This document discusses open education and its future directions. It covers several topics:
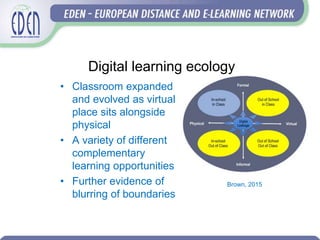
- The changing digital landscape and need for students to become critical users of online resources.
- The affordances of different digital technologies for learning, such as enabling interaction, feedback, and personalization.
- Open practices like OER, MOOCs, and e-textbooks and their impact on learners, teachers, and researchers.
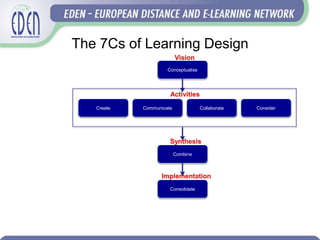
- The role of continuing professional development and learning design frameworks in helping teachers develop innovative learning interventions using technology.
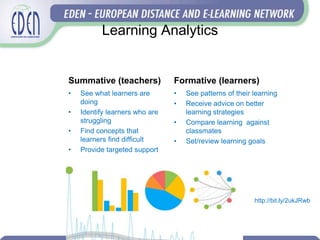
- The potential of learning analytics to provide formative feedback to learners and summative insights for teachers.