This document discusses both the opportunities and challenges of social media and open practices in education. It summarizes that:
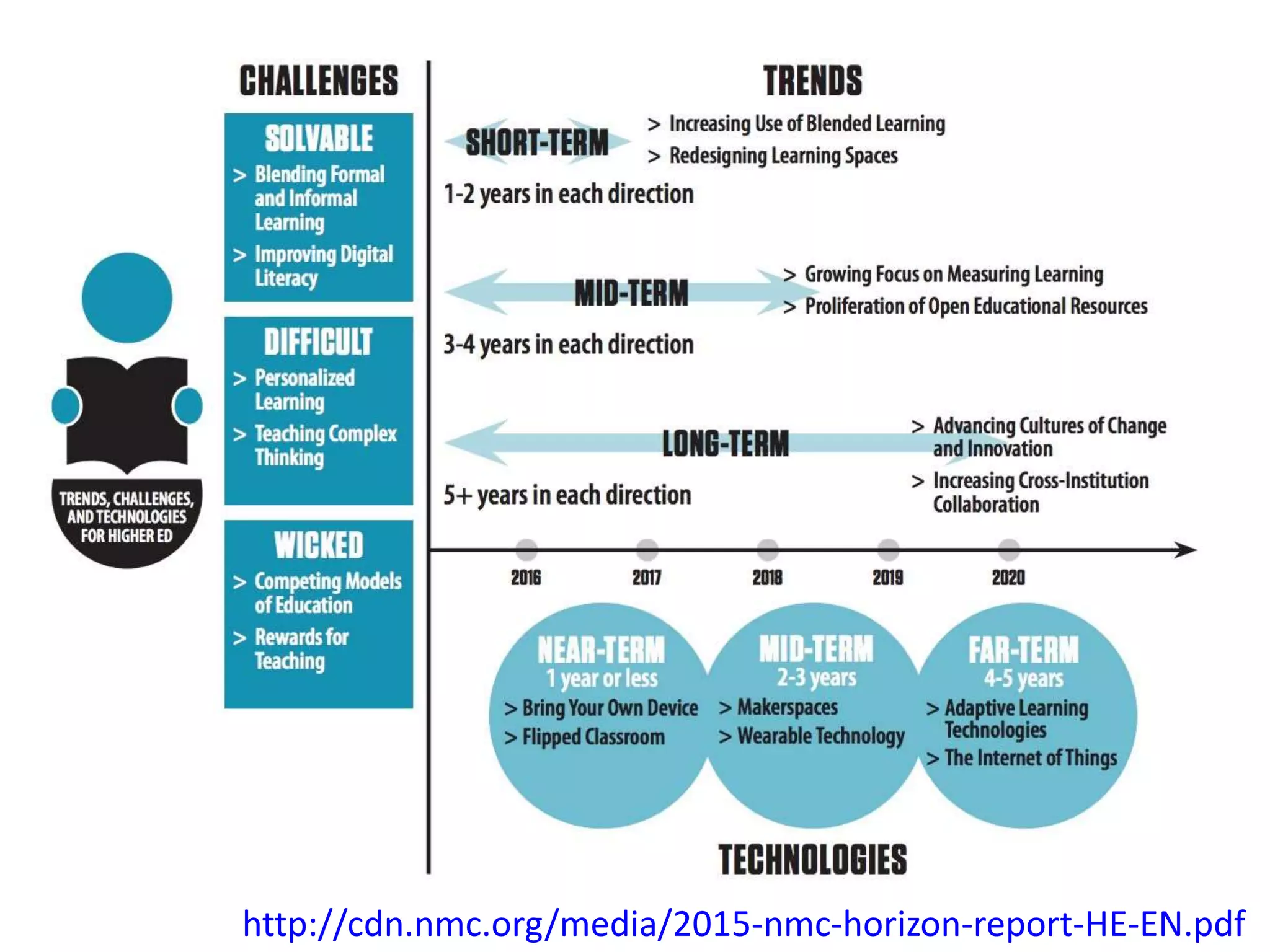
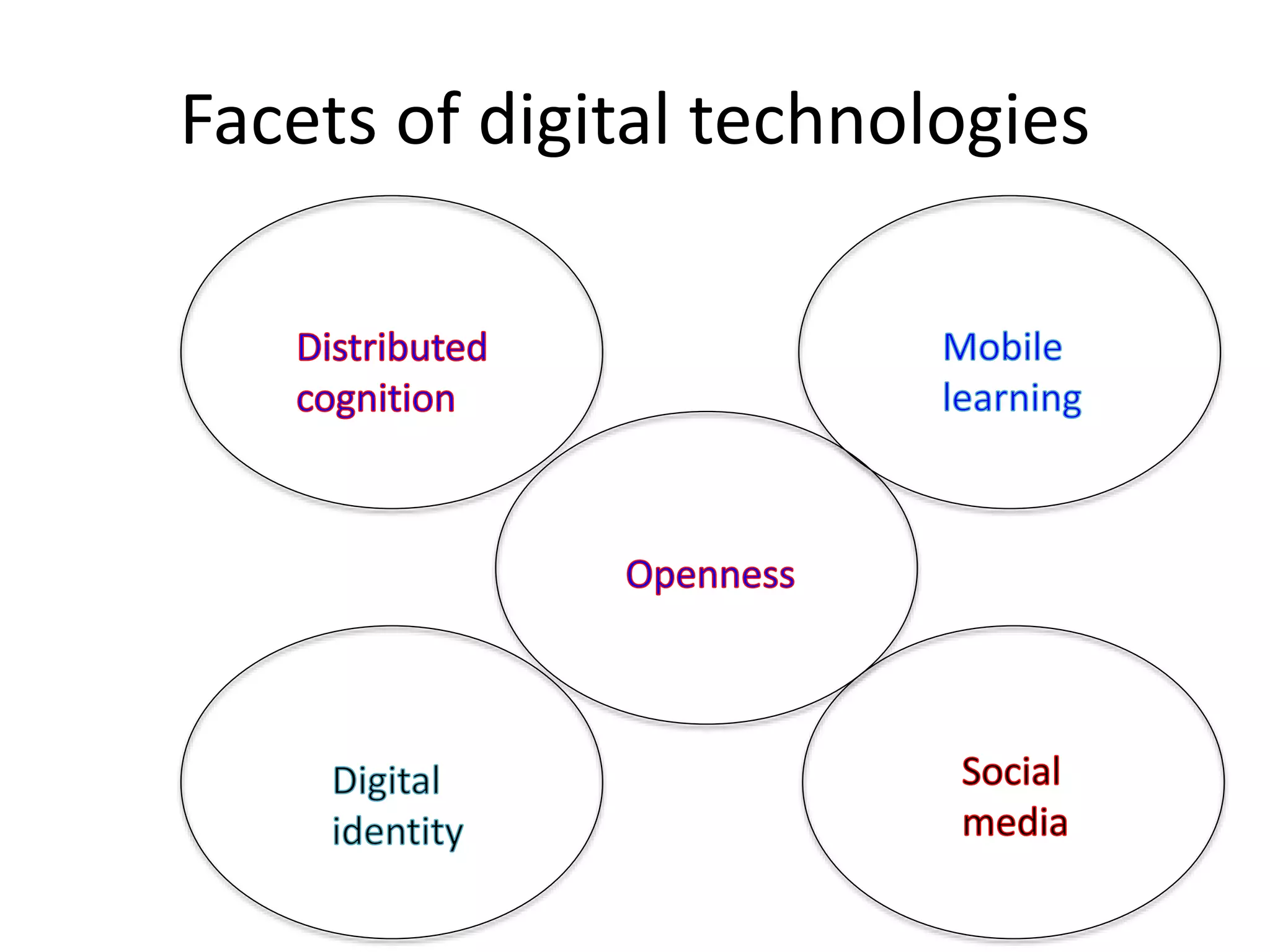
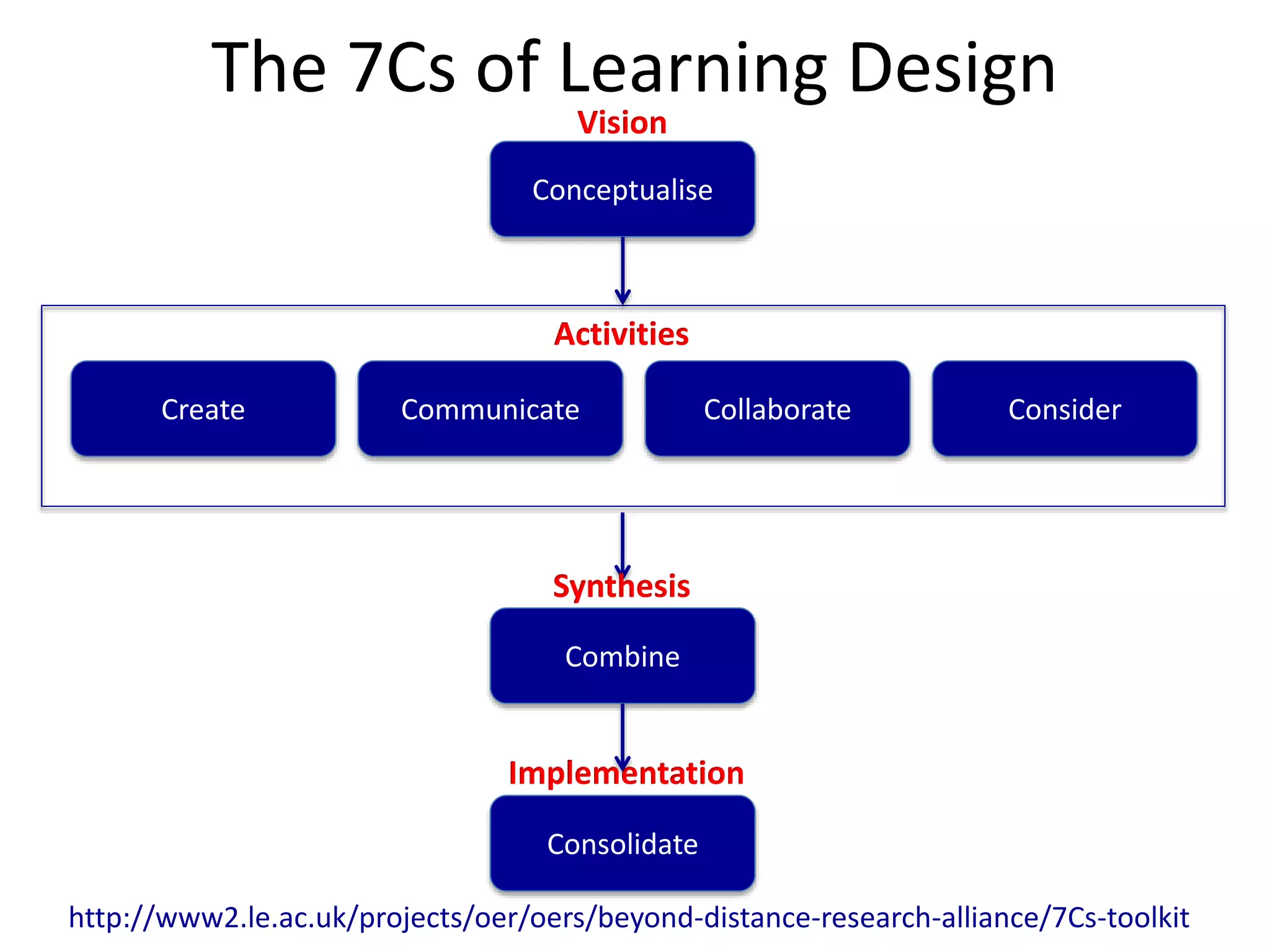
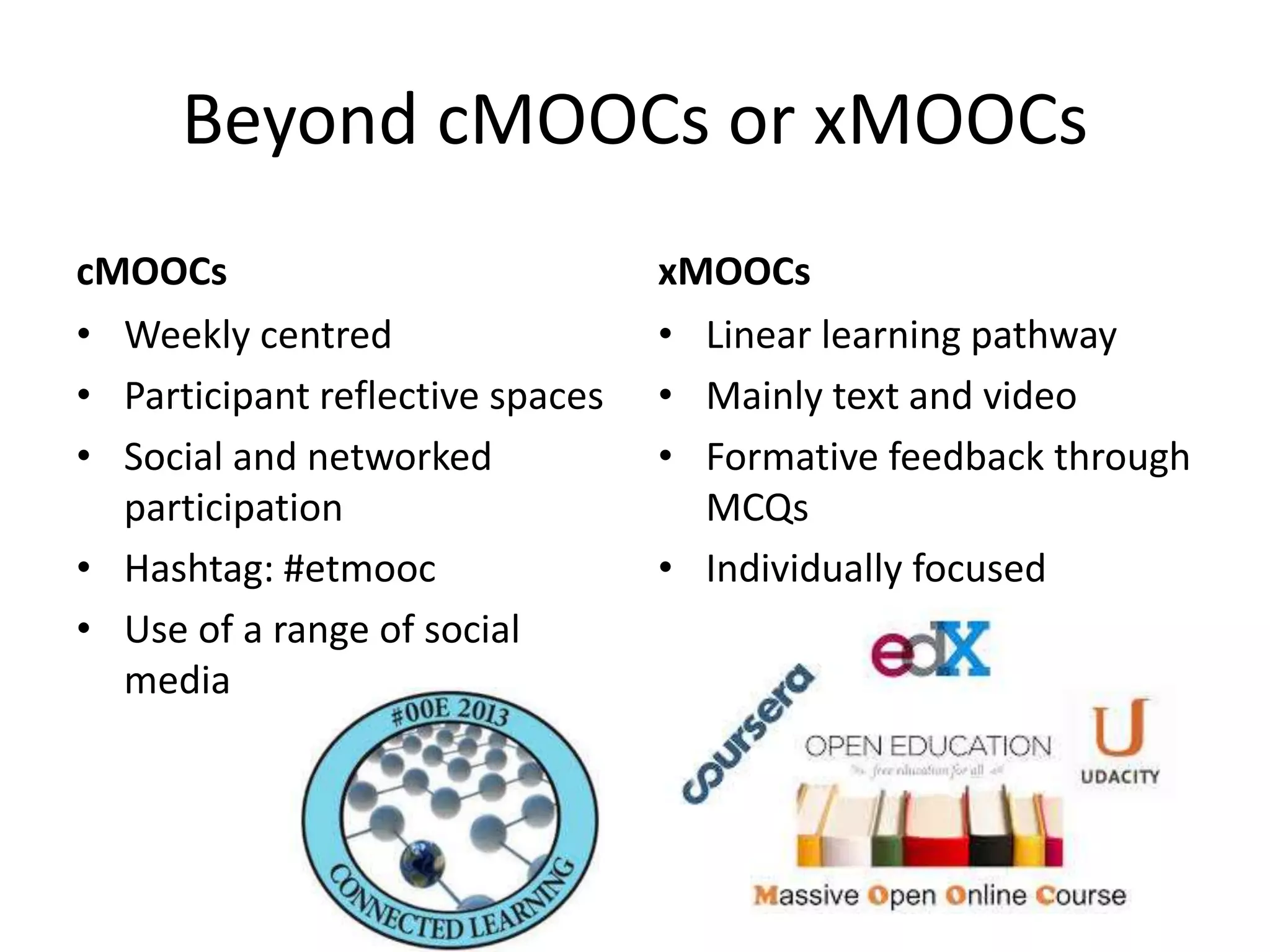
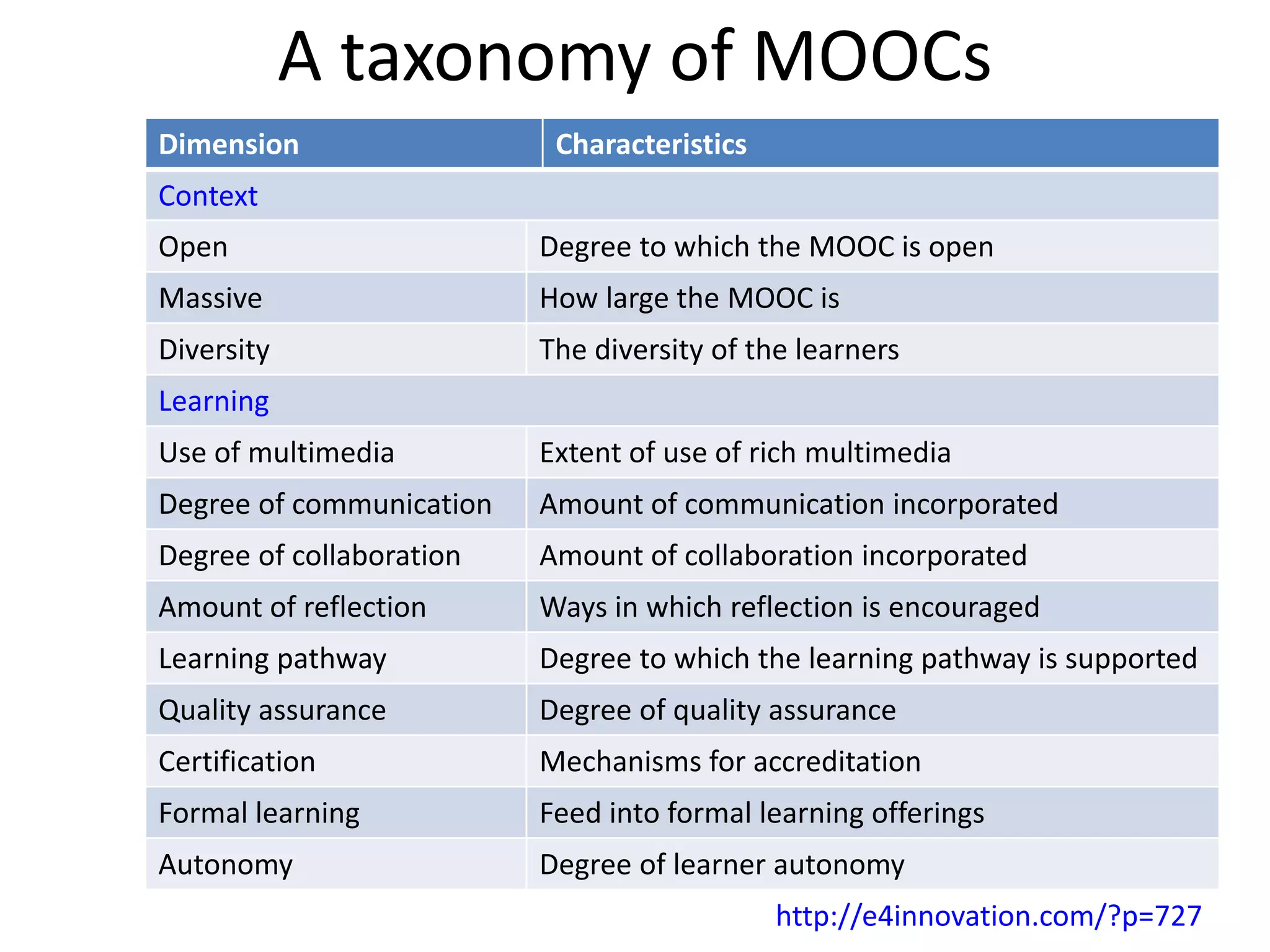
1. Digital technologies enable more open practices like open educational resources and MOOCs, but this also challenges existing business models and issues around quality and accreditation.
2. Mobile learning allows learning anywhere anytime, but overdependence on devices can be problematic.
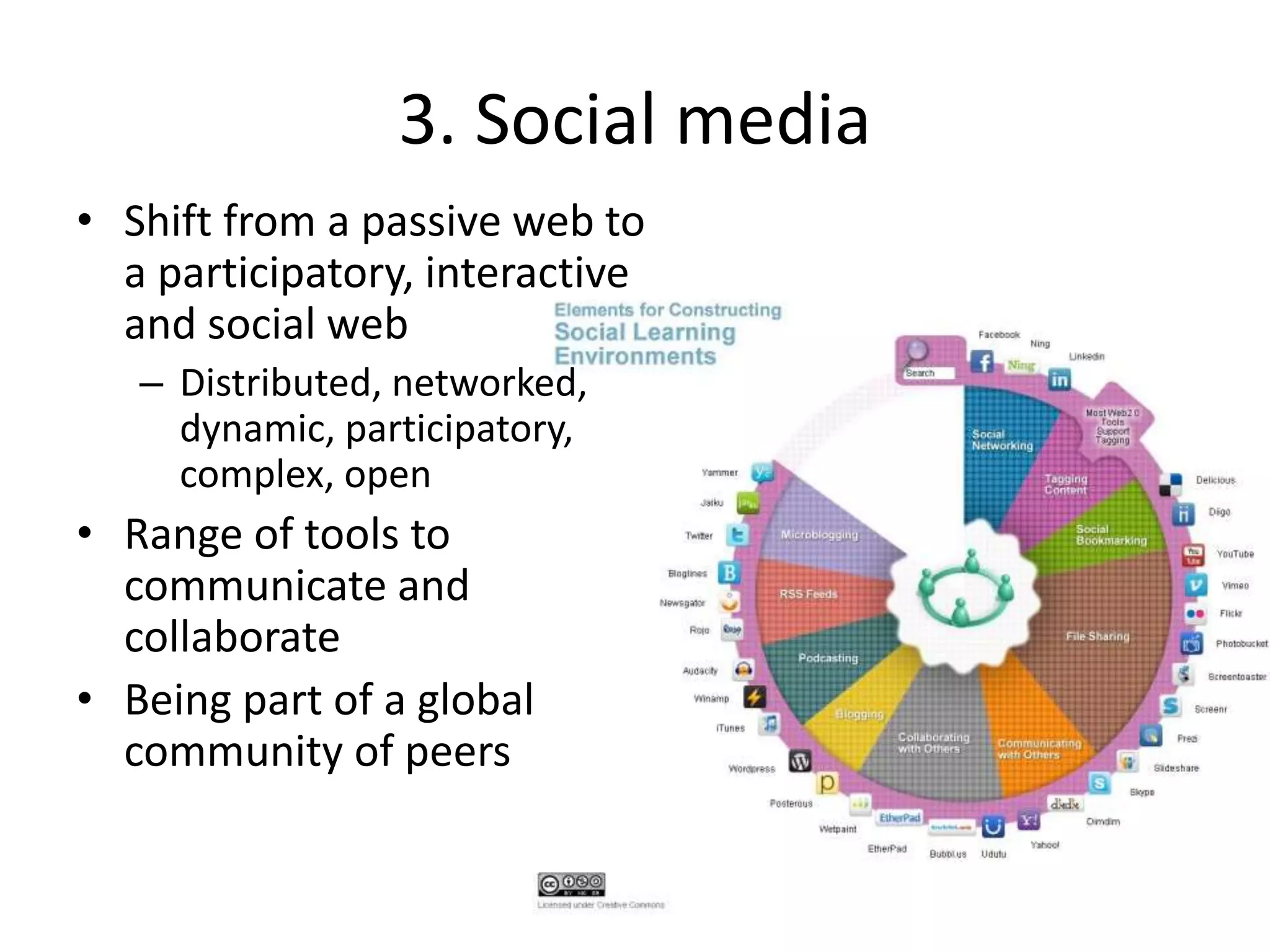
3. Social media provides rich ways to communicate and collaborate globally, but also raises issues regarding privacy, misuse of data, and distraction.
4. While digital identities and distributed cognition can enhance learning, they also require new digital literacy skills to avoid risks like getting lost in information or overdependence on machines.