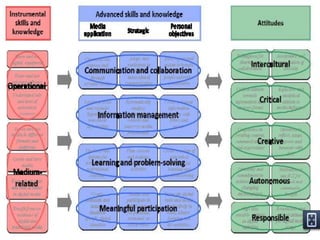
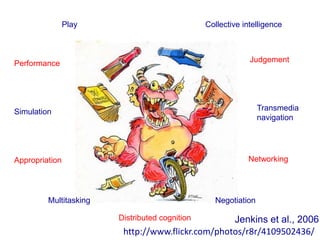
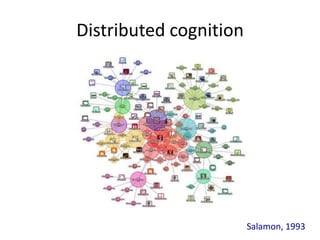
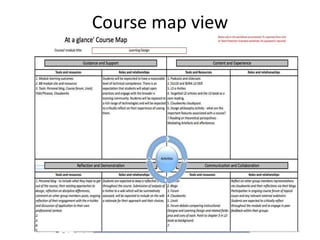
The document discusses new digital technologies and their implications for learning, teaching, and research. It outlines how technologies are transforming communication and collaboration through tools for finding, creating, managing, and sharing information in networked environments. This shifts education towards more open and participatory practices. However, technologies are not fully exploited and can replicate bad pedagogy without sufficient skills and time. The document advocates for learning design approaches to create explicit courses that encourage reflection and sharing. This changes the nature of education and implies disruptive and complex opportunities through co-evolving social systems.