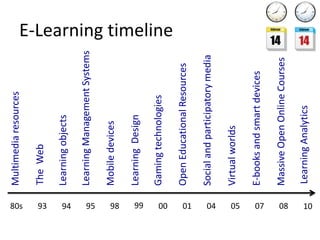
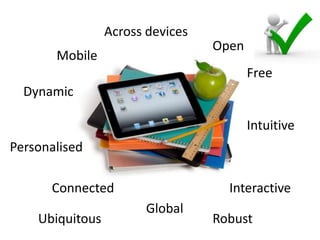
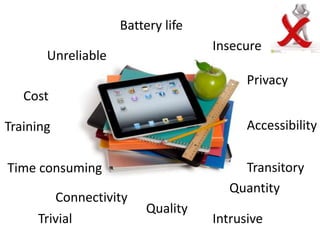
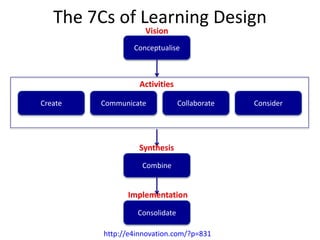
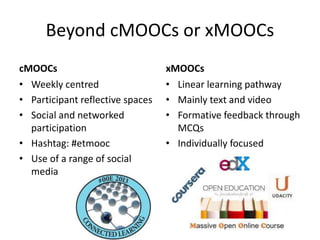
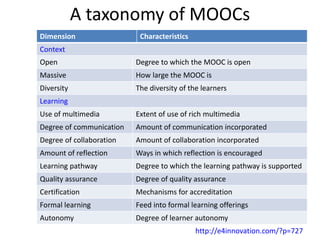
1. The document discusses emerging technologies in education and their impact on learning, including issues around openness, mobile learning, social media, digital identity and distributed cognition.
2. It notes both benefits like access to resources and interaction, as well as challenges such as information overload, lack of digital skills, and privacy issues.
3. The author argues that while technologies enable new forms of learning, there is also a need to slow down and focus on quality of engagement between teachers and learners to promote deep learning.