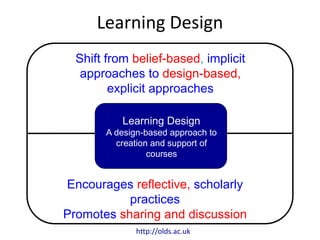
The document outlines strategies for designing and evaluating effective learning activities. It introduces the 7Cs framework for learning design, which involves conceptualizing a course vision, capturing resources, communicating activities, collaborating, considering outcomes and assessment, combining elements, and consolidating the design. Each step of the 7Cs process is described in detail. The document emphasizes the importance of aligning learning outcomes, teaching activities, and assessment. A variety of learning design tools and approaches are also presented, such as course mapping, activity profiling, storyboarding, and rubrics for evaluation.