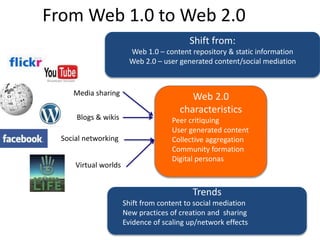
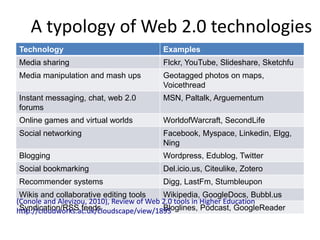
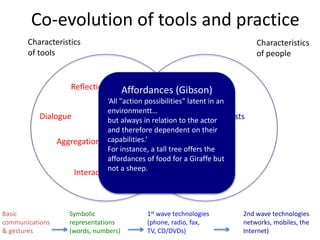
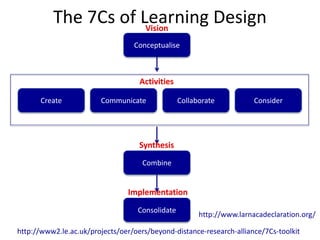
Digital literacies and digital identities were discussed. Key points included:
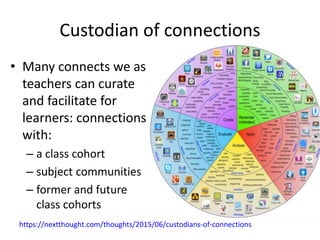
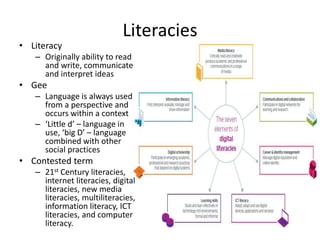
1) Digital literacies involve social practices and meaning making with digital tools, going beyond just skills to include competence and participation.
2) Digital identity involves how one presents and interacts online through facets like reputation, impact, and openness. Issues around privacy, interpretation, and vulnerability were raised.
3) The future will involve challenges around disaggregation of education, needing new digital literacies, business models, and pedagogies as boundaries continue to blur with technology advancement.