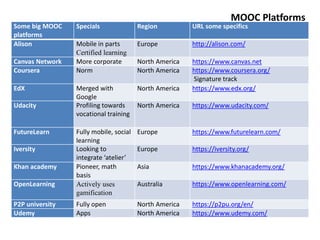
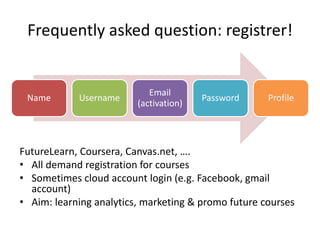
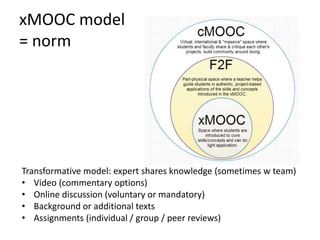
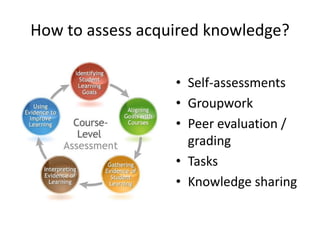
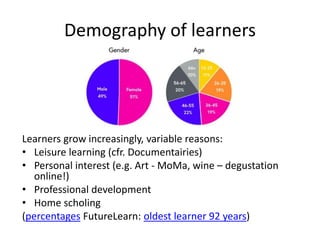
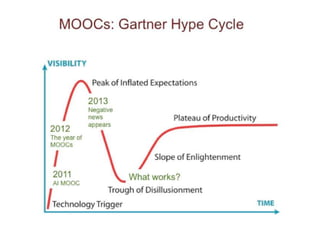
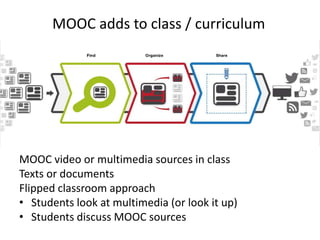
MOOCs provide opportunities for teachers and learners. For teachers, MOOCs allow for professional development by learning new content and teaching styles. MOOCs can also be added to traditional classes by using MOOC content and discussions. For learners, MOOCs increase access to education and provide flexible, self-paced learning. However, learners need computer access and time to benefit. MOOCs are also driving changes to education through the globalization and digitization of learning.