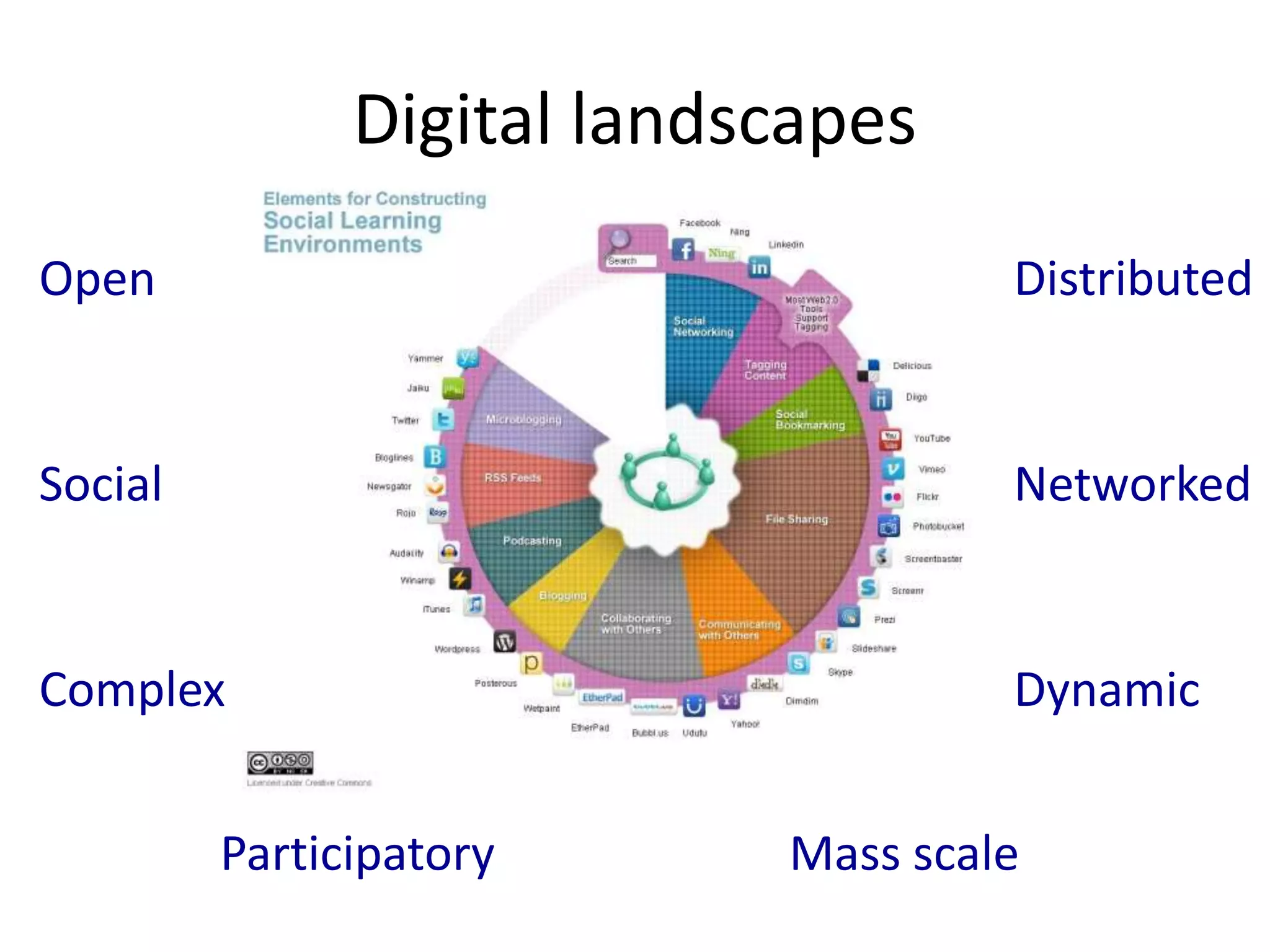
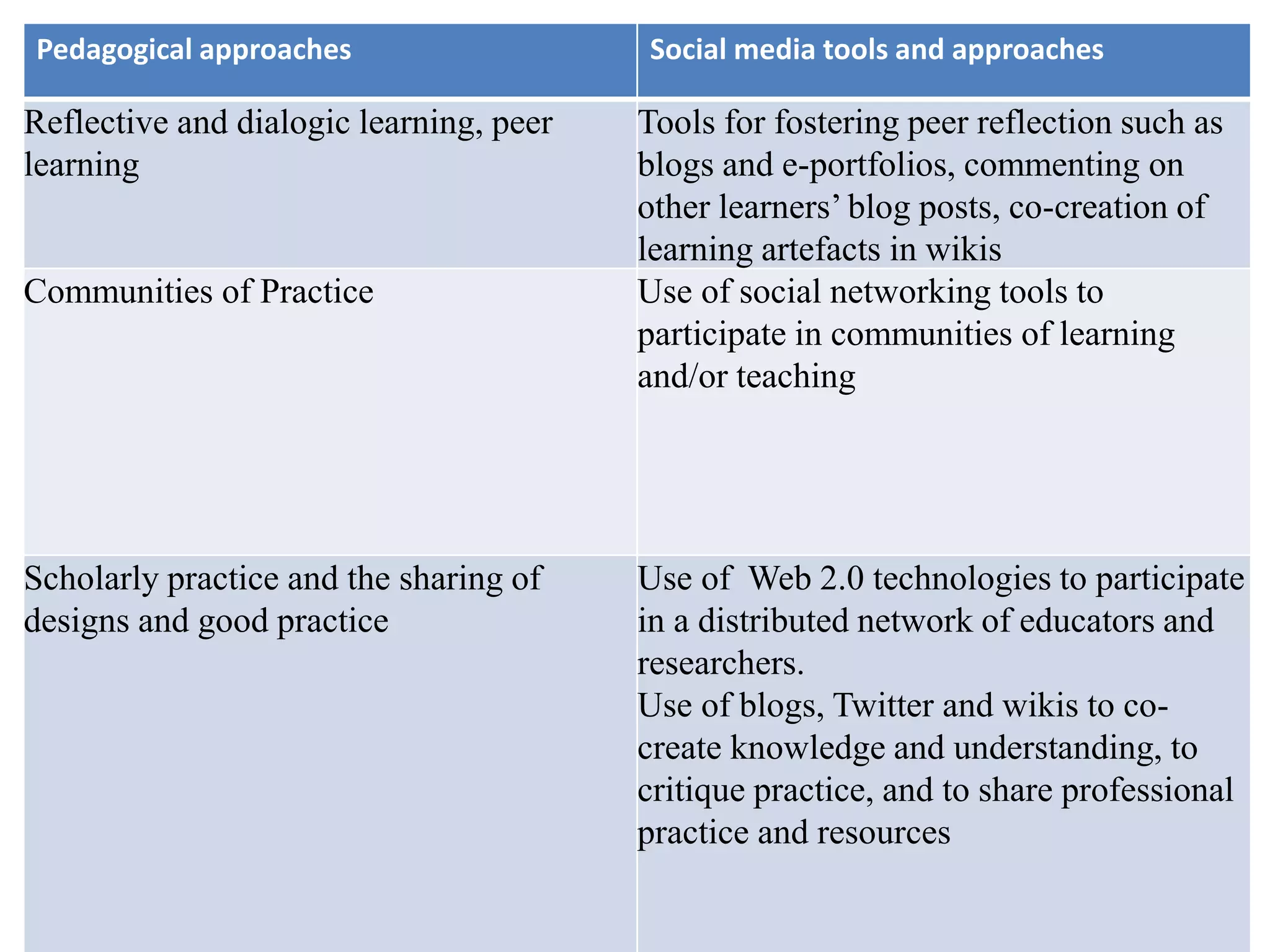
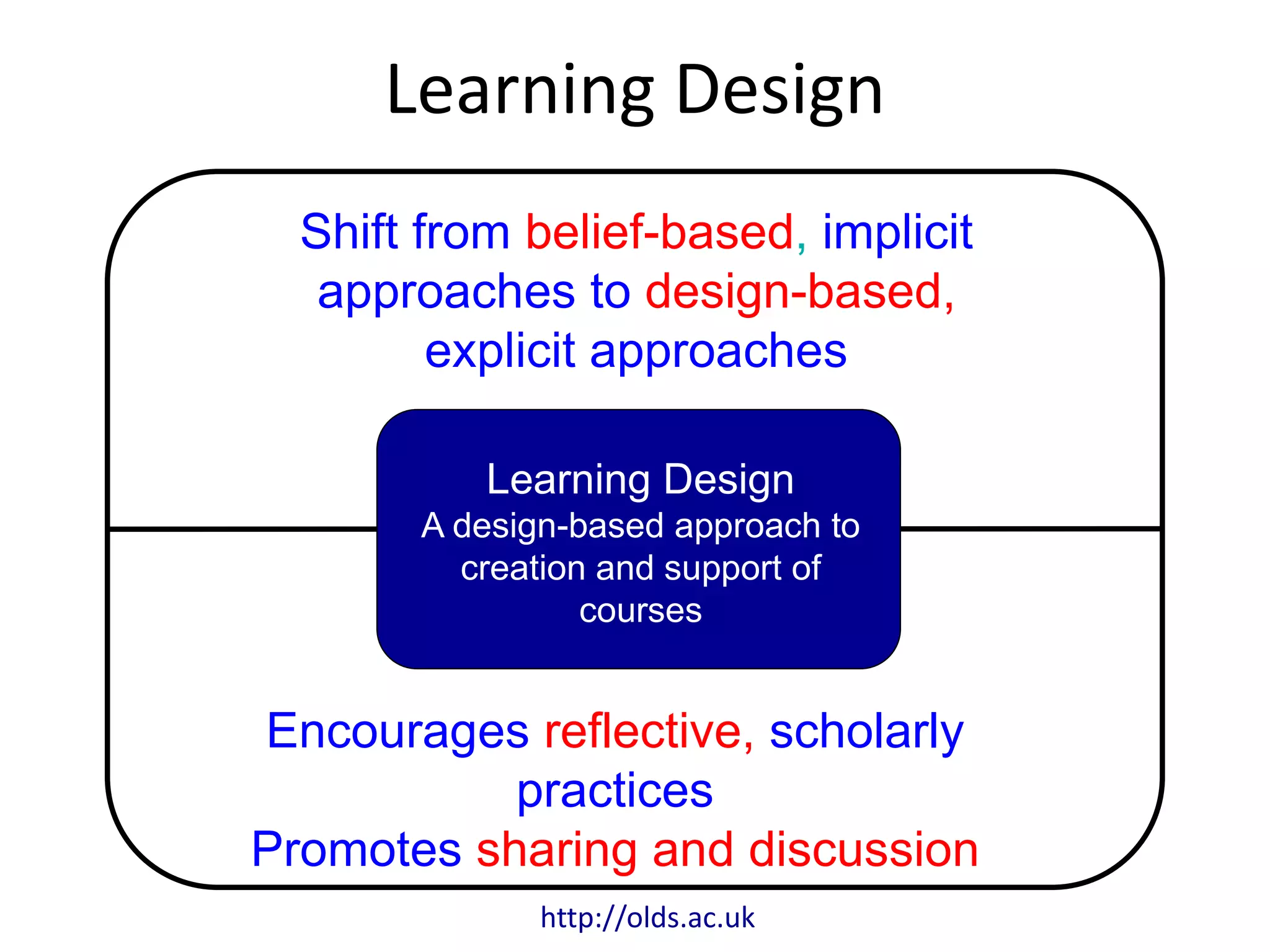
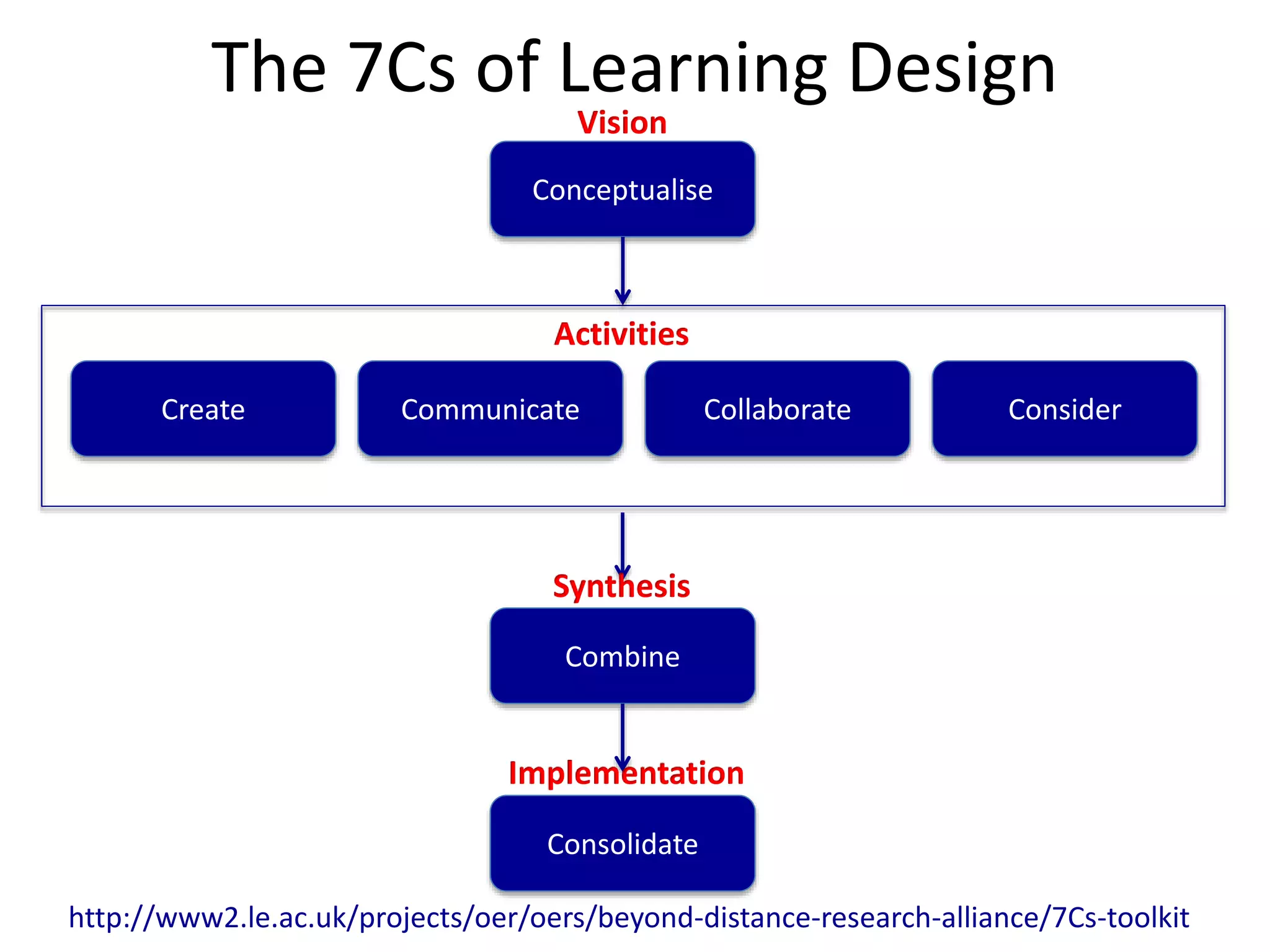
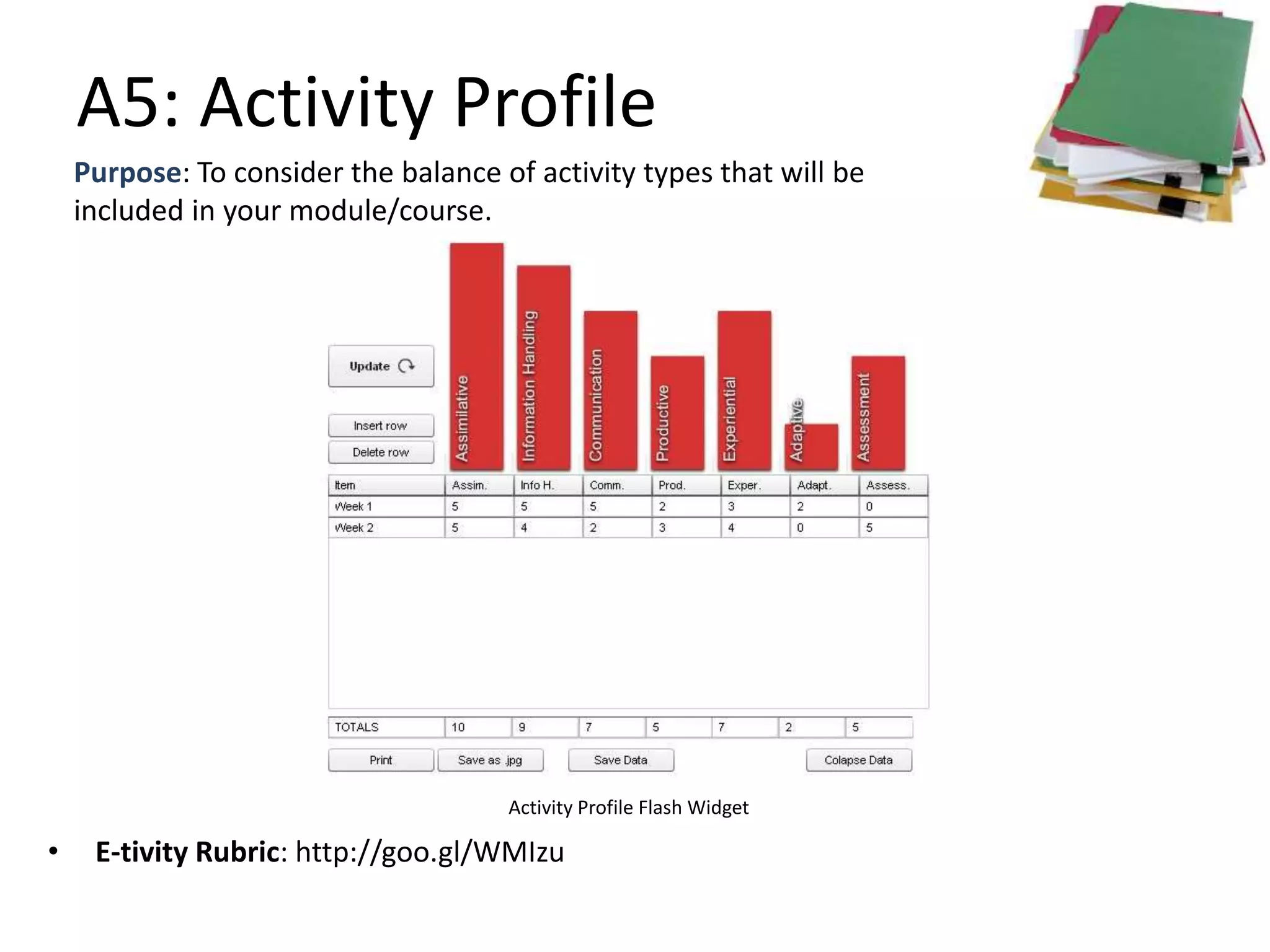
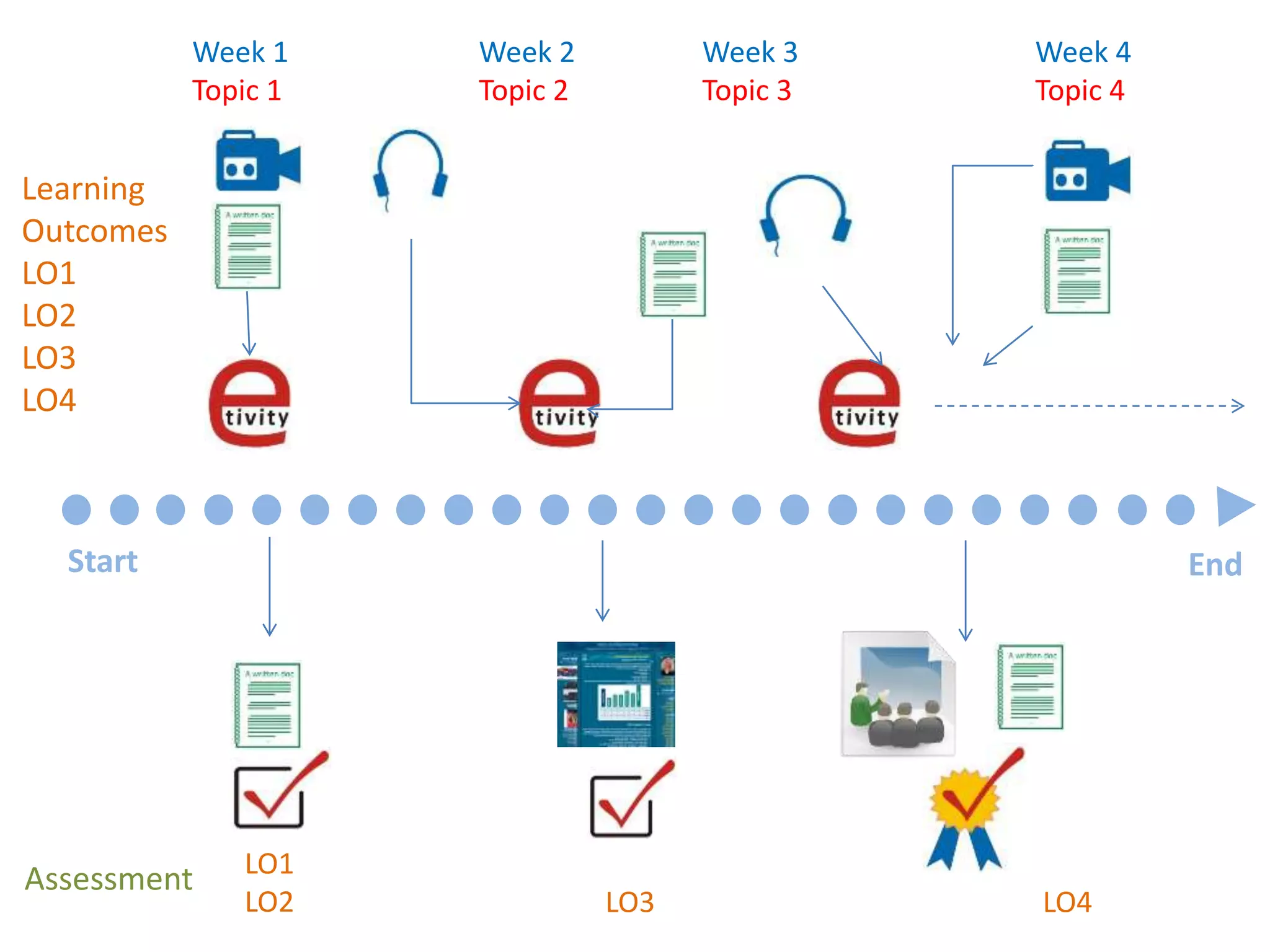
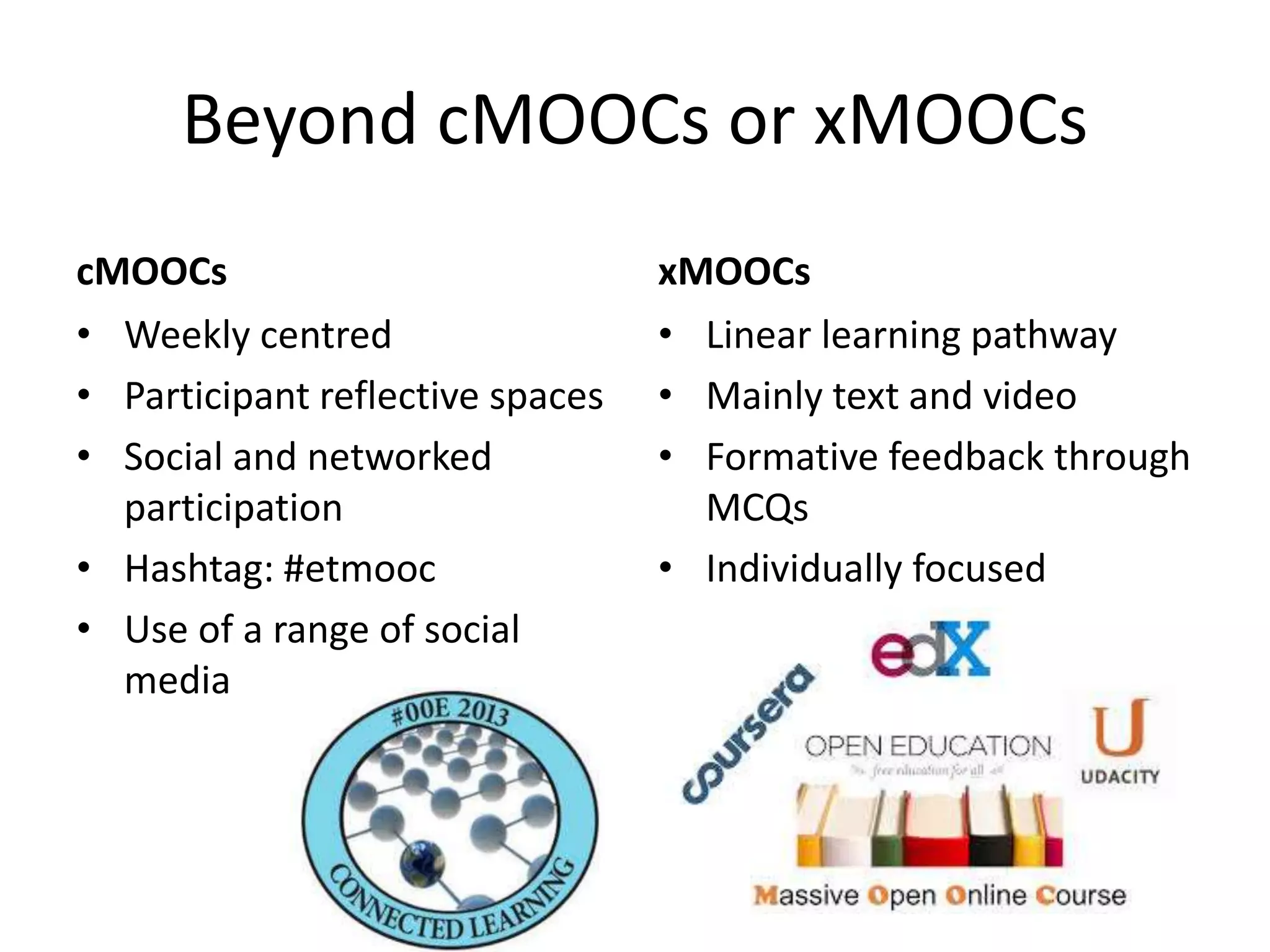
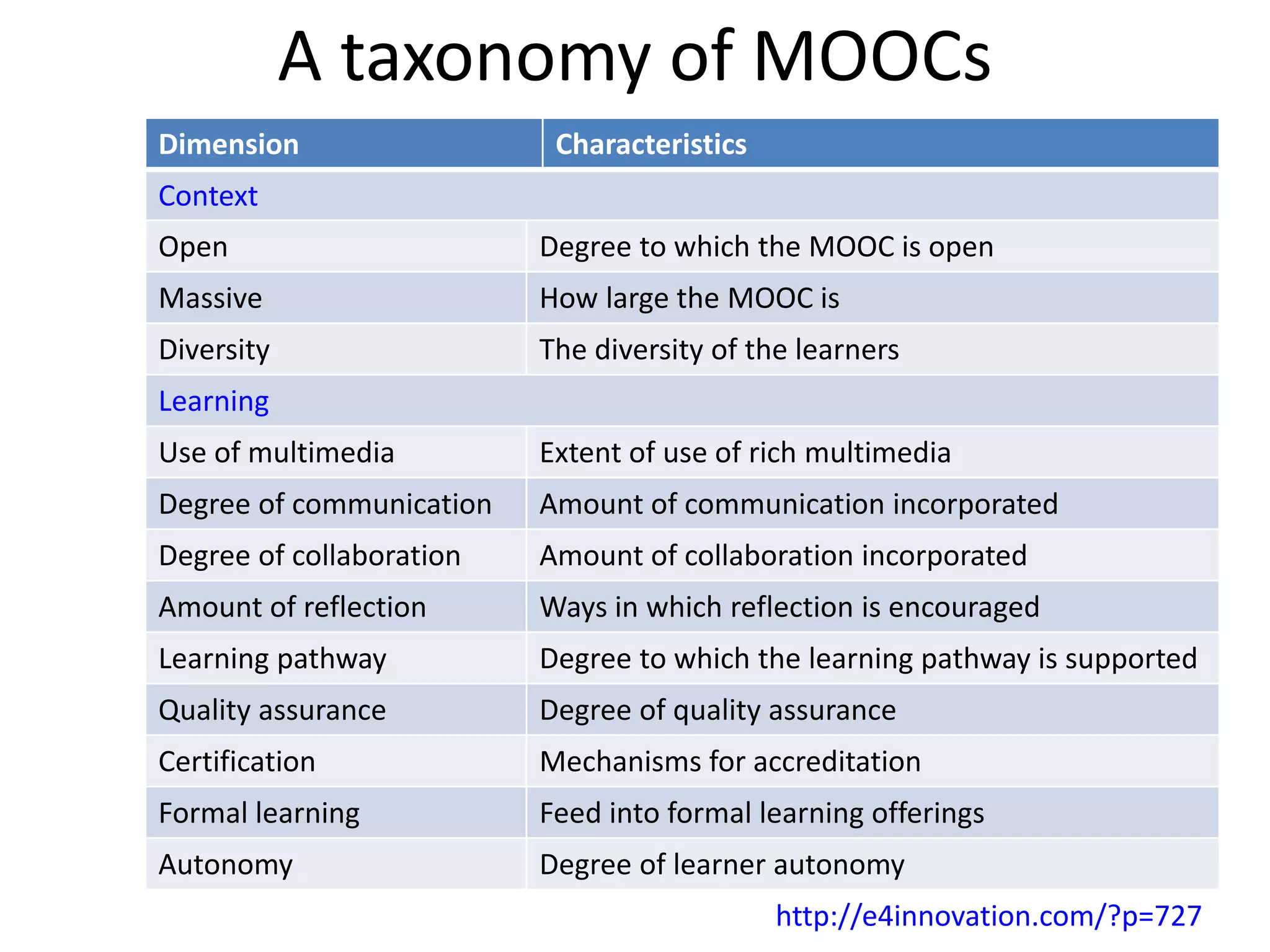
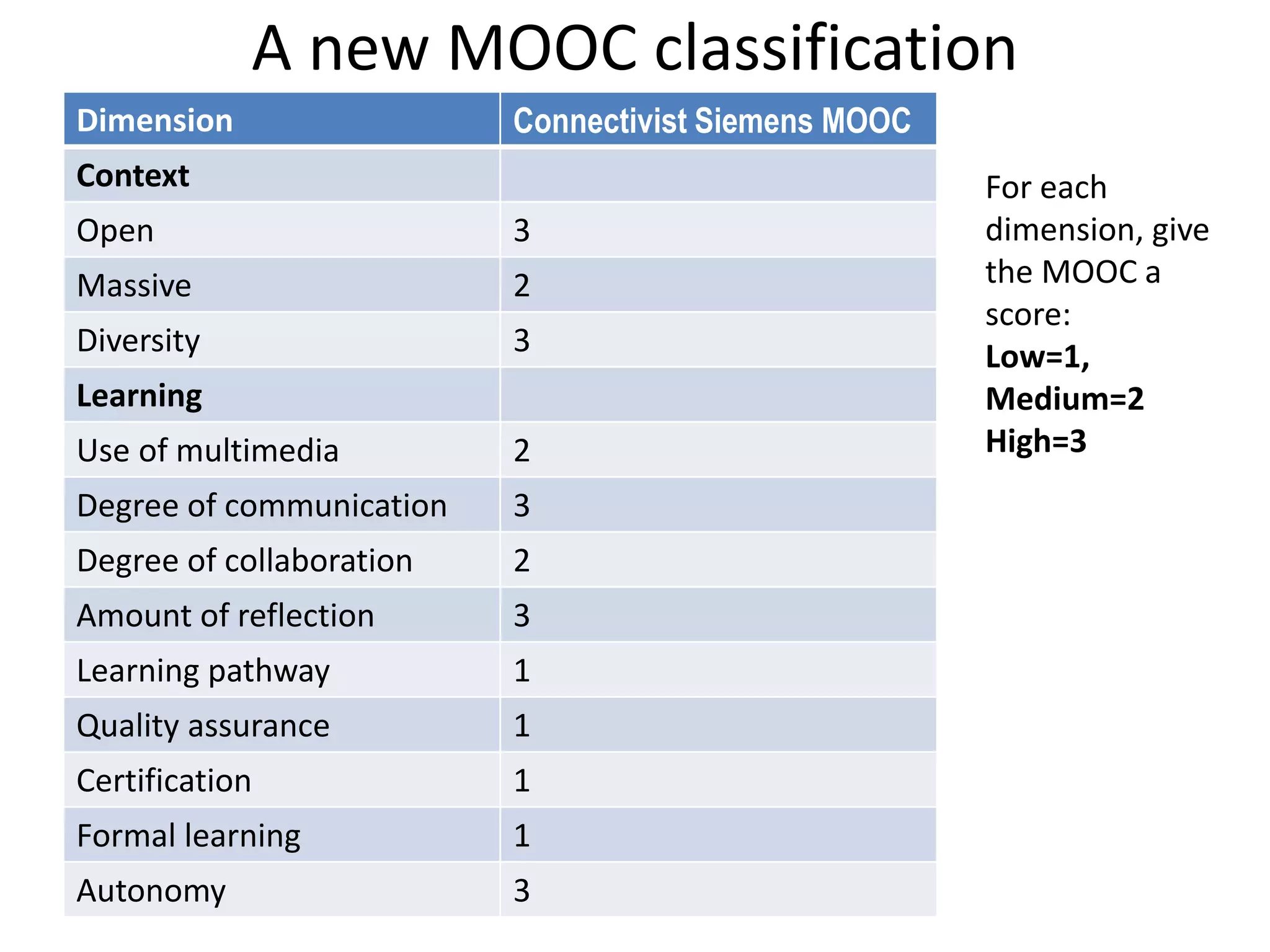
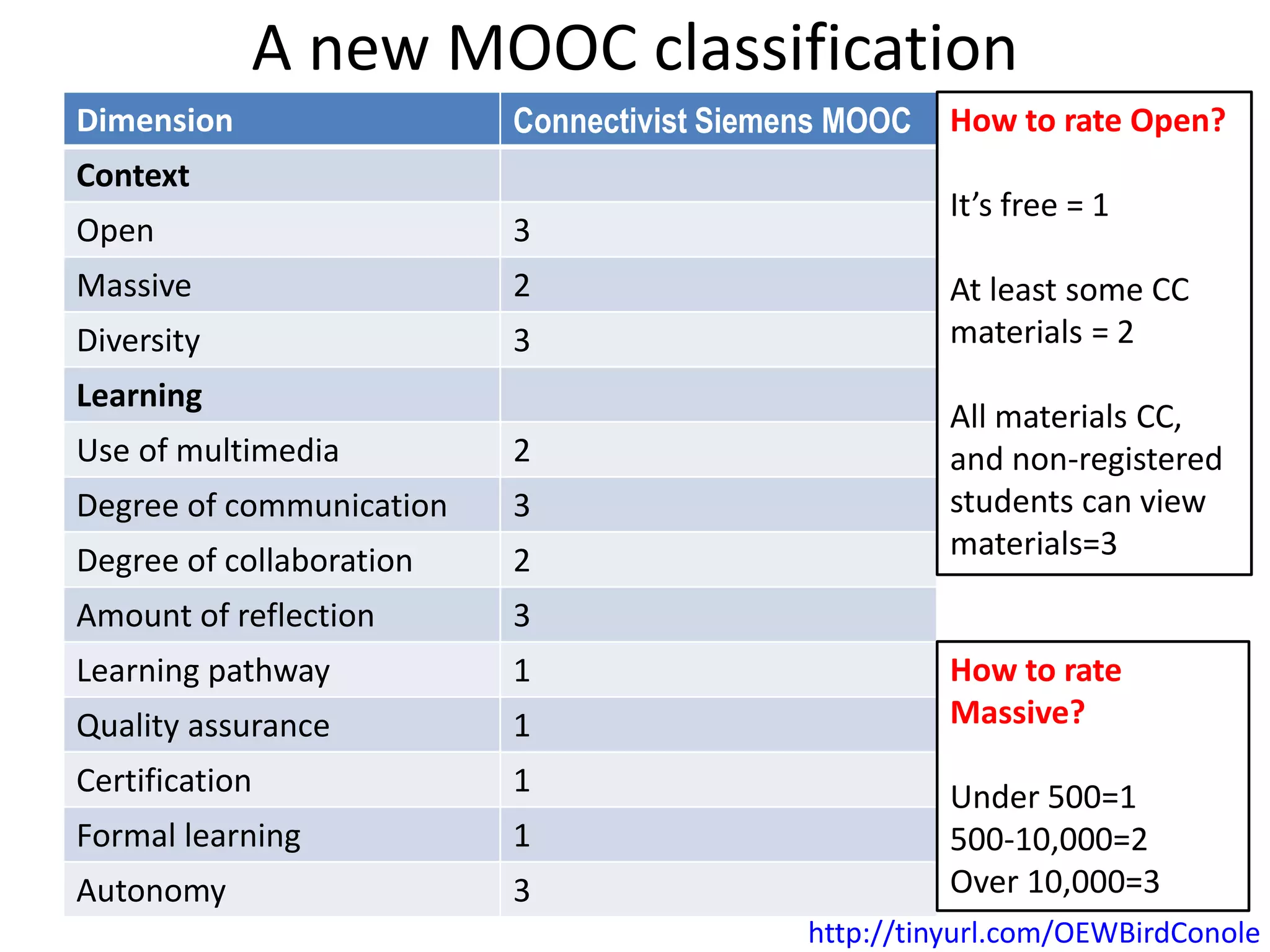
This document outlines Designing Effective MOOCs by Gráinne Conole. It discusses barriers to adoption of e-learning, digital landscapes, pedagogical approaches and how social media tools can support them. It also covers learning design principles, the 7Cs framework, and evaluating course success. MOOCs are challenging formal education and new business models are emerging while ways to accredit informal learning are being explored.