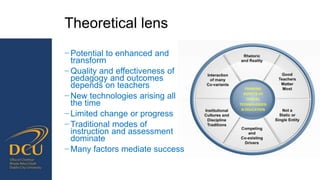
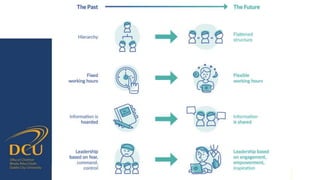
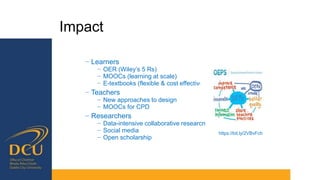
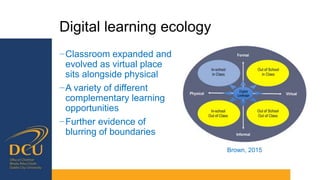
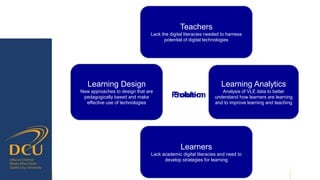
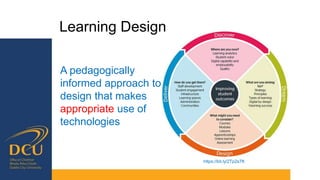
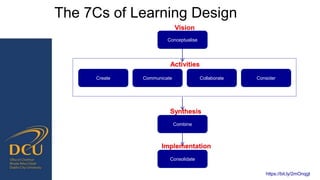
Gráinne Conole gave a presentation on key trends and implications for the future of technology enhanced learning. She discussed 10 top trends including how digital technologies are shifting identities, boundaries, and ownership of information. She emphasized that effective pedagogy depends on understanding learners, educators, and the learning environment. New approaches to learning design and analytics were presented as opportunities to improve teaching and learning, but continuous professional development for educators is needed to develop digital literacies and harness technology's potential. While technology affords many opportunities, its impact depends greatly on implementation and mindsets around educational change.