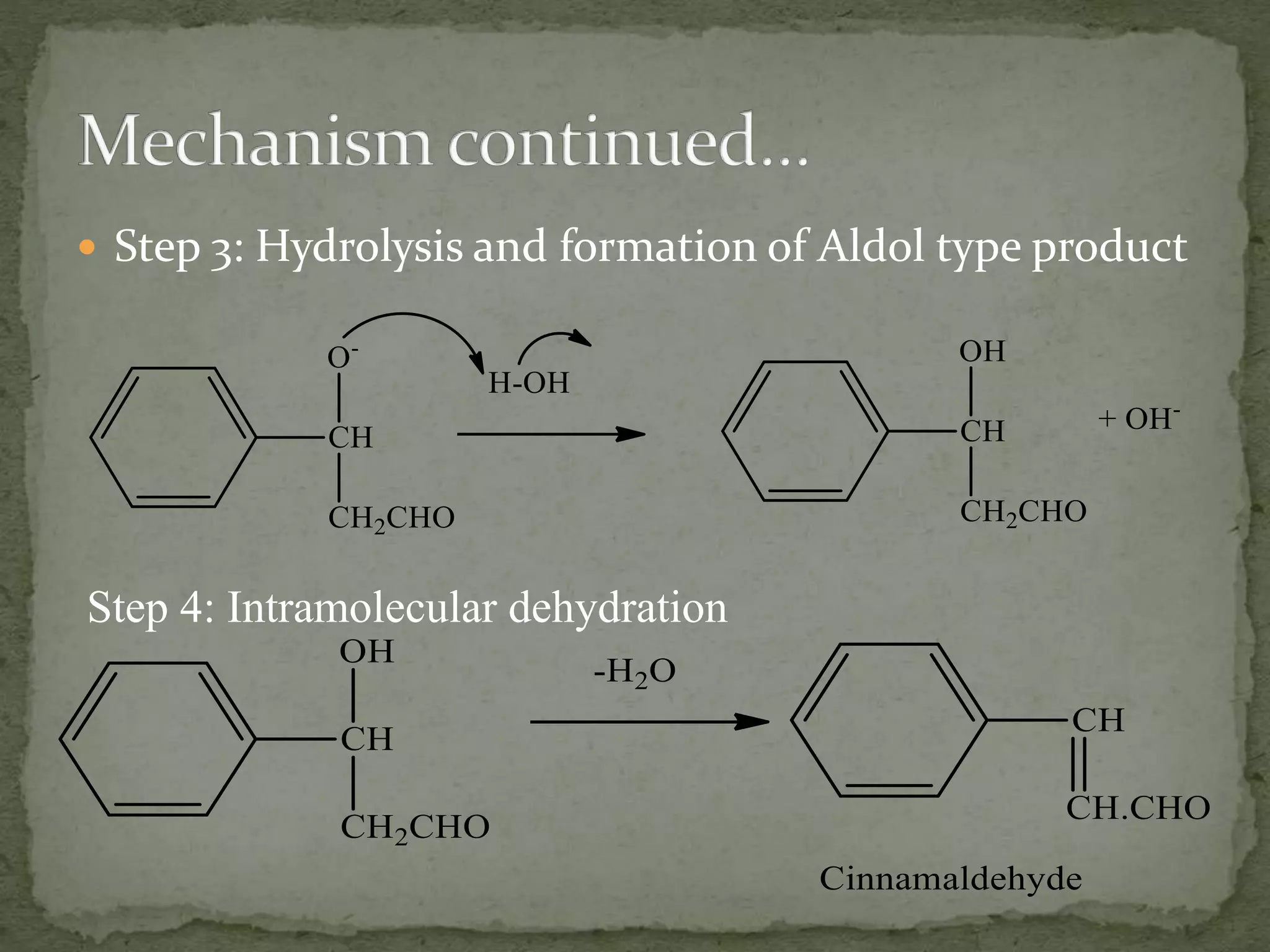
The aldol condensation reaction involves the reaction of two carbonyl compounds in the presence of a strong base to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone. The reaction proceeds through the formation of an enolate ion intermediate that acts as a nucleophile, attacking the carbonyl carbon of the other molecule. This forms a carbon-carbon bond between the α-carbon of the donor molecule and the carbonyl carbon of the acceptor molecule. The reaction allows for the facile synthesis of larger molecules from simple starting materials.