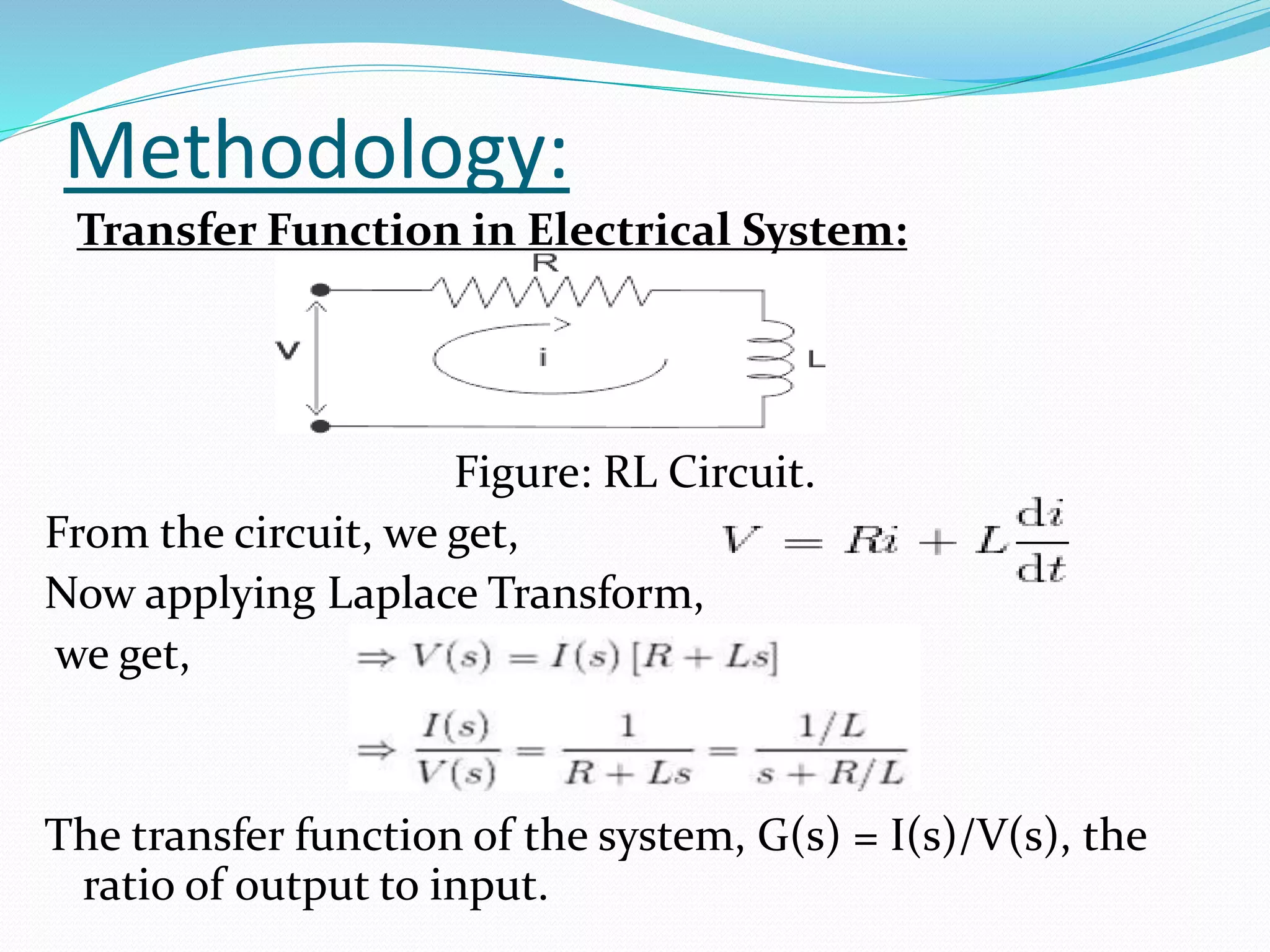
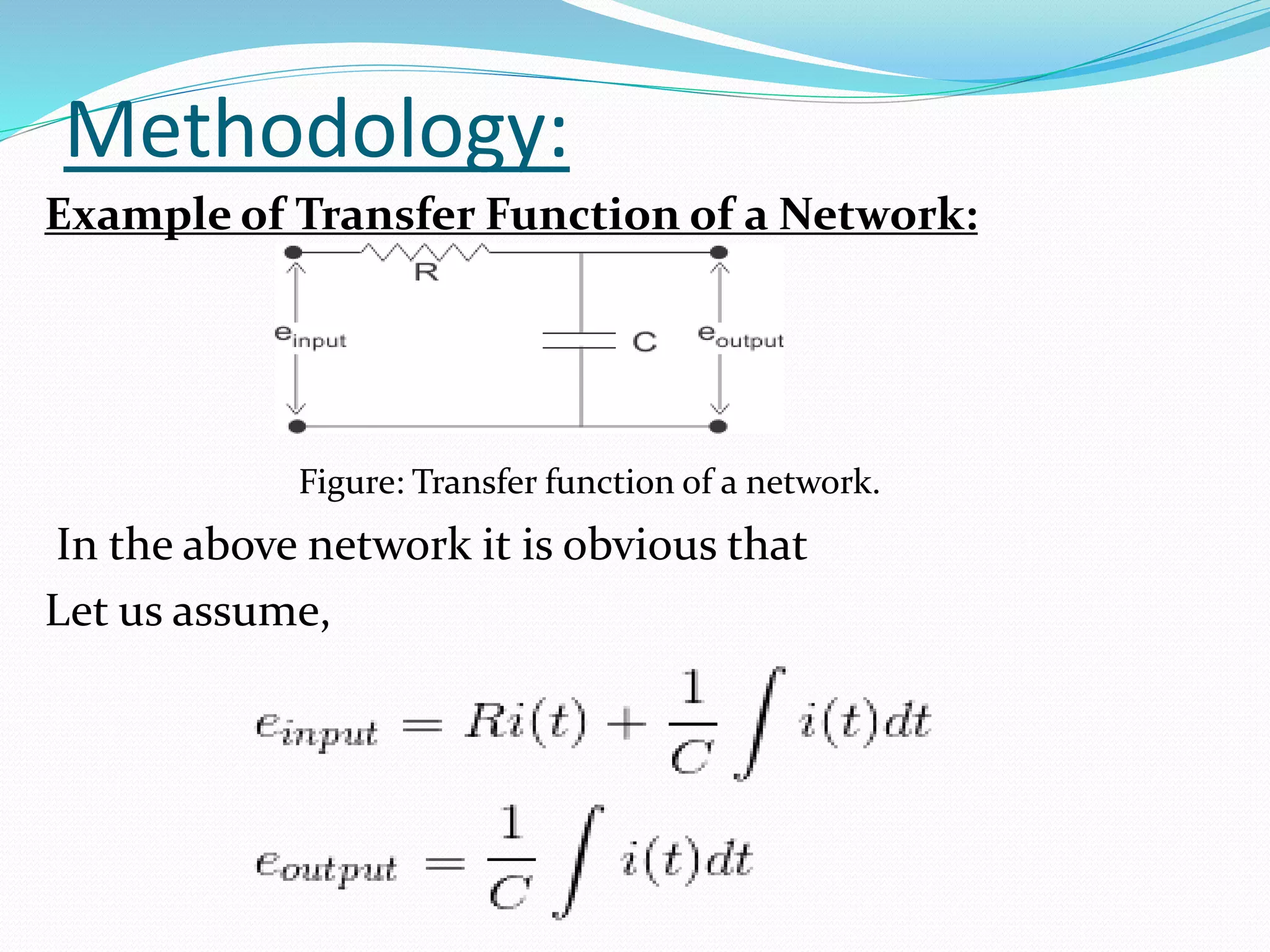
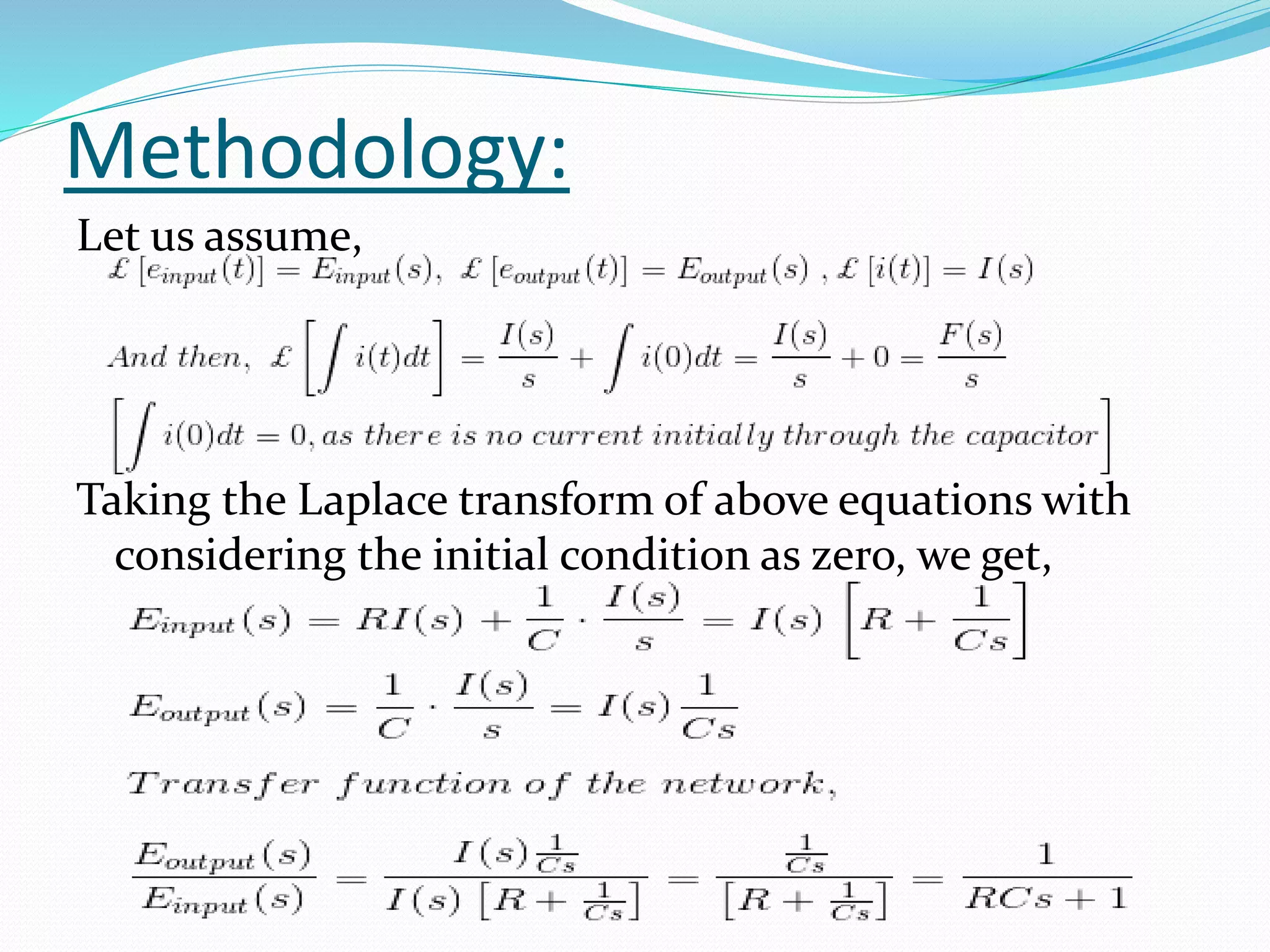
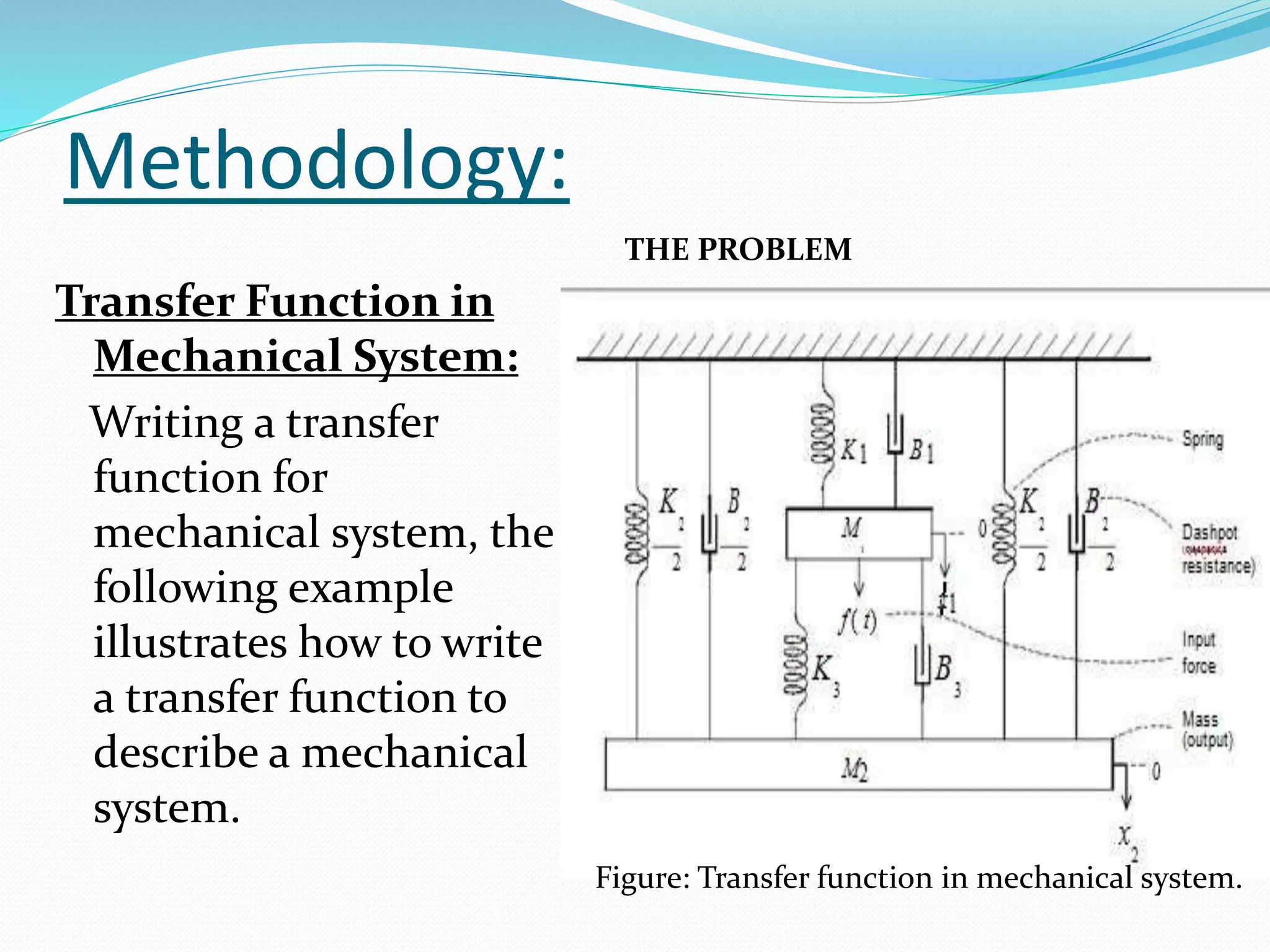
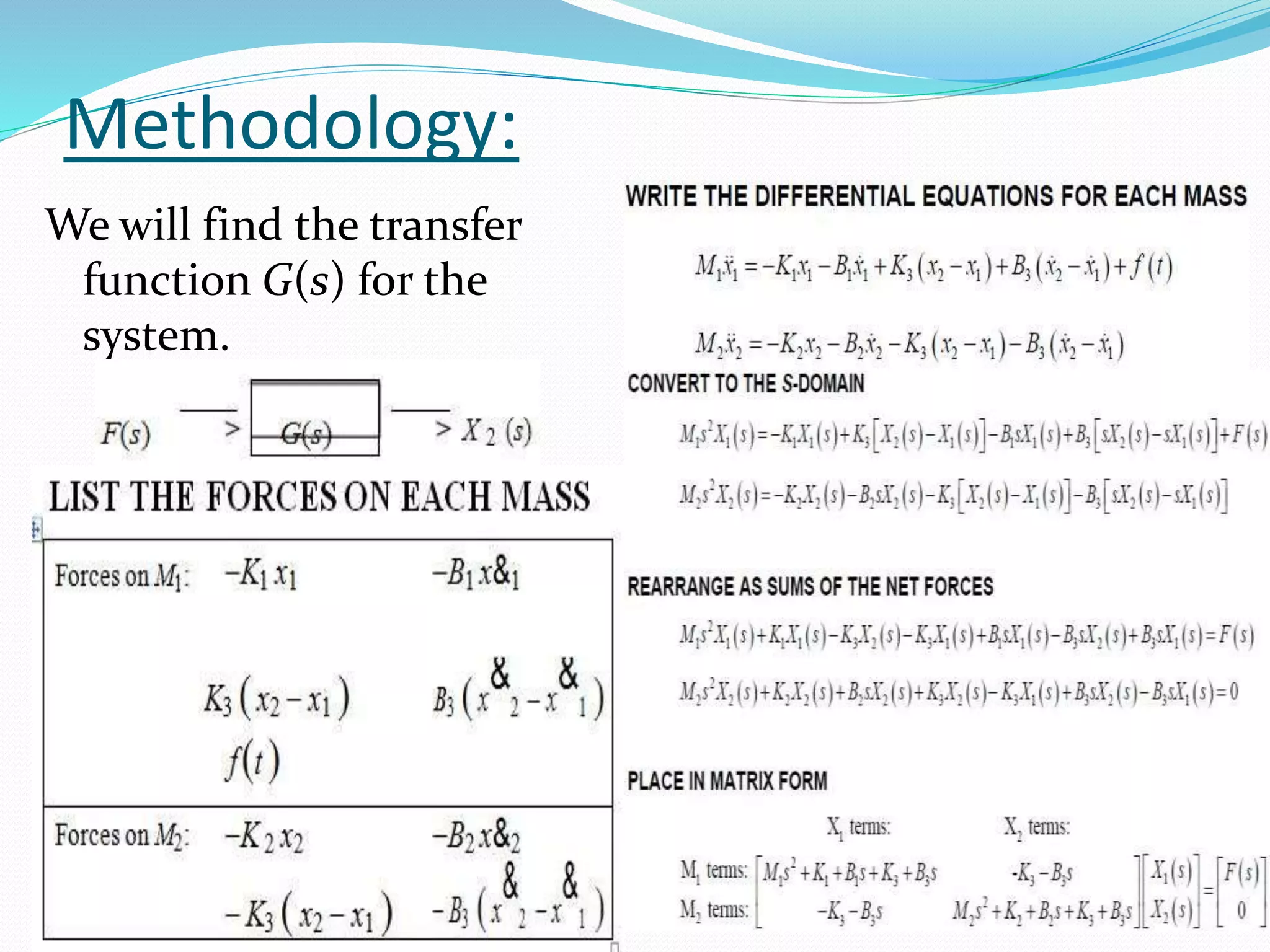
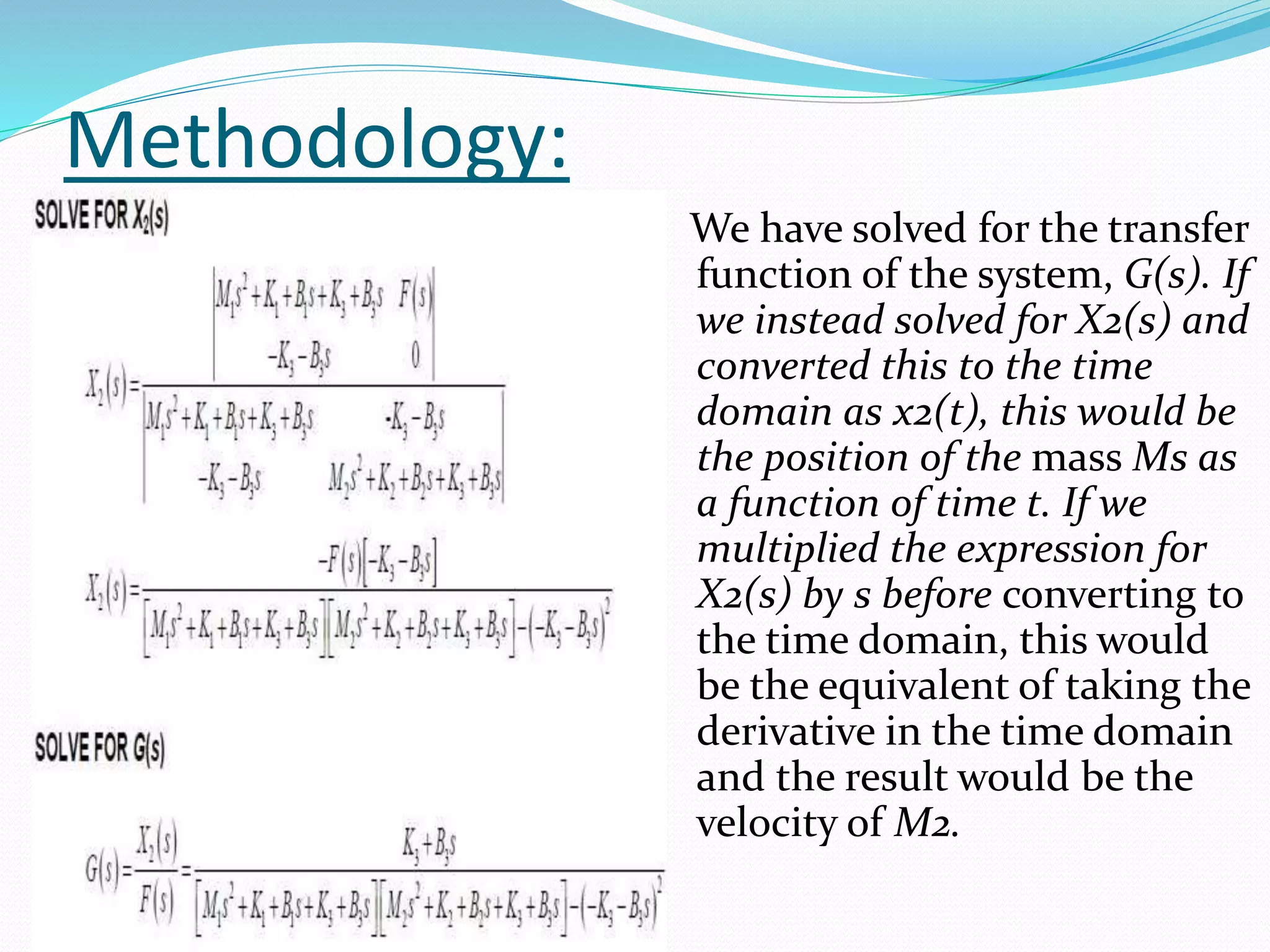
The document discusses the transfer function in control systems, highlighting its definition, objectives, methodologies, and applications in electrical and mechanical systems. It emphasizes the importance of transfer functions for analyzing system behavior and output response while also mentioning limitations such as its applicability only to linear systems. The conclusion notes that although transfer functions are foundational in classical control engineering, state space representations are now often preferred for complex systems.