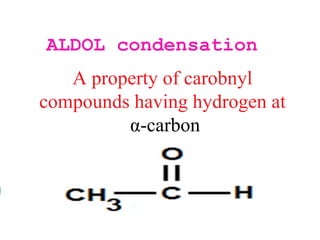
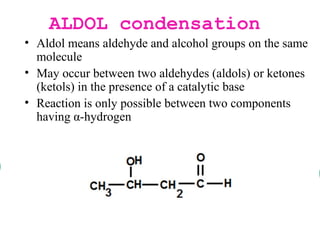
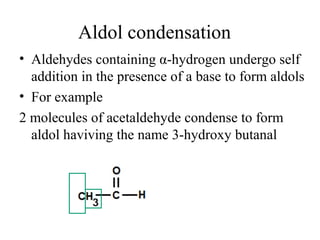
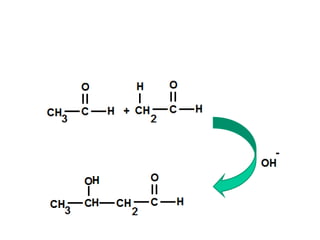
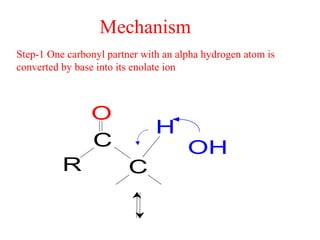
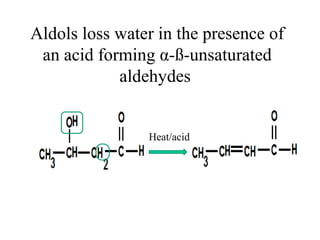
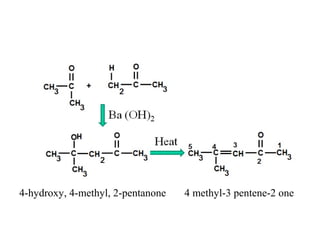
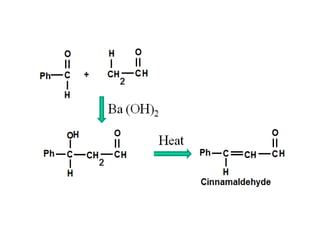
- Aldol condensation is a reaction that occurs between two carbonyl compounds, such as aldehydes or ketones, in the presence of a base. This forms a β-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone.
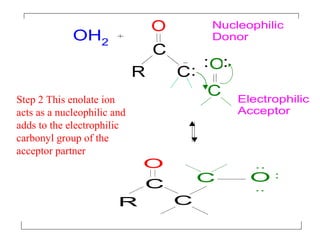
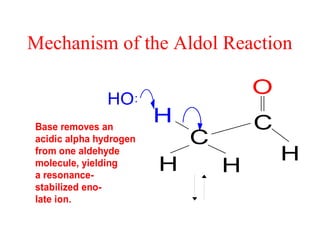
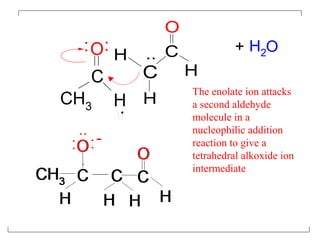
- The reaction involves the base deprotonating one of the carbonyl compounds to form an enolate ion. This acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of the other reactant.
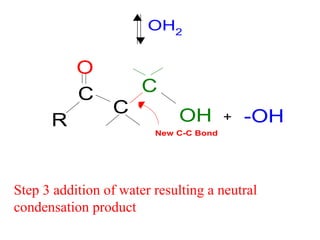
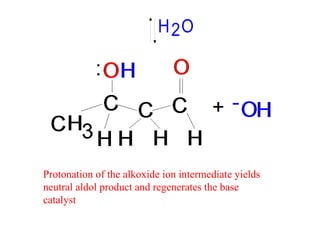
- After addition of water, an aldol or ketol product is formed containing both original R groups and a new C-C bond, along with an alcohol group.