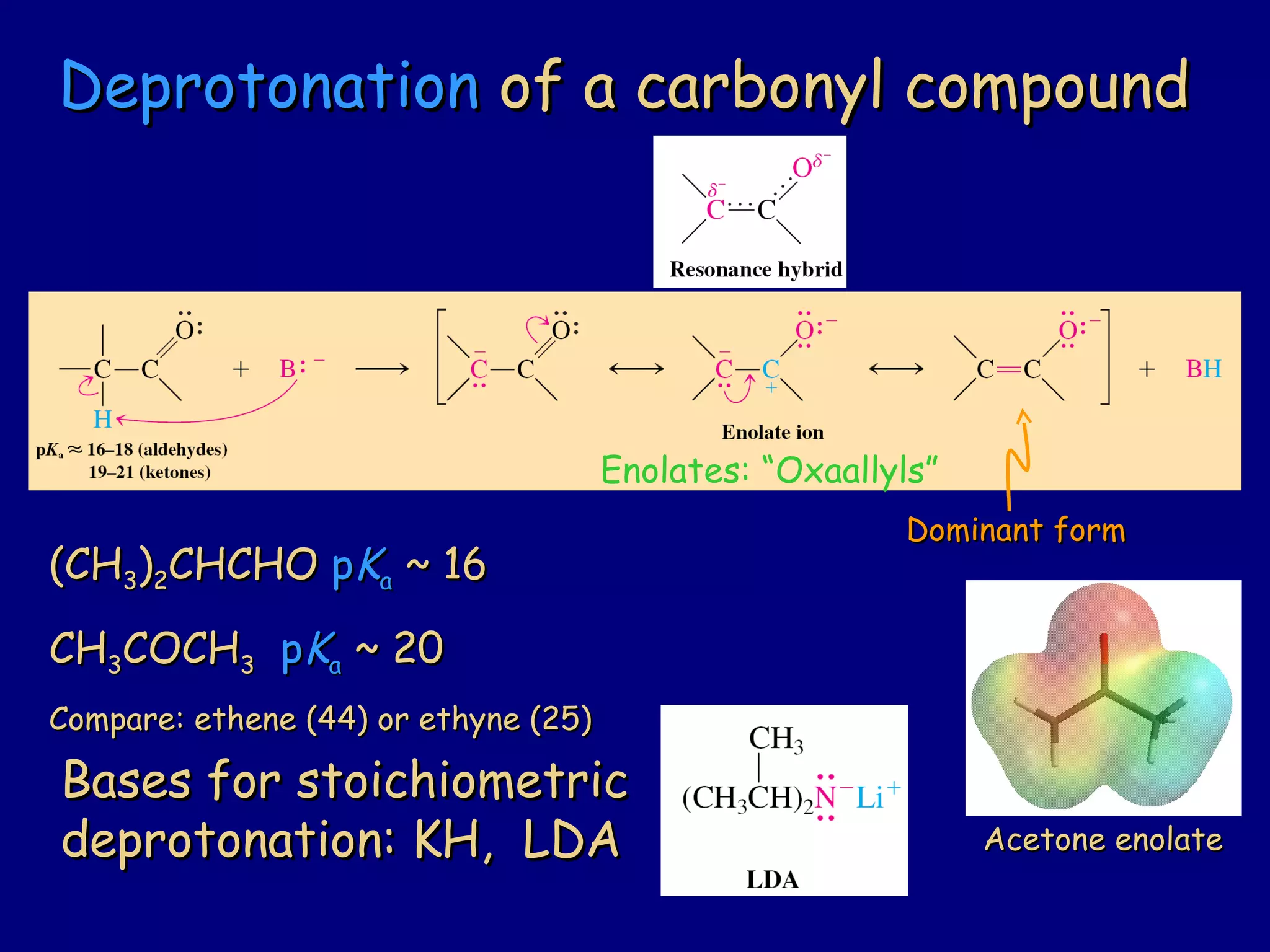
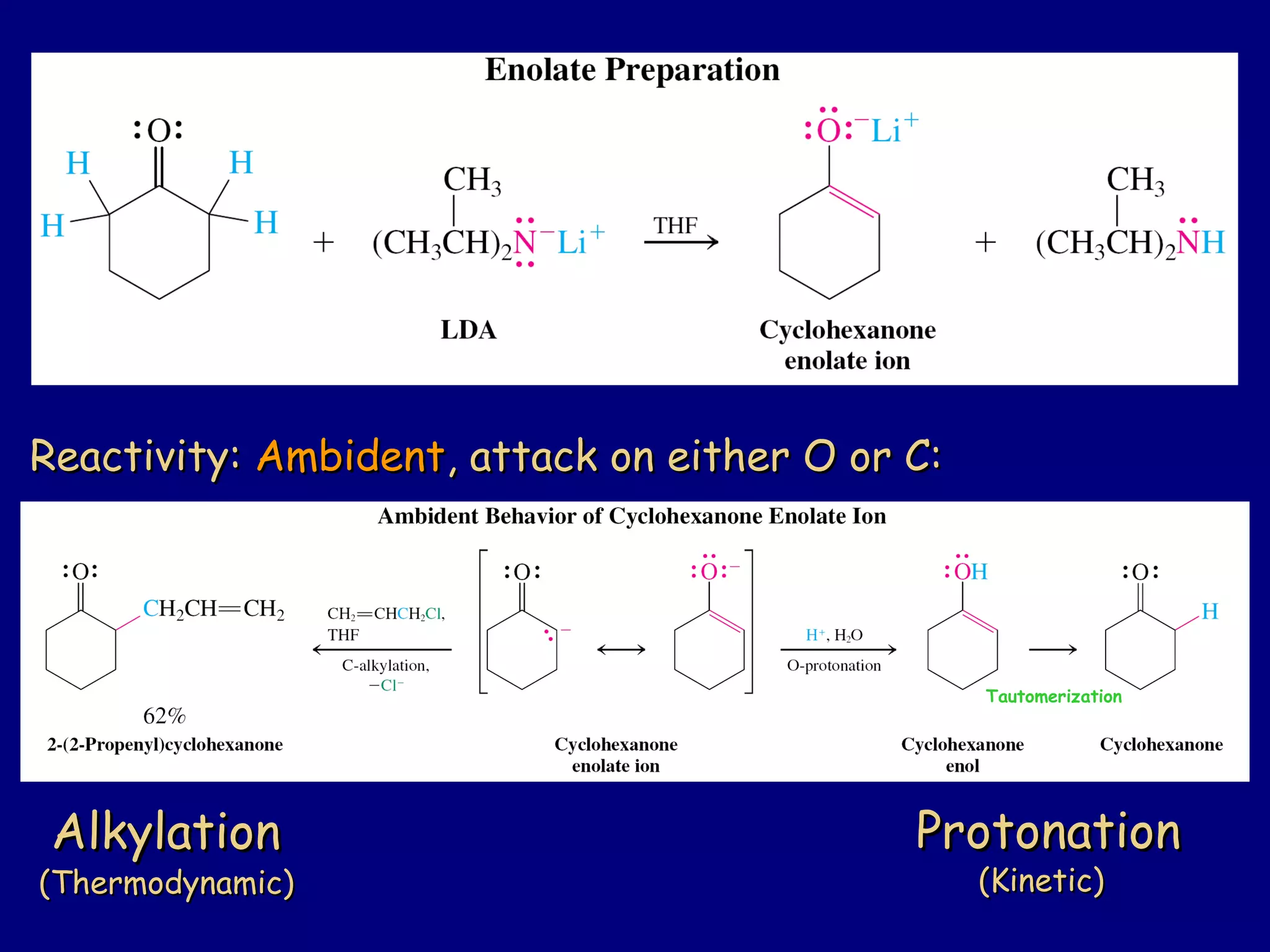
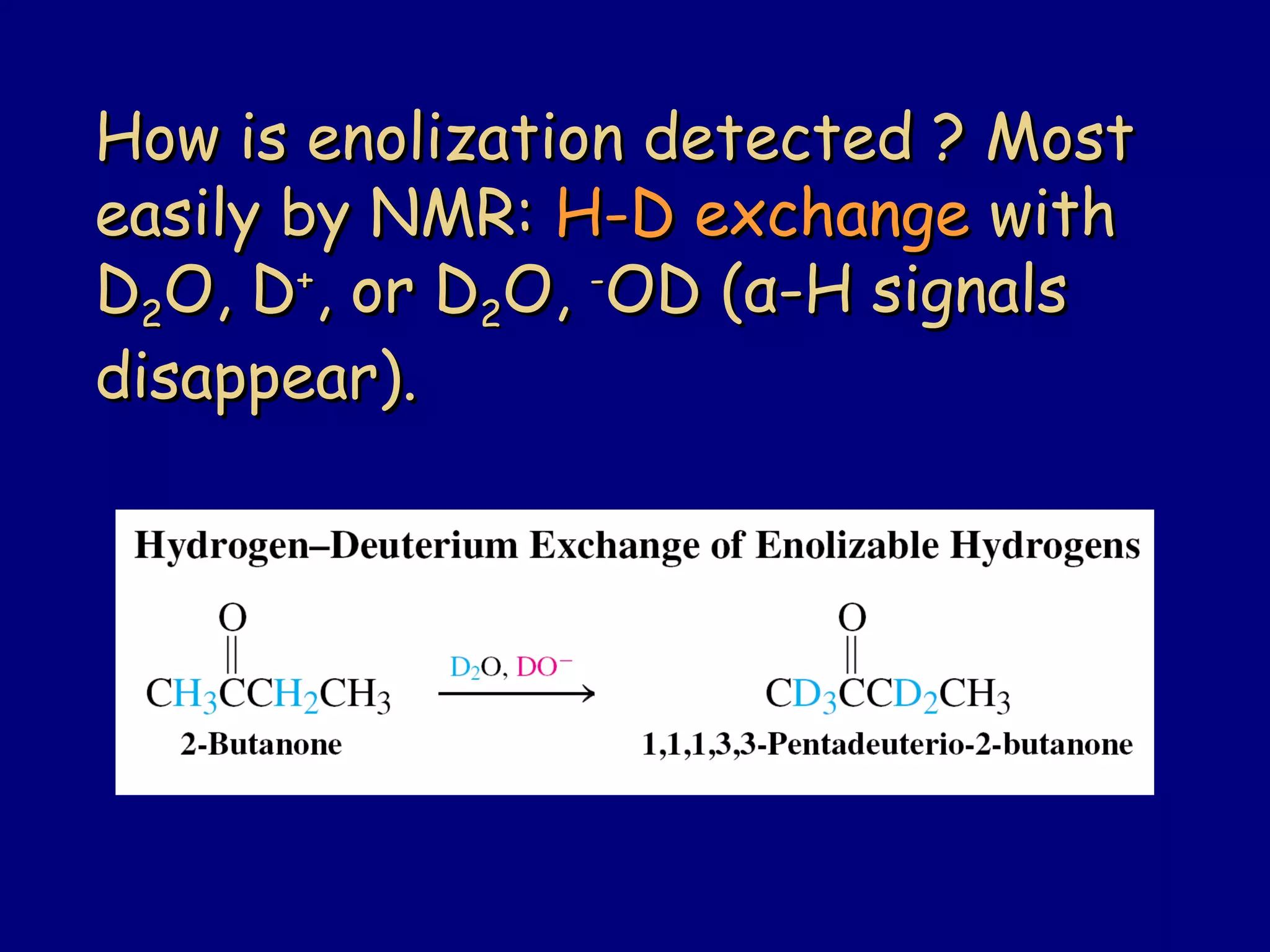
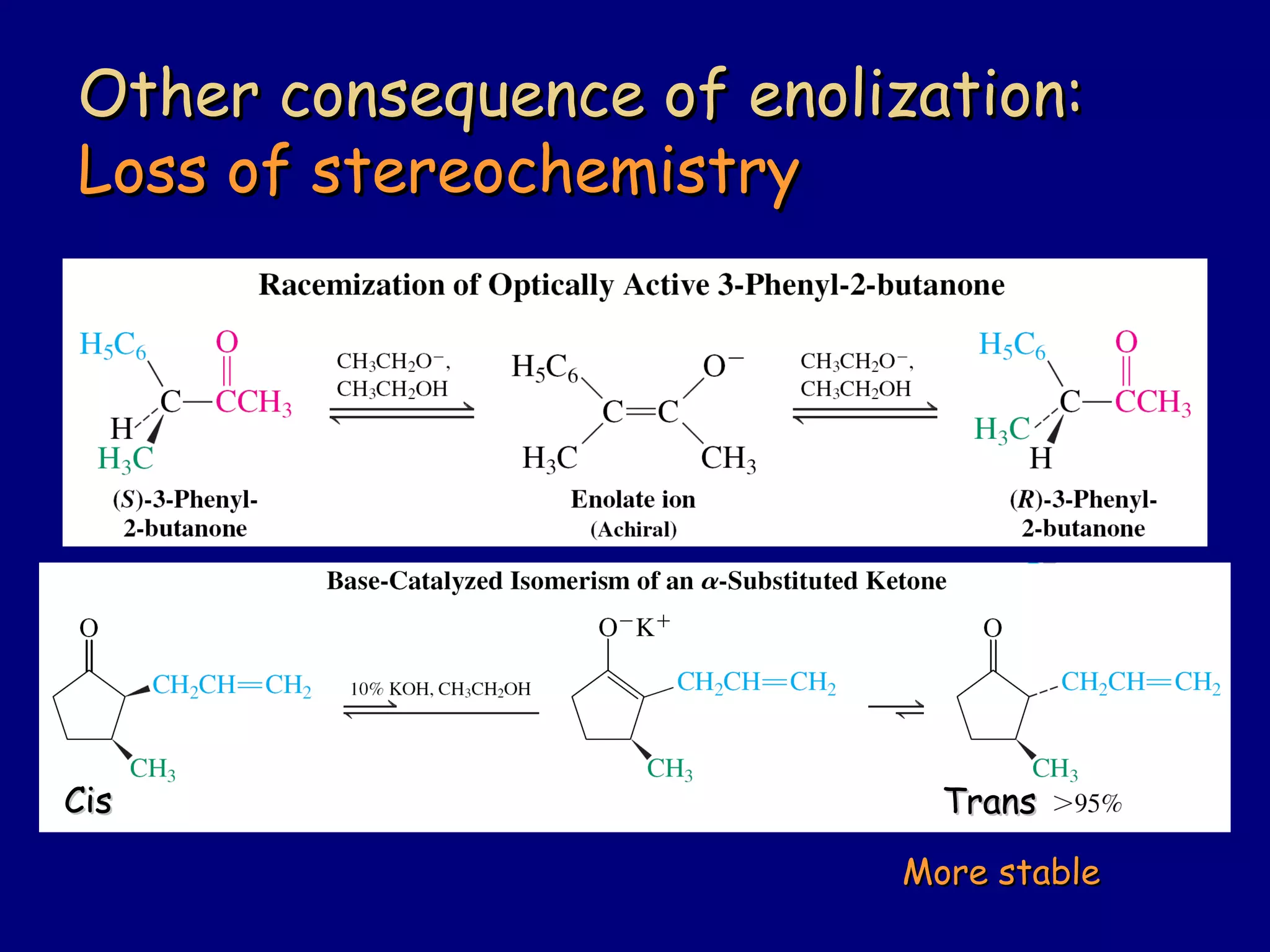
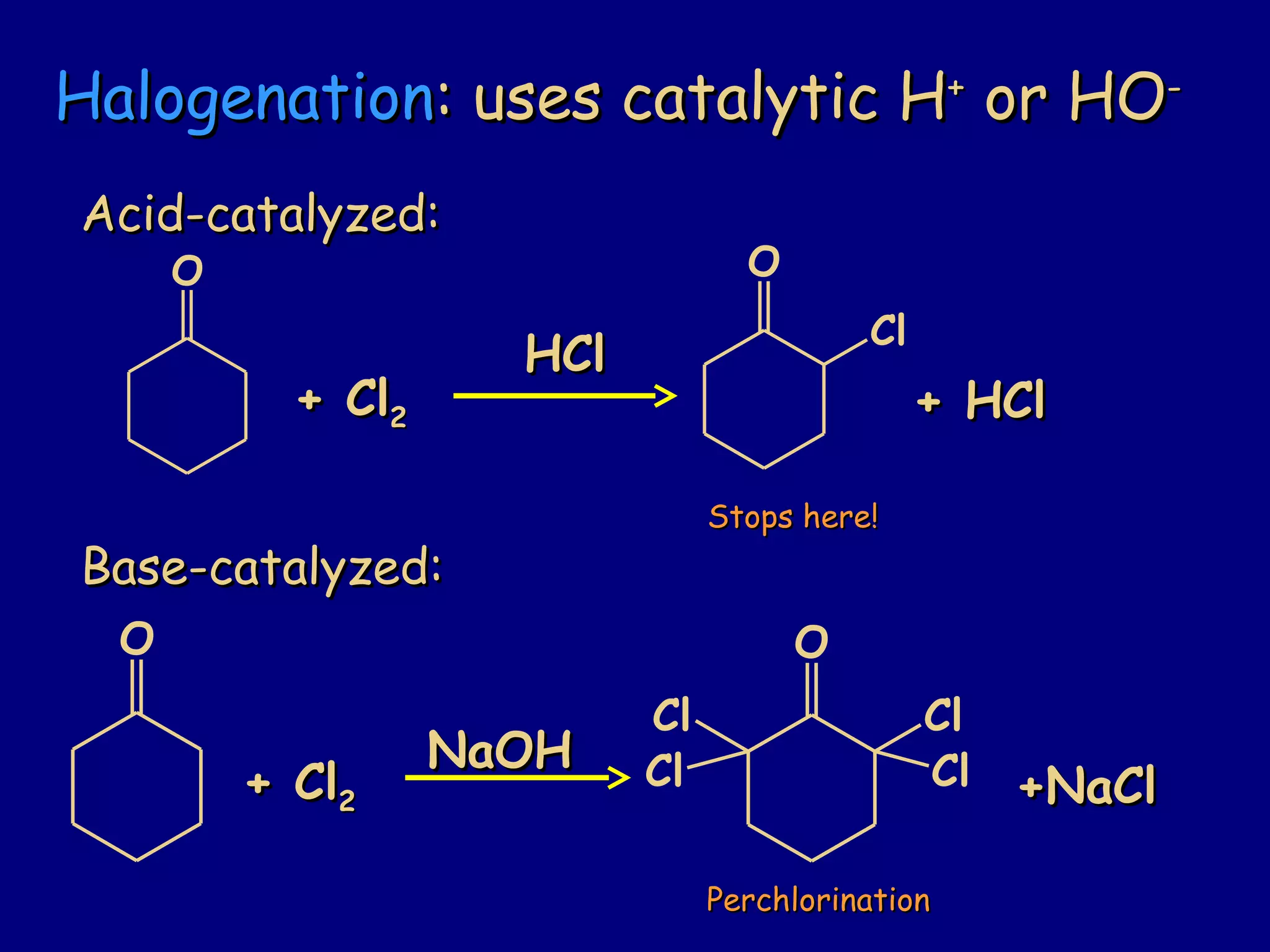
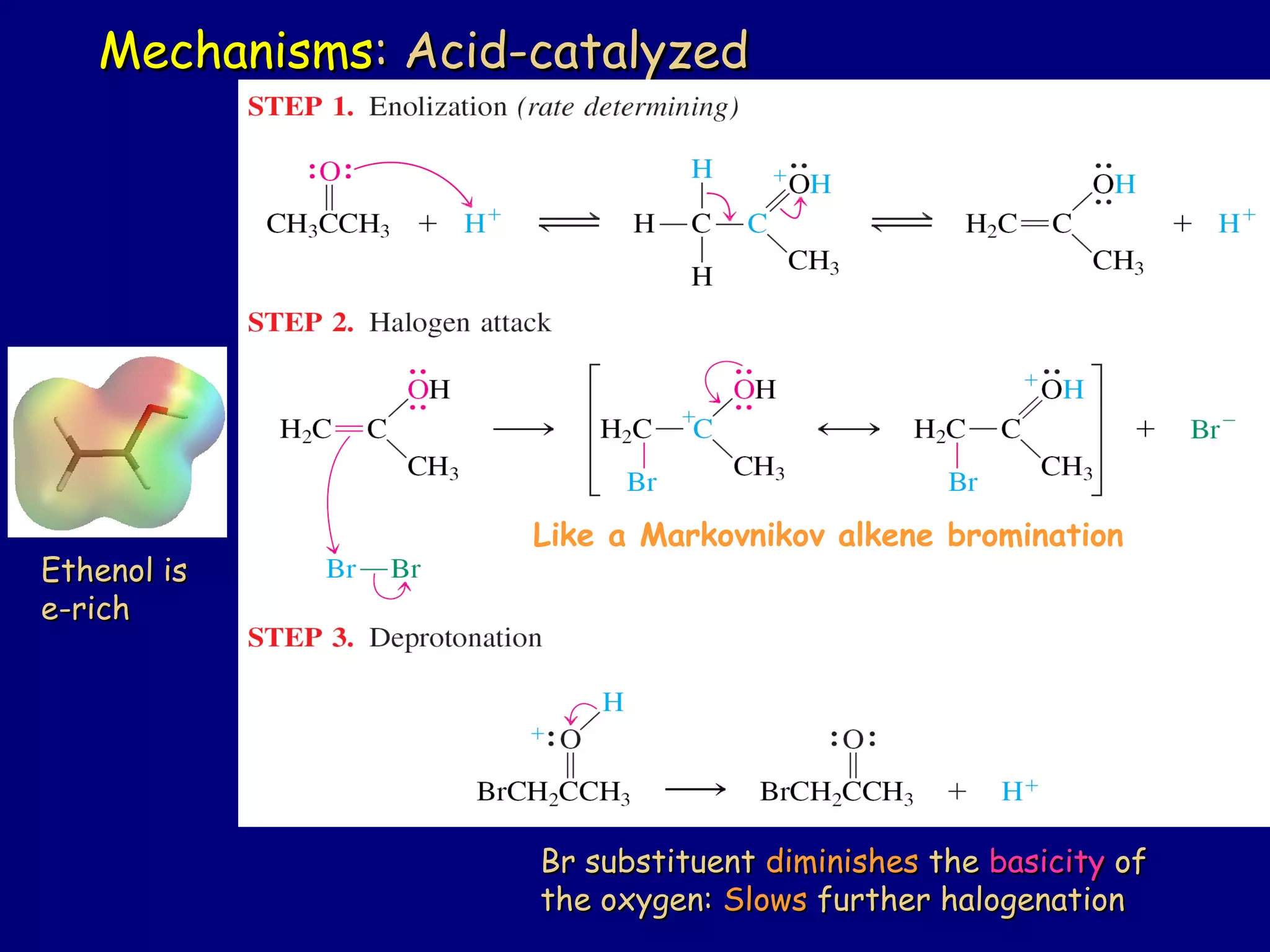
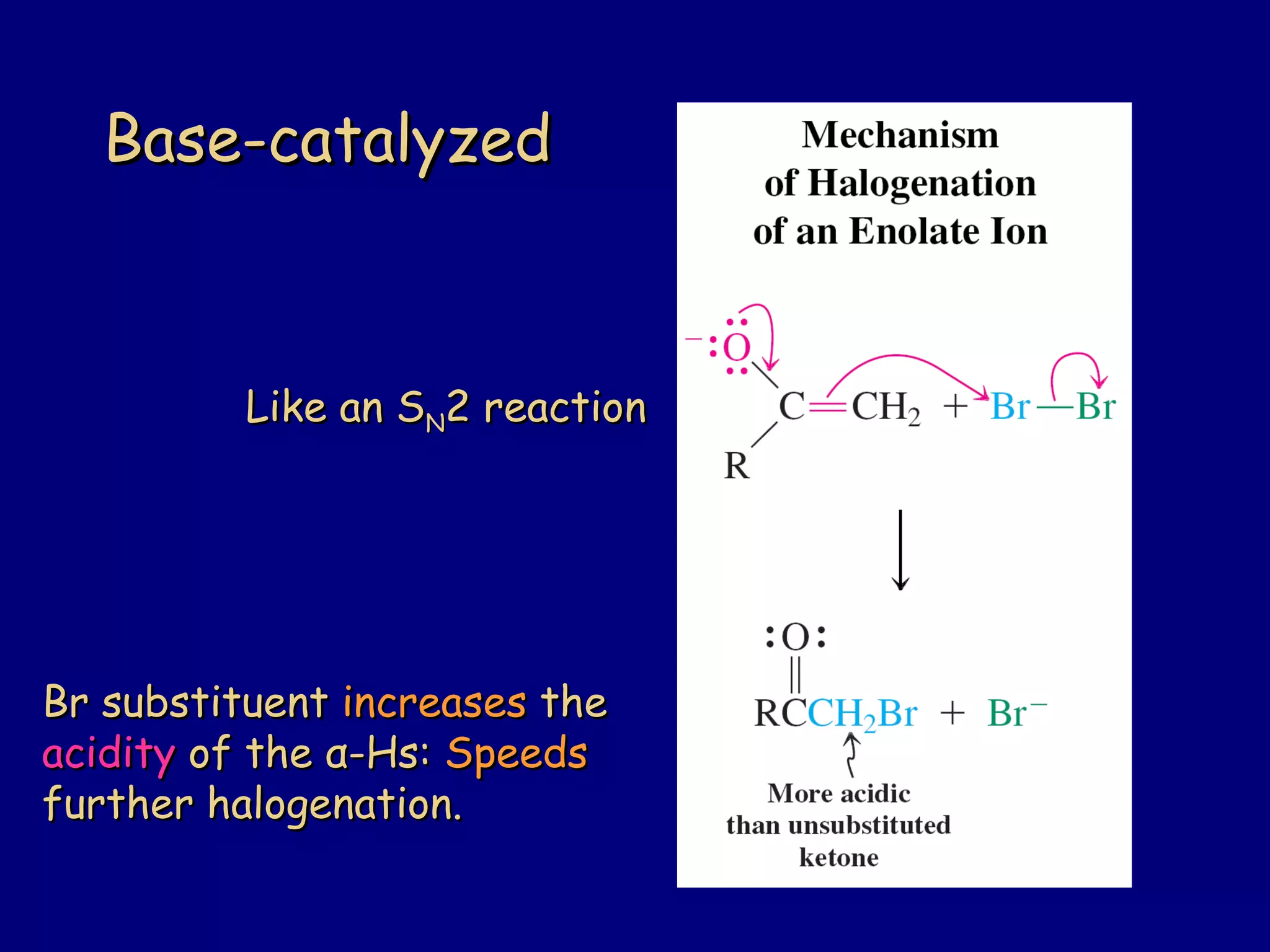
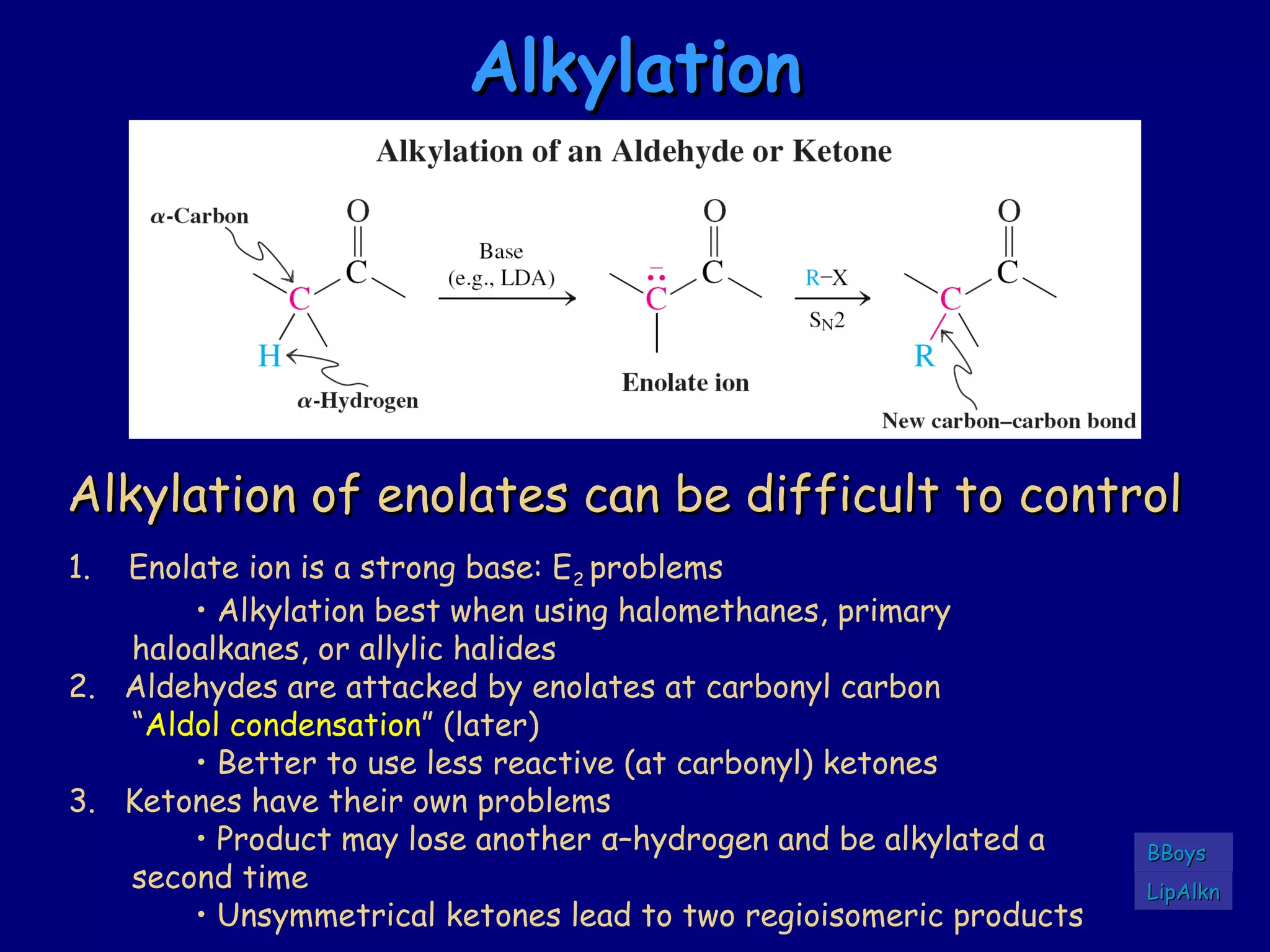
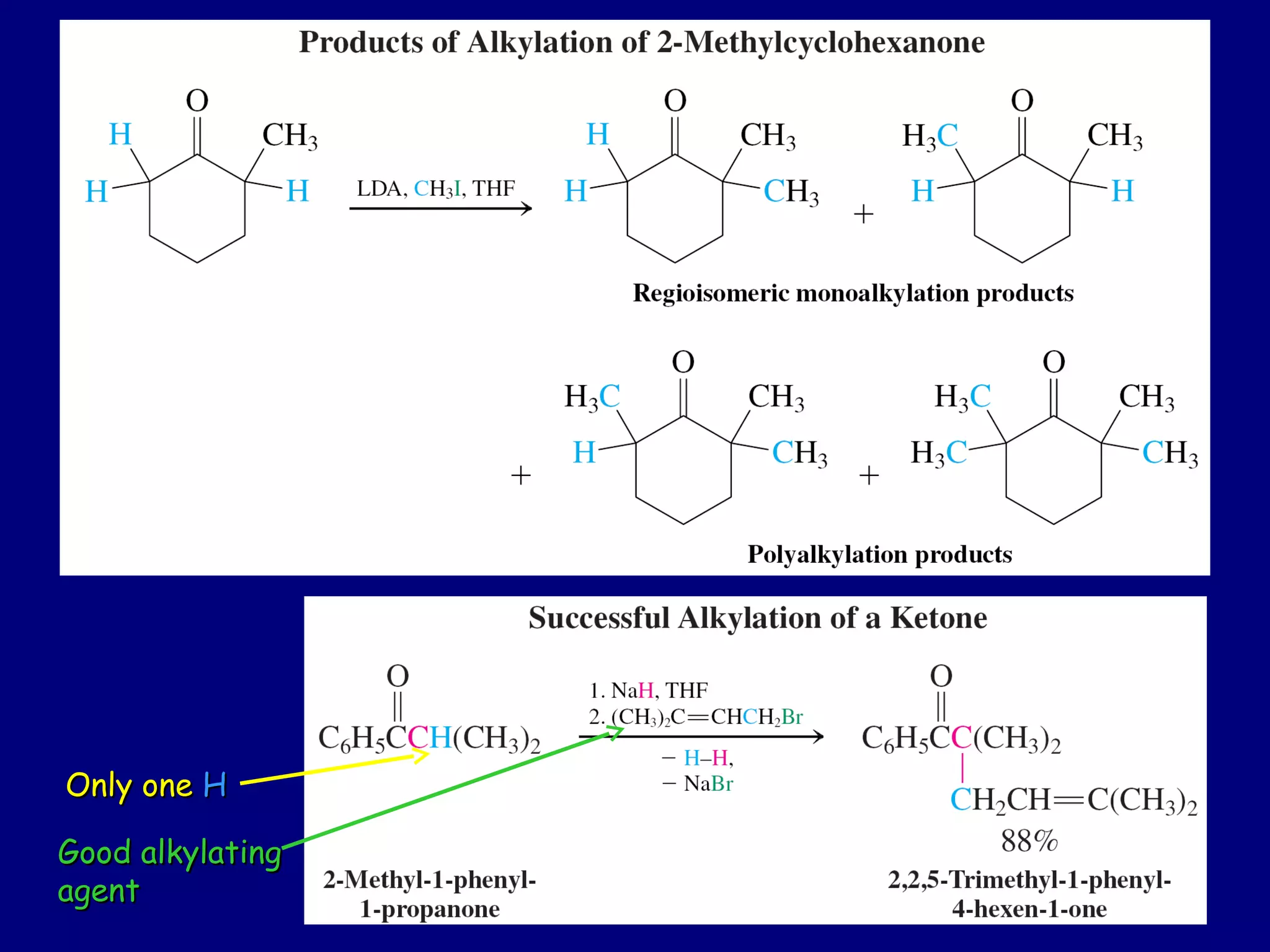
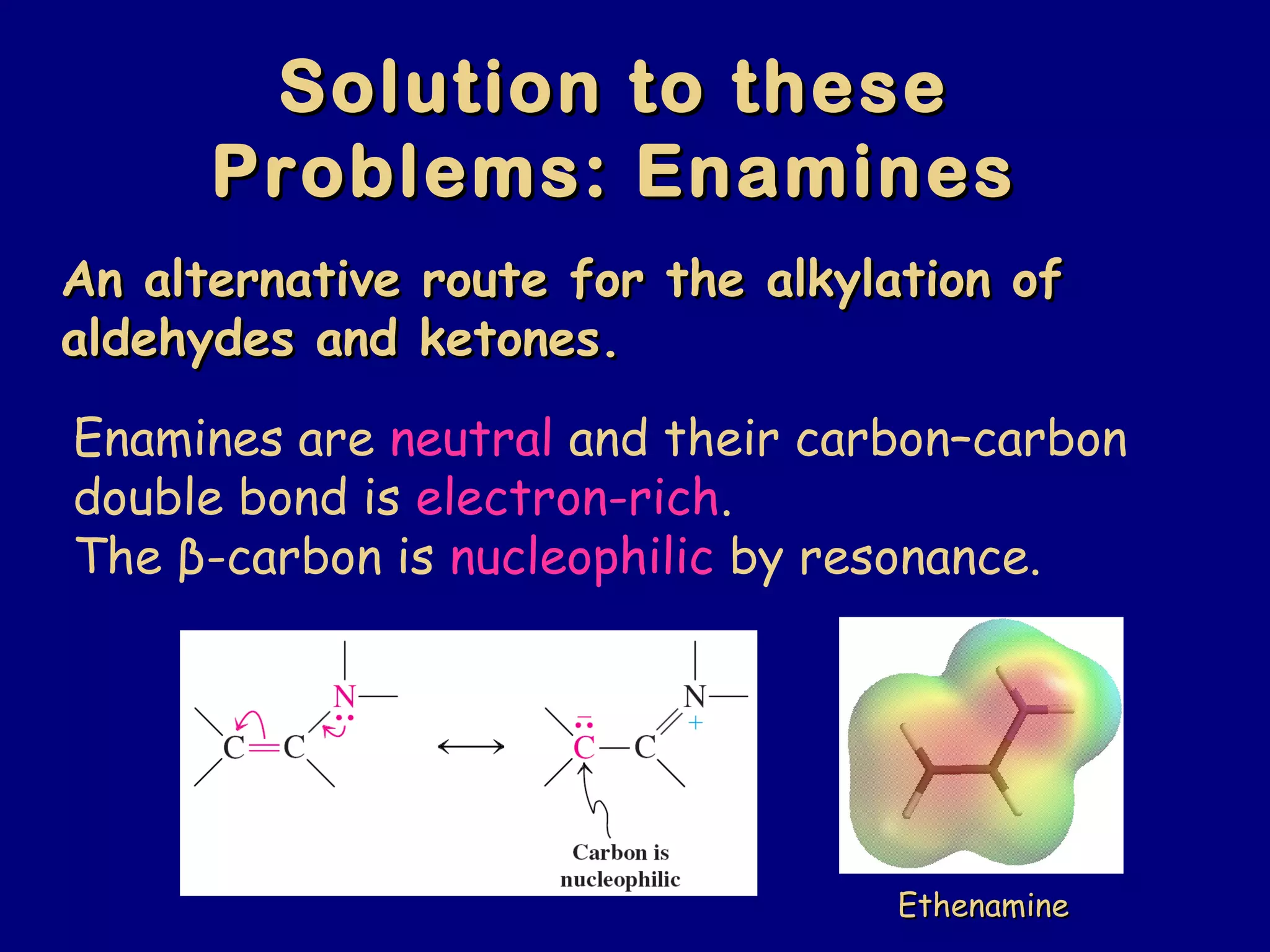
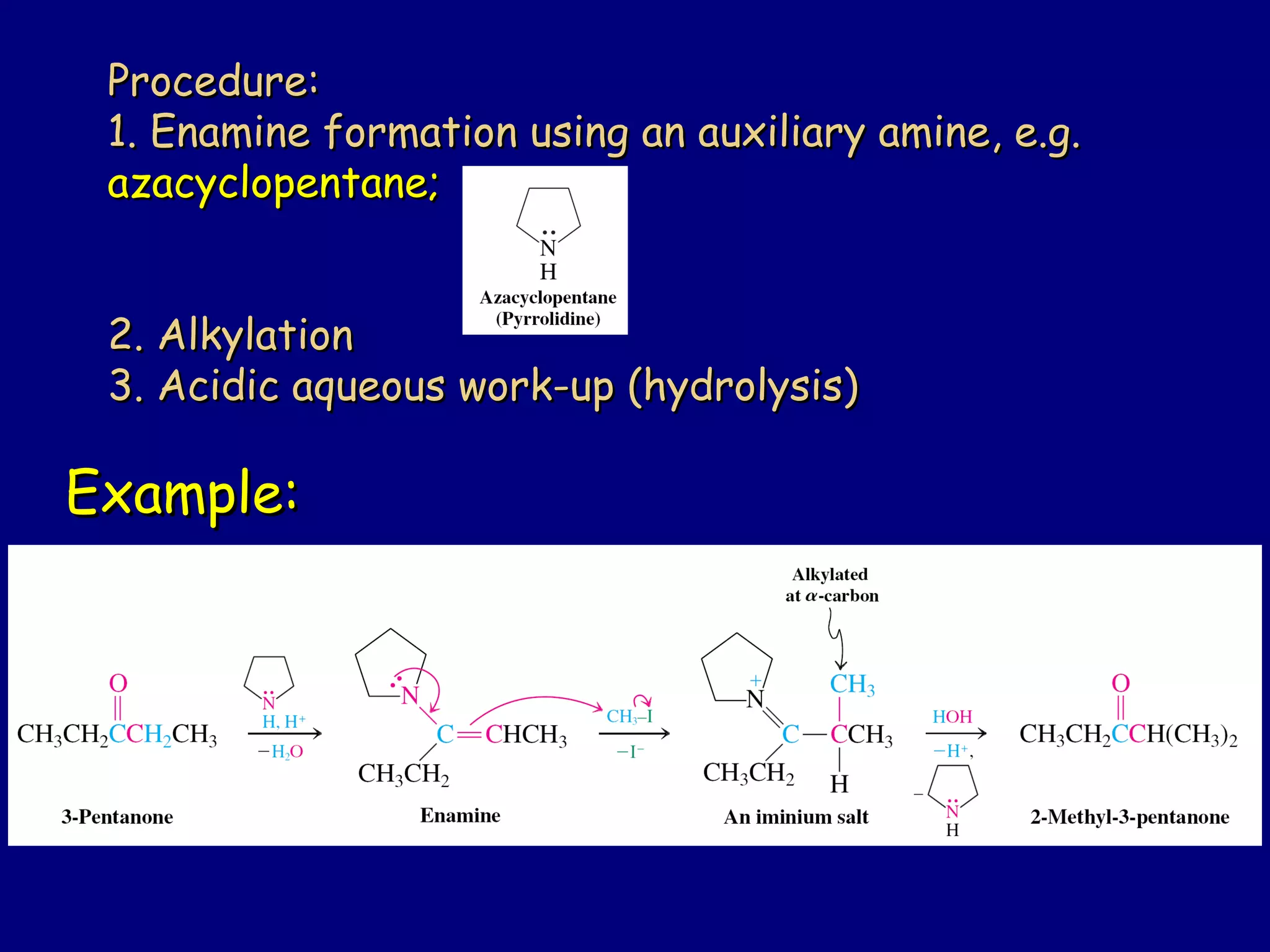
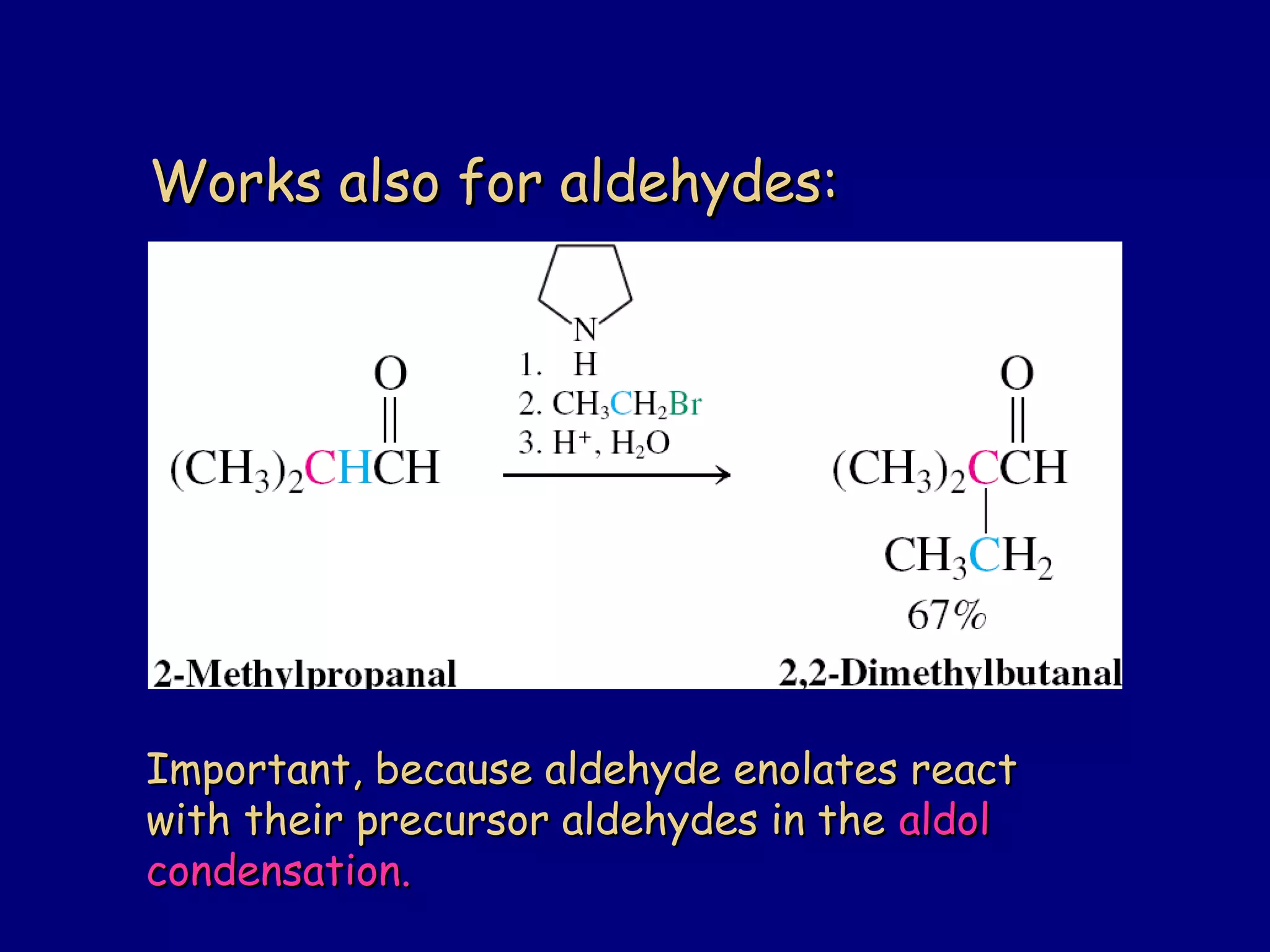
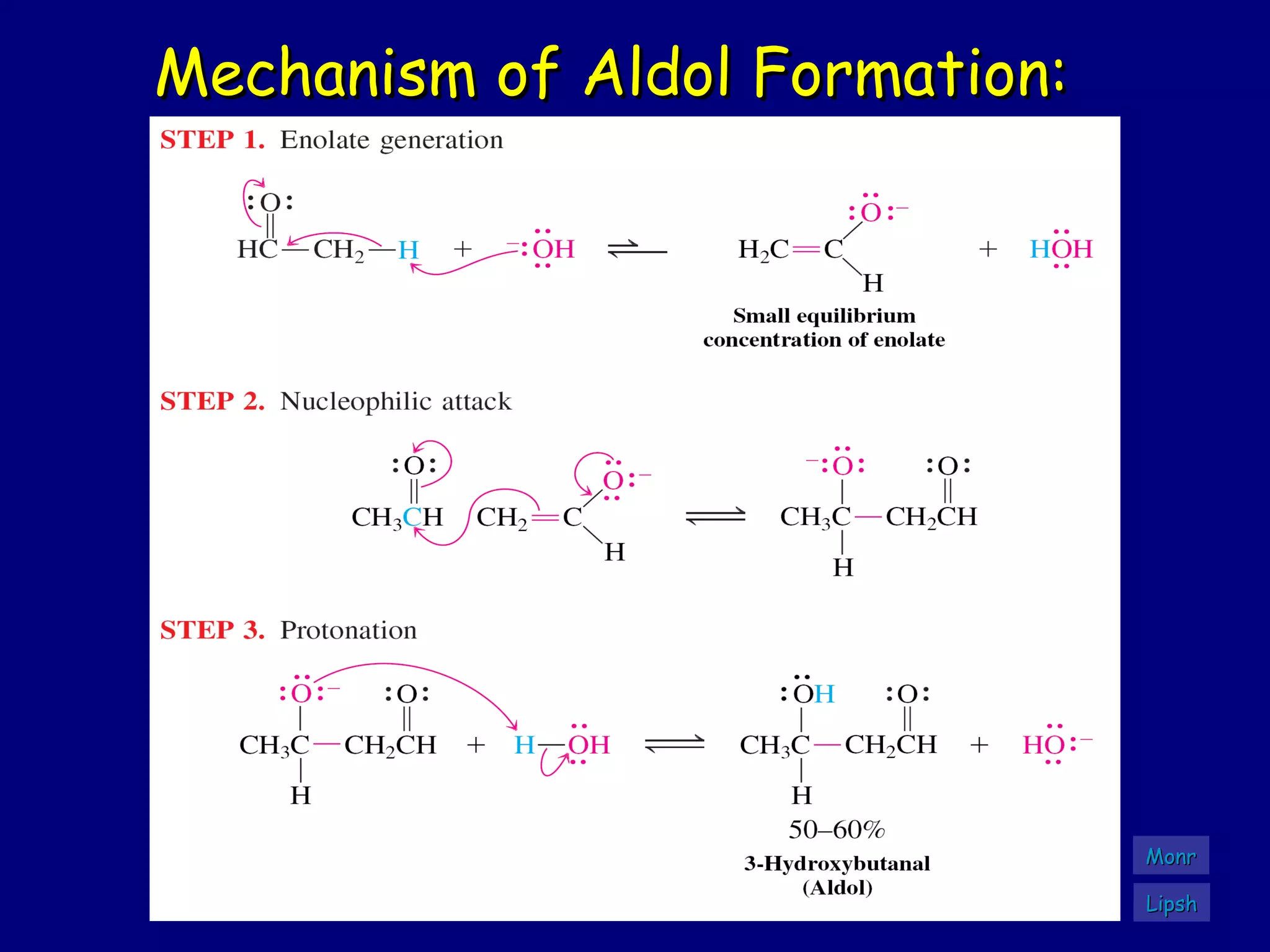
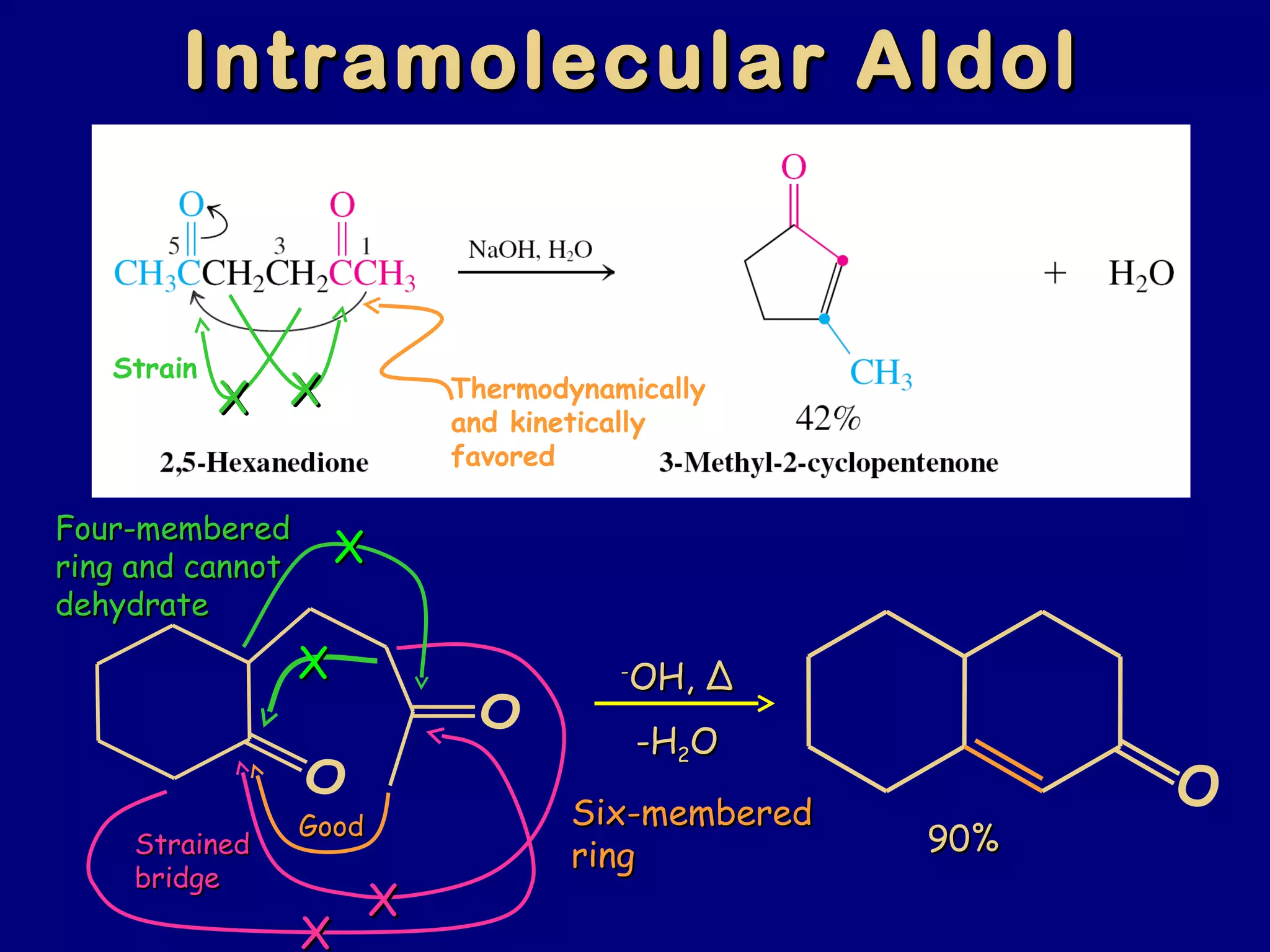
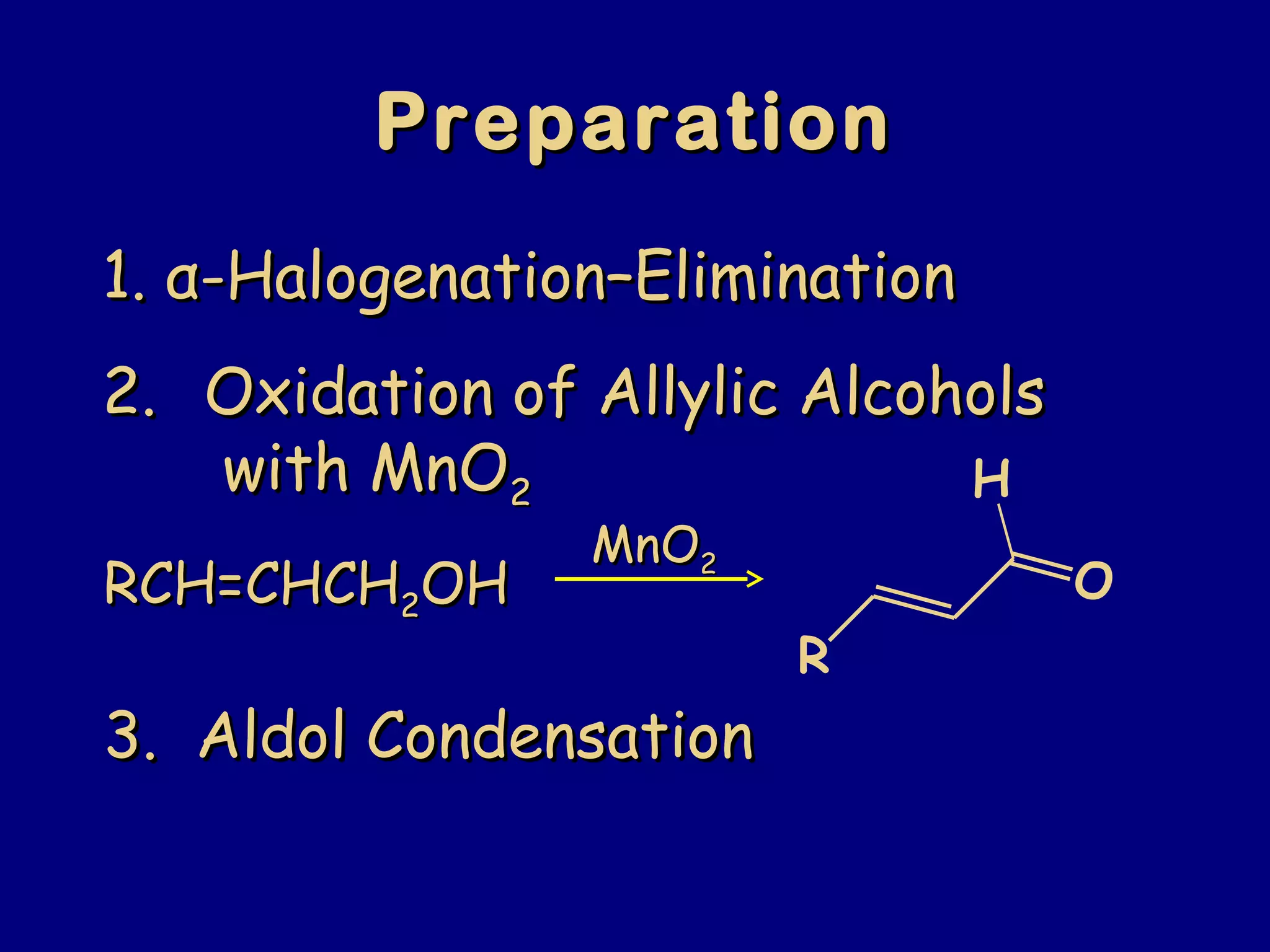
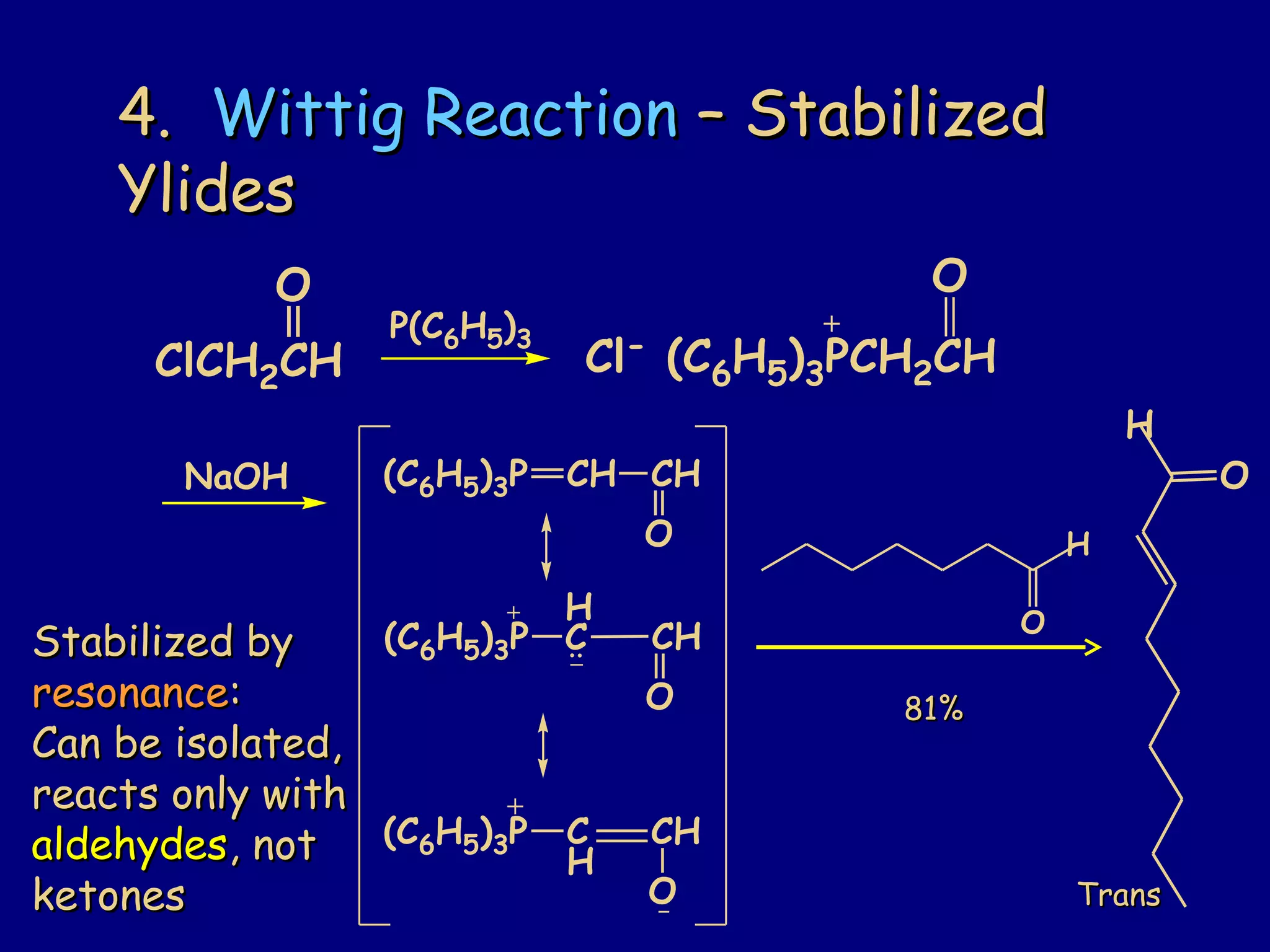
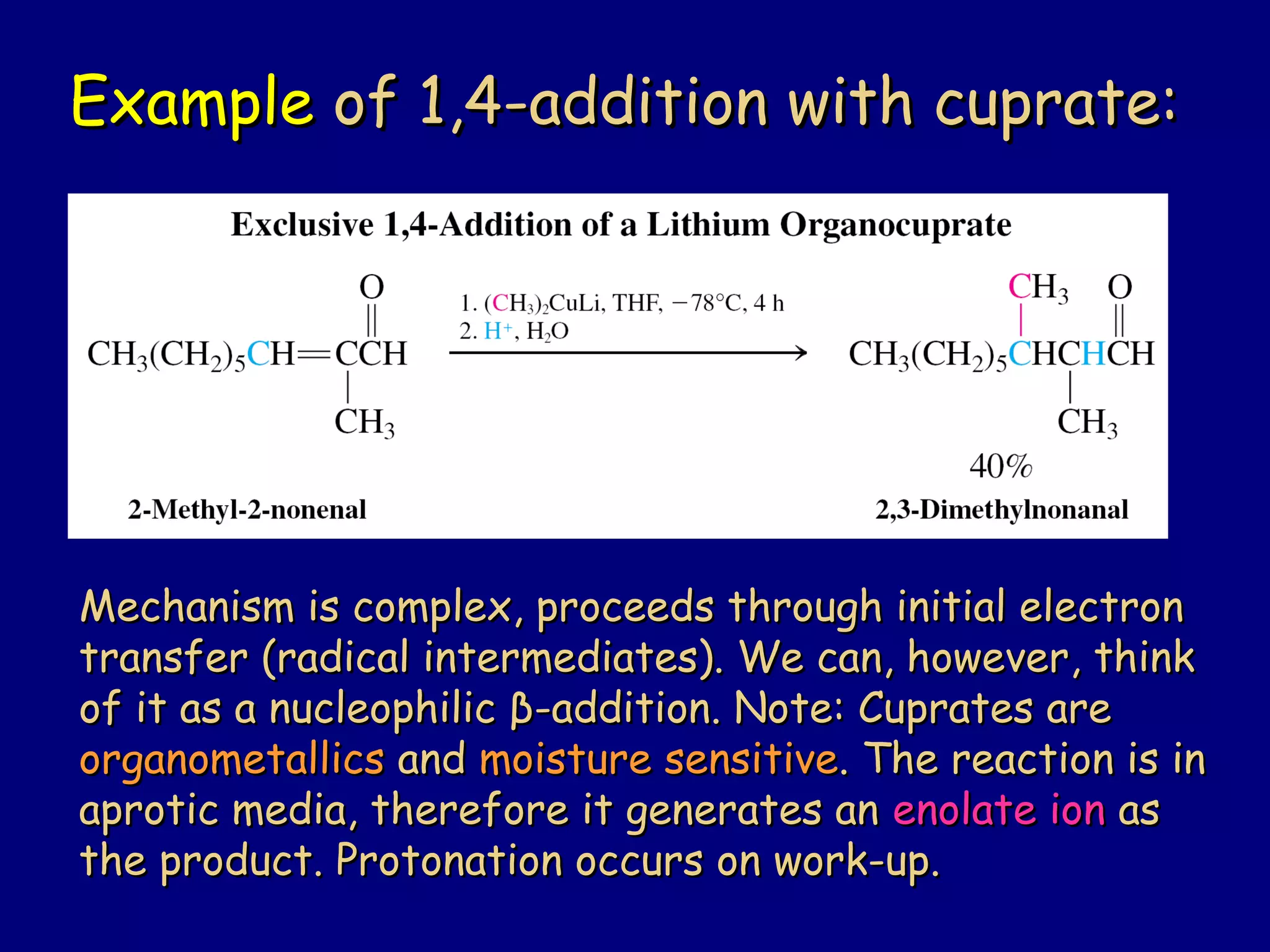
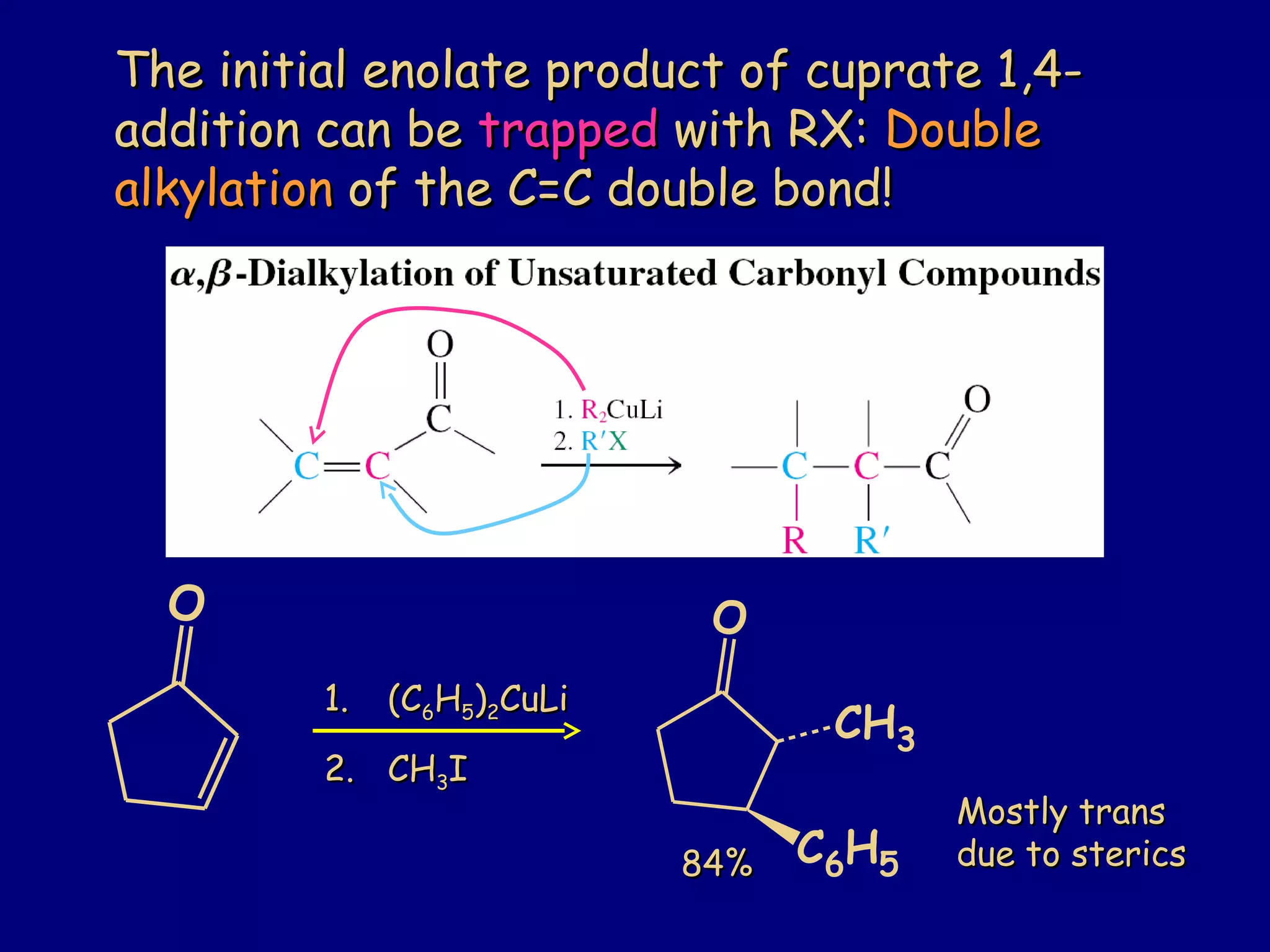
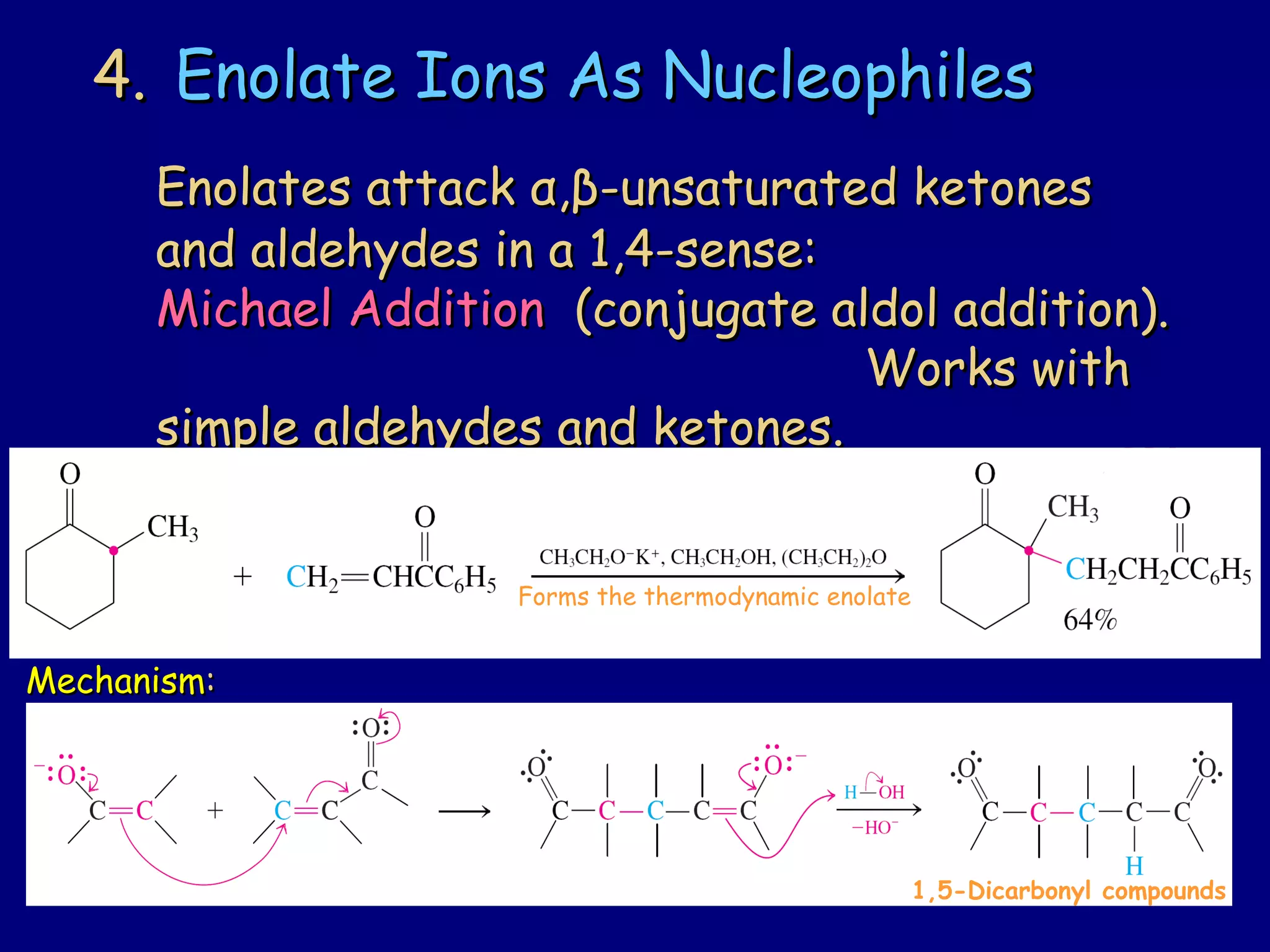
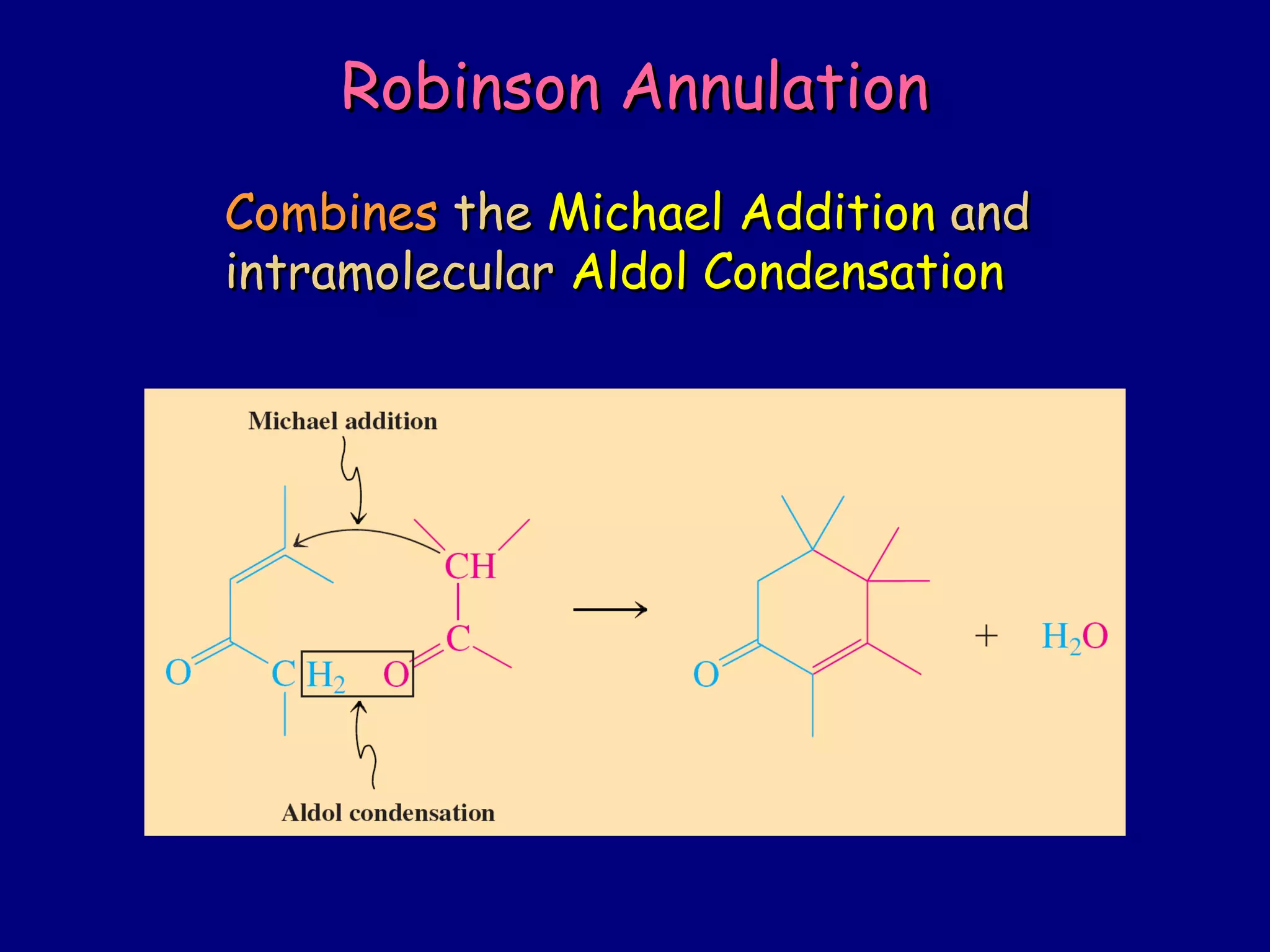
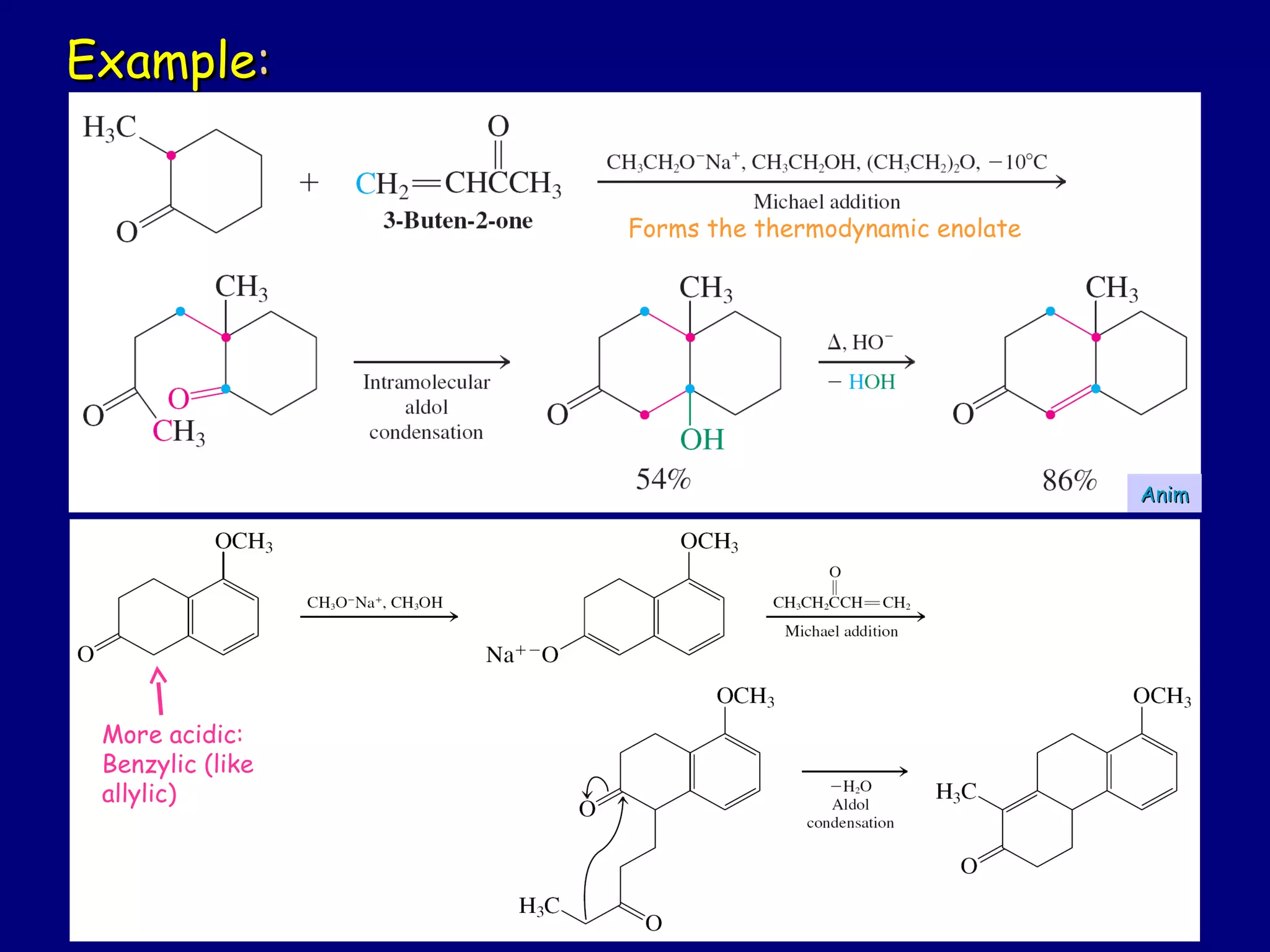
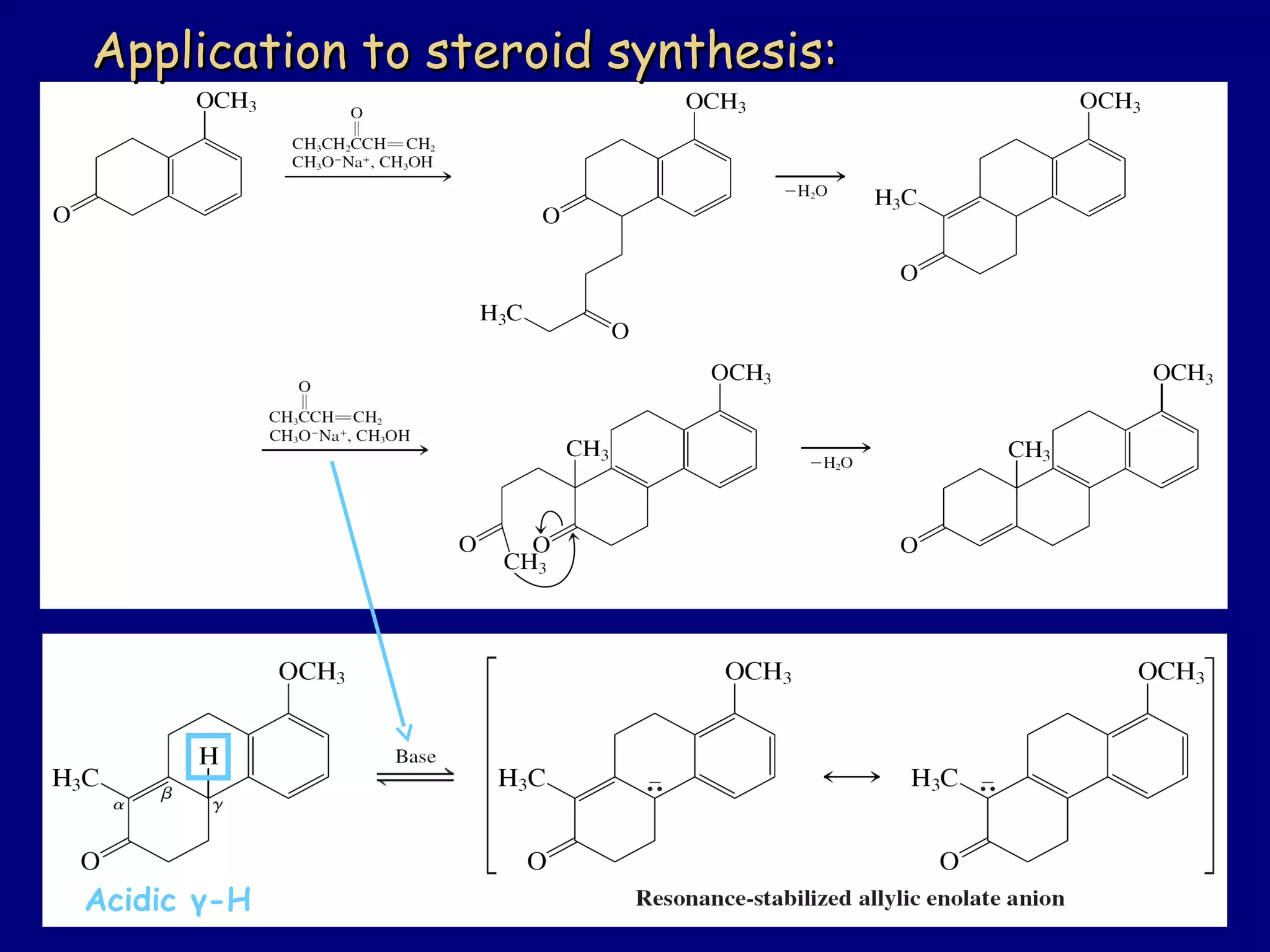
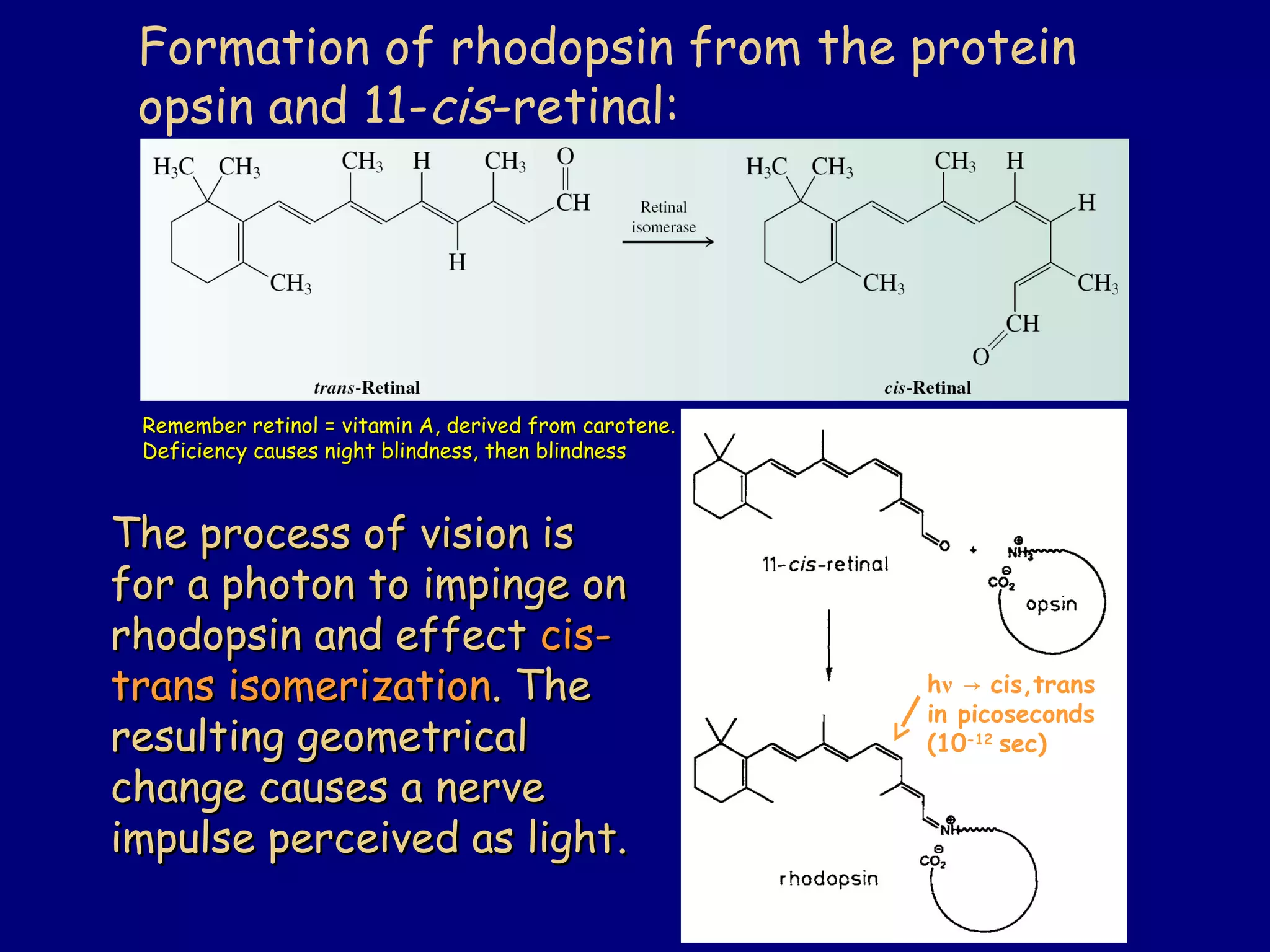
- α-Hydrogens in carbonyl compounds are acidic and can be deprotonated to form enolates using bases like KH or LDA.
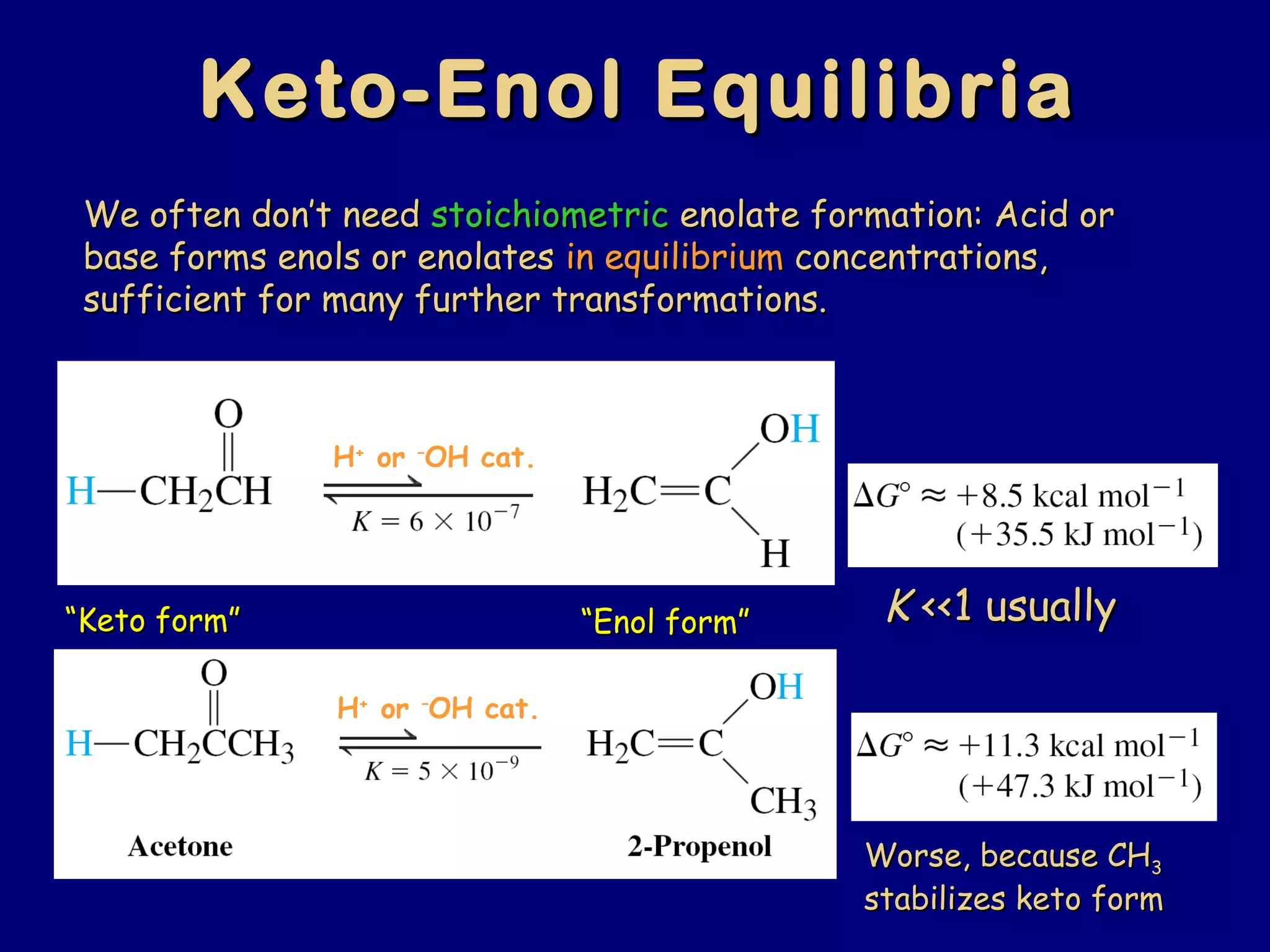
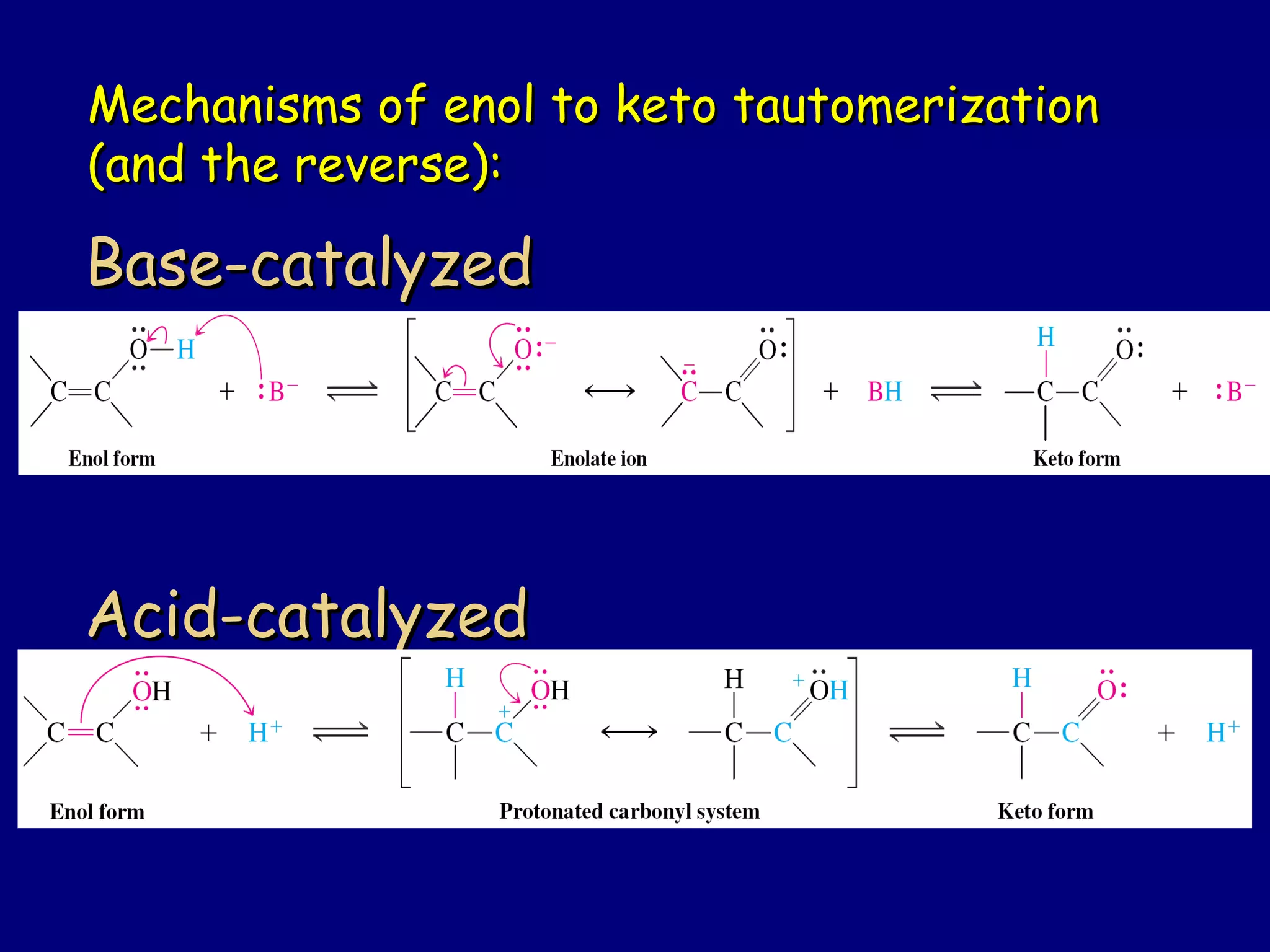
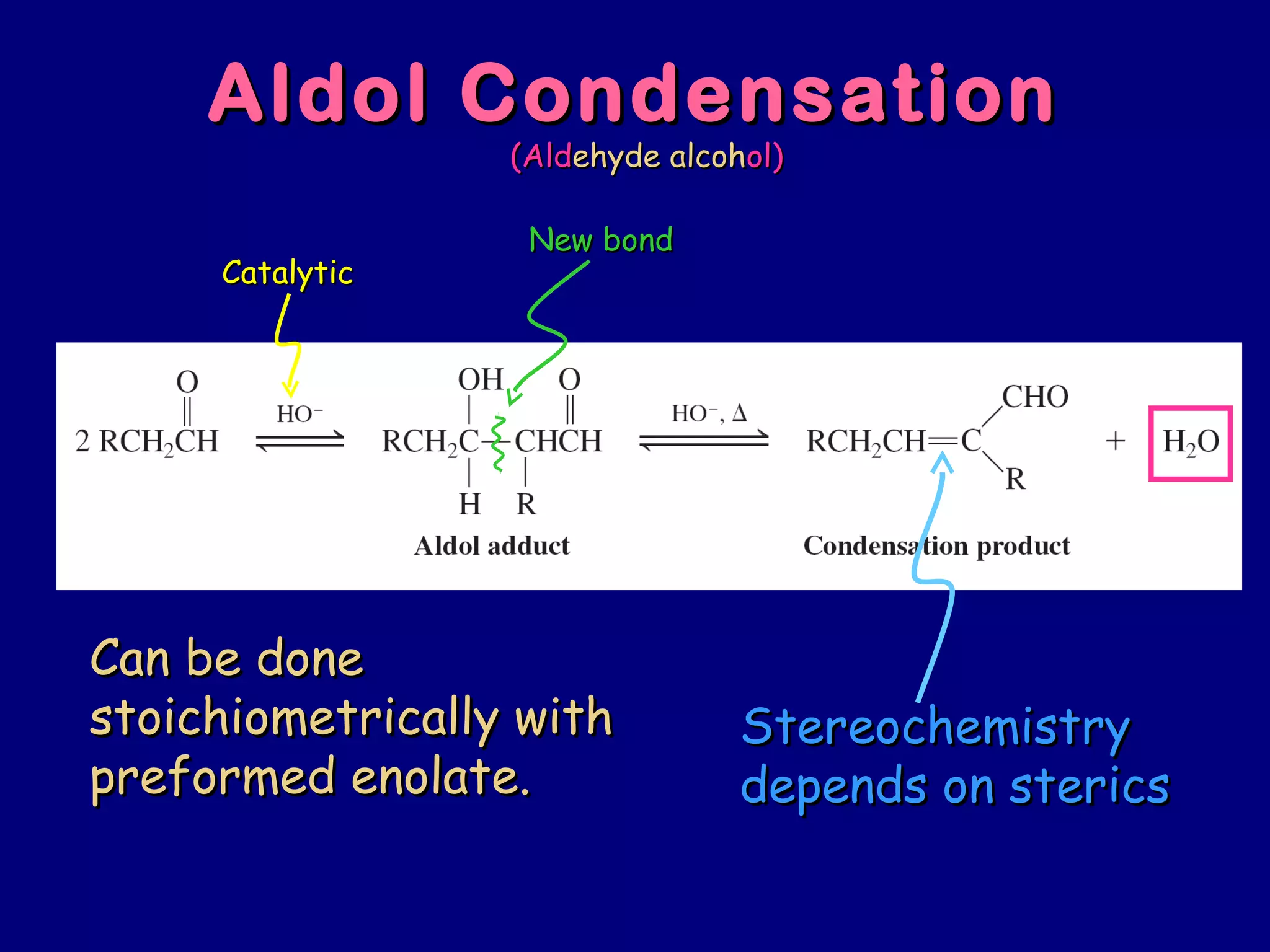
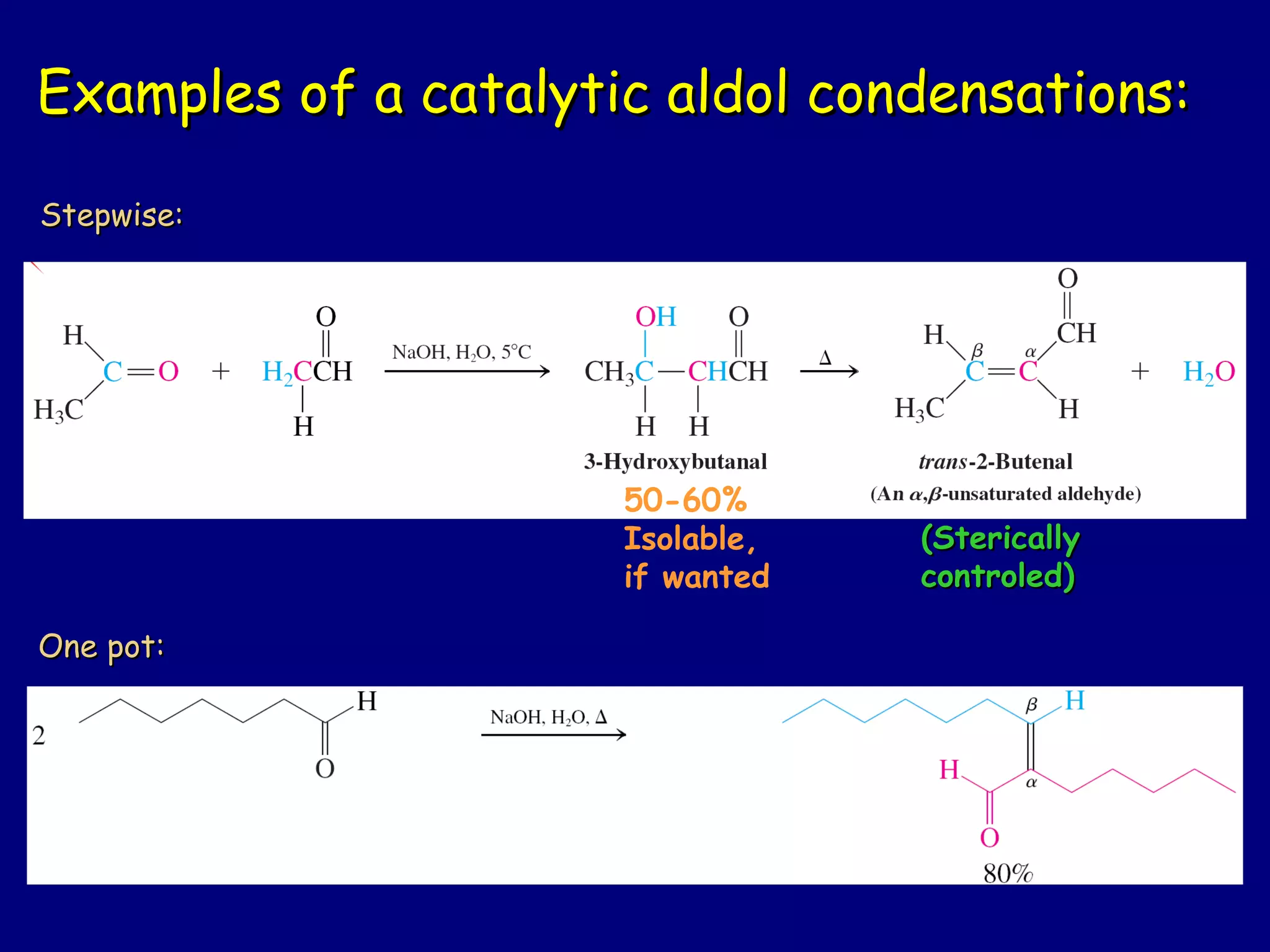
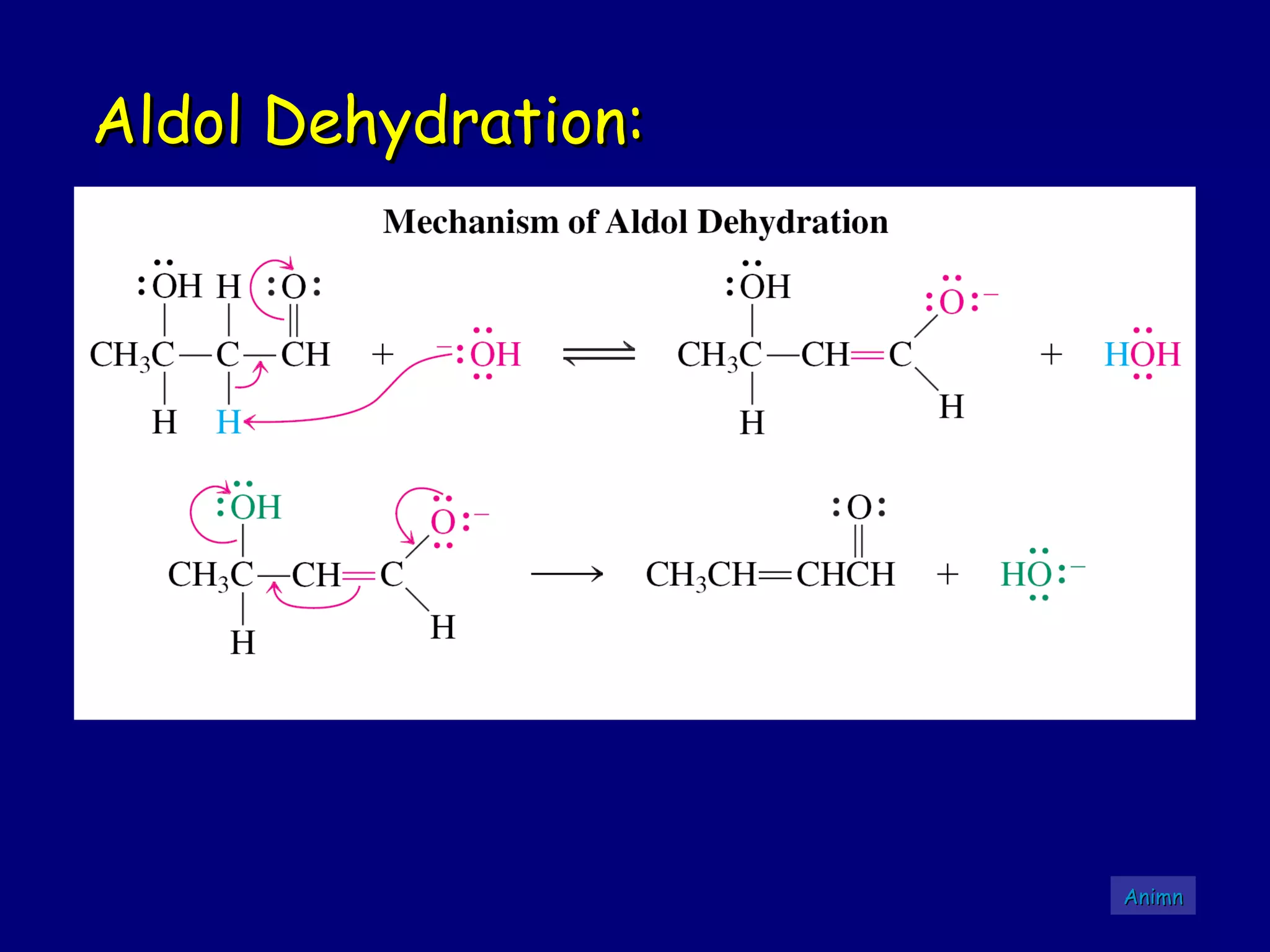
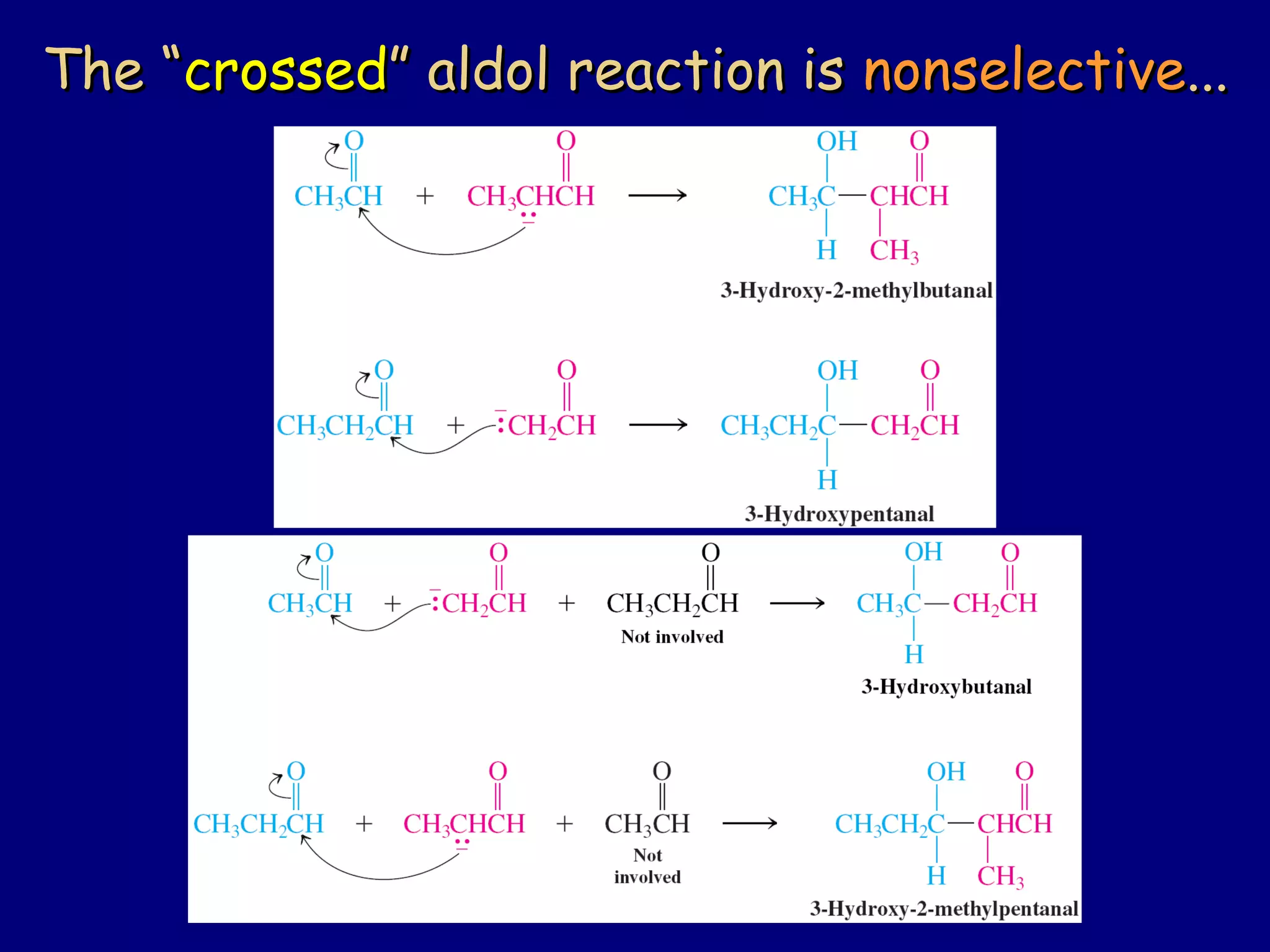
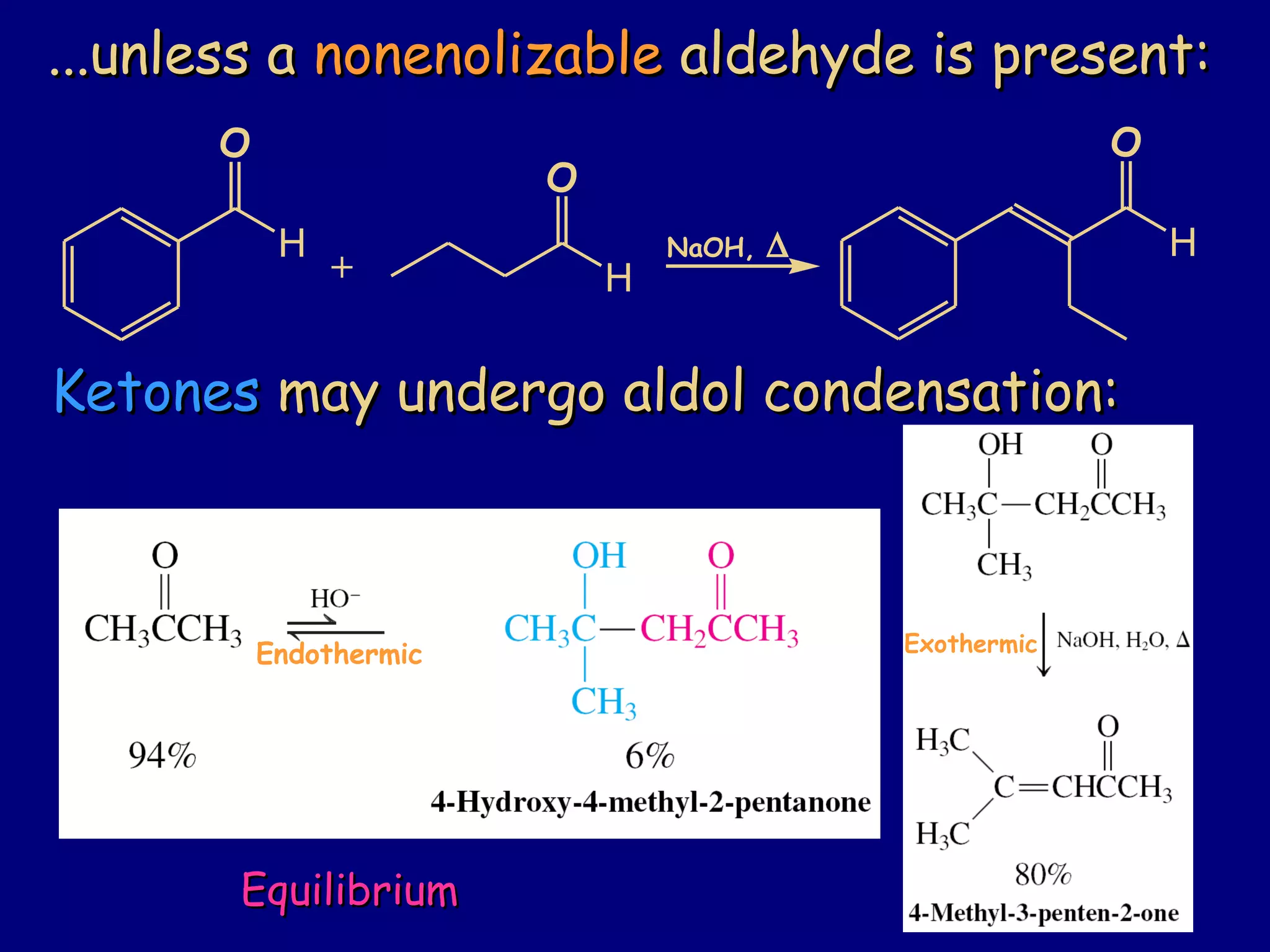
- Enolates are nucleophilic and can undergo reactions like alkylation, halogenation, and aldol condensation. They tautomerize between keto and enol forms.
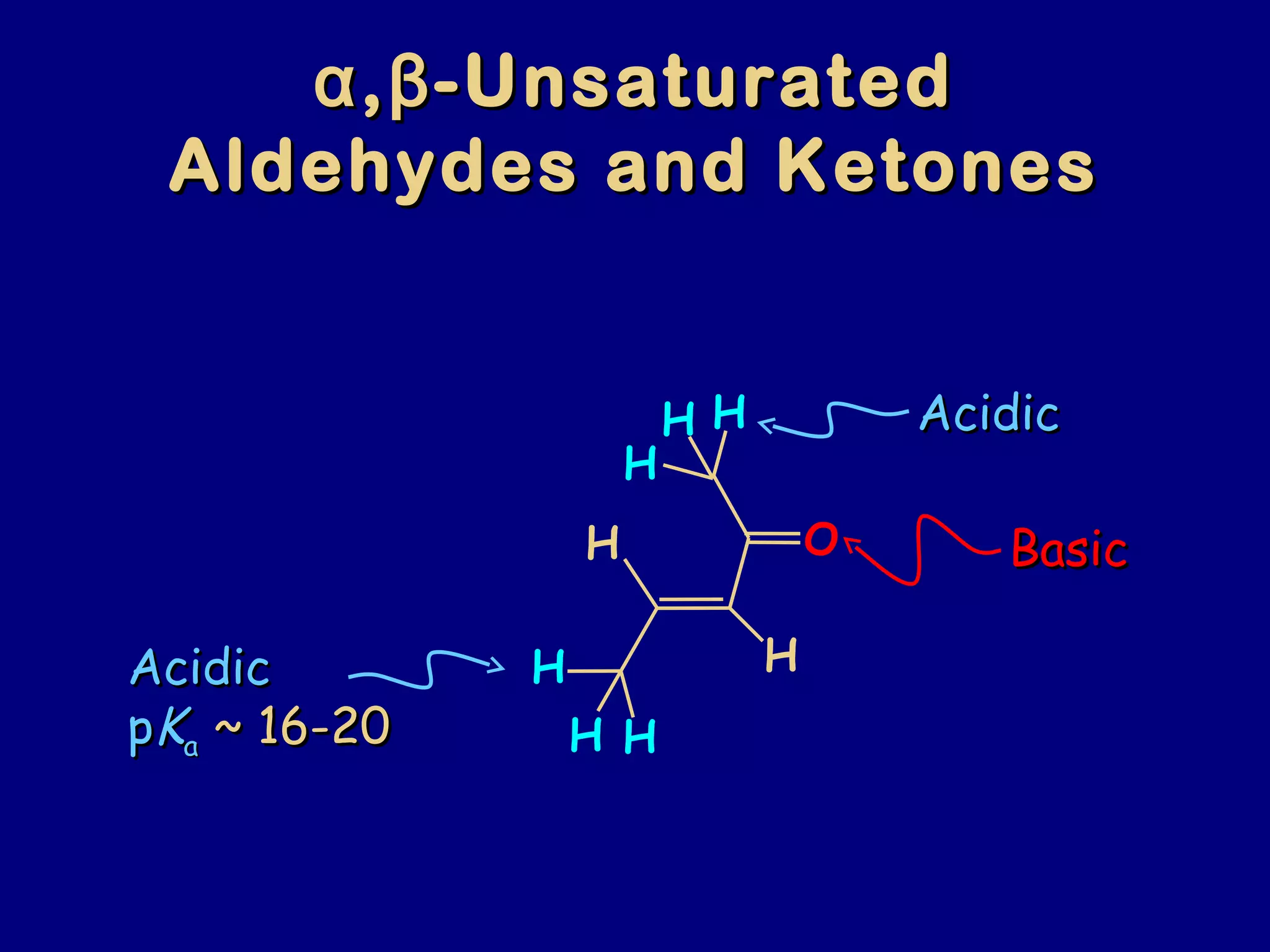
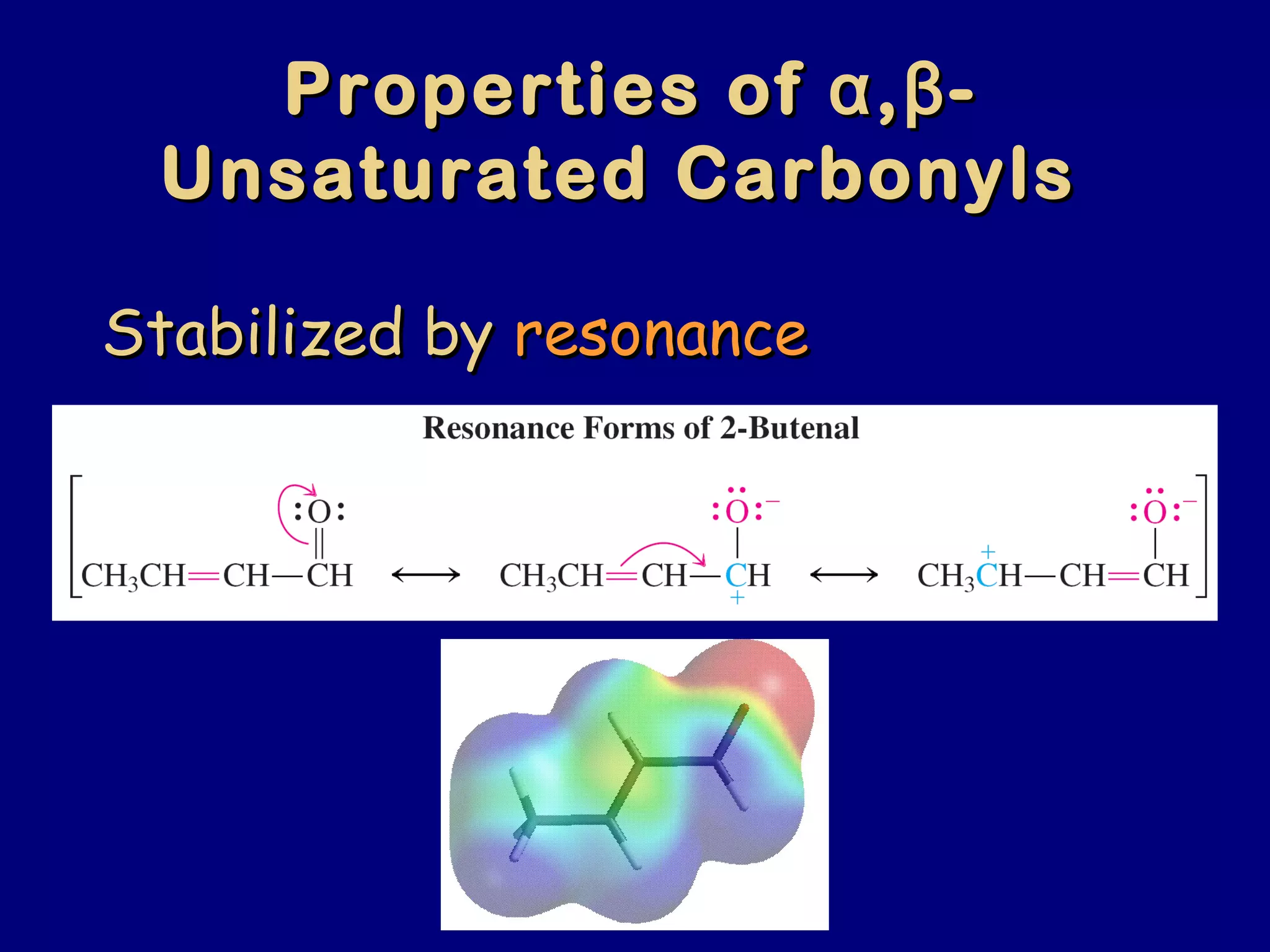
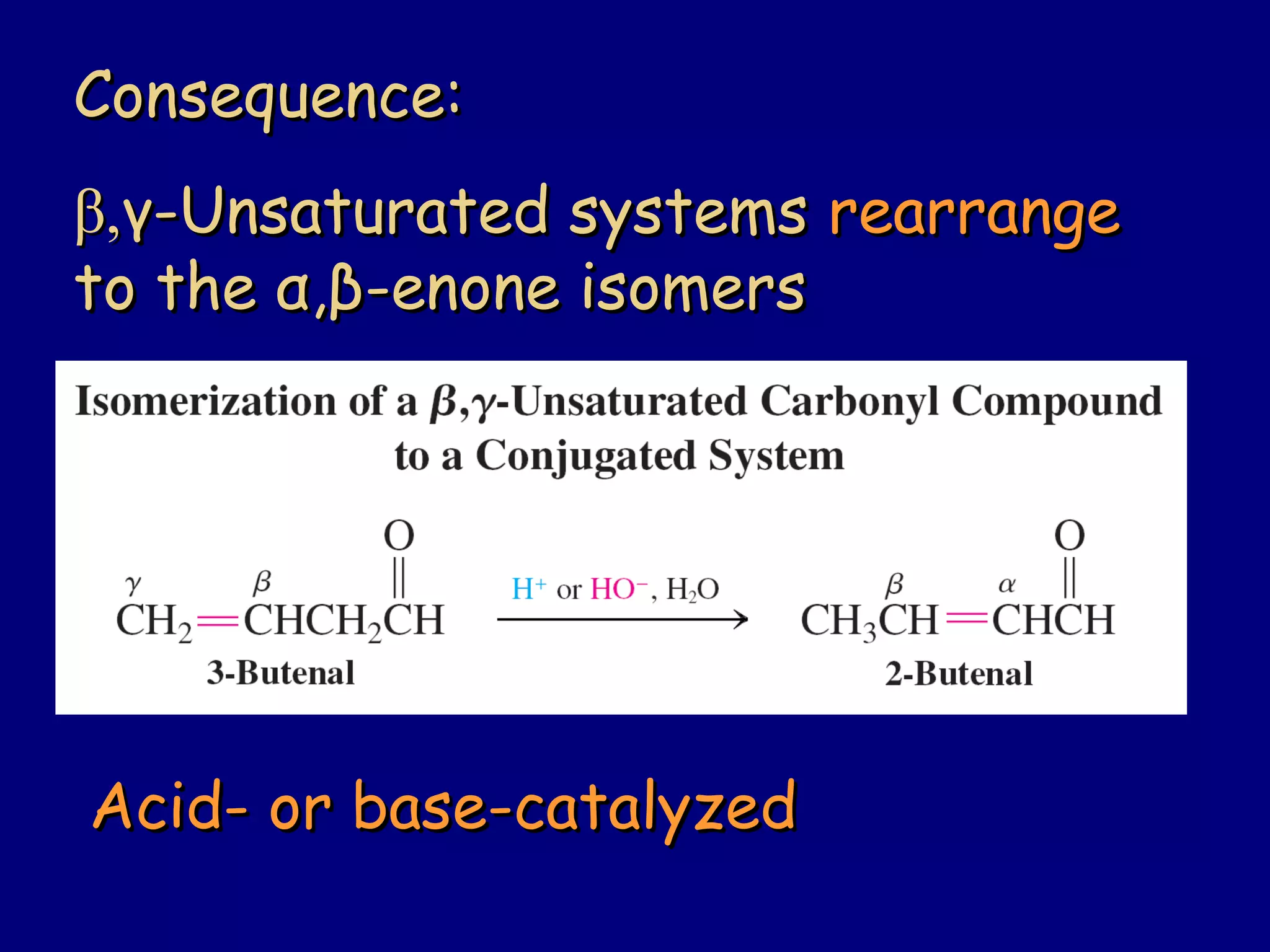
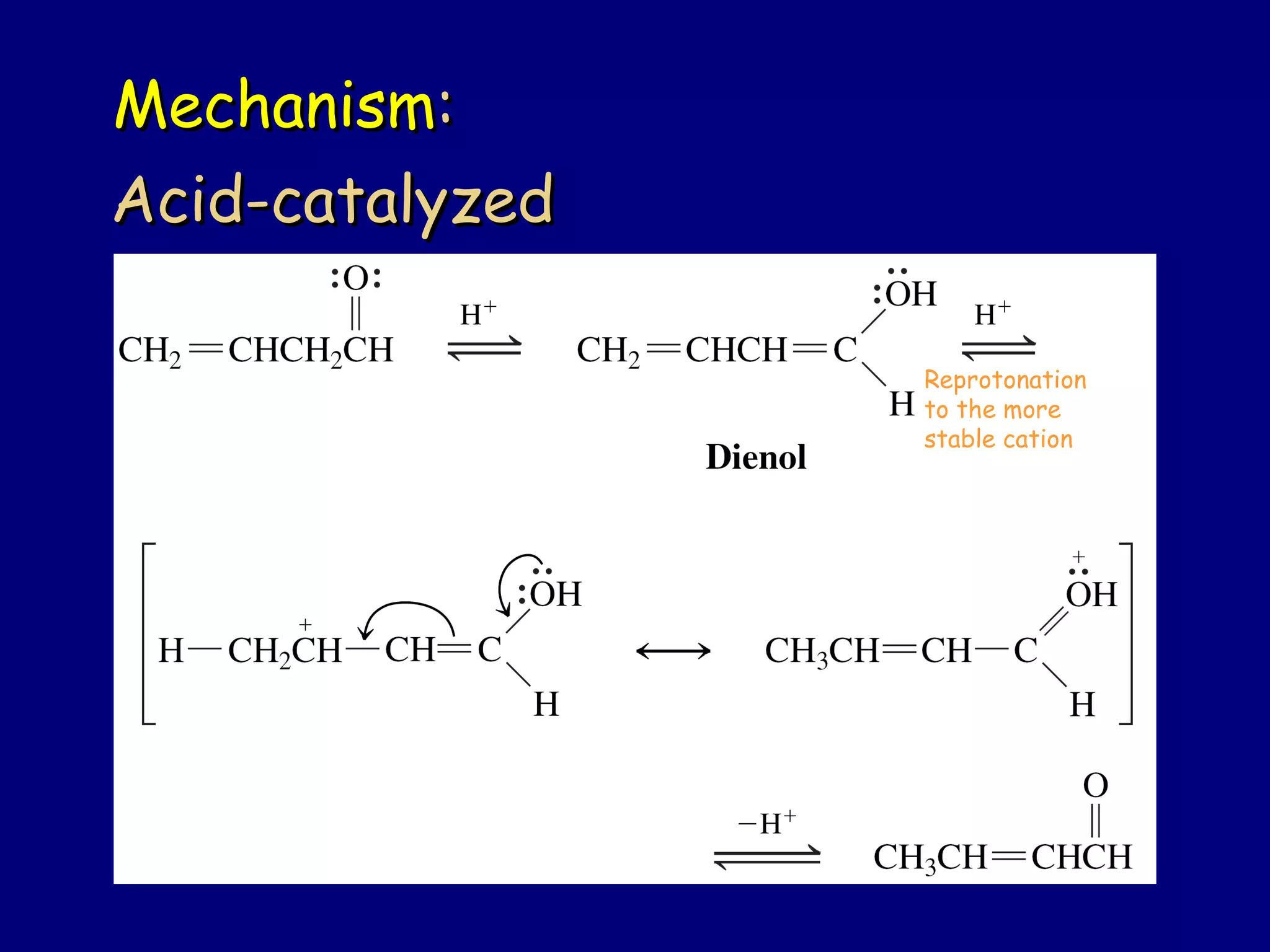
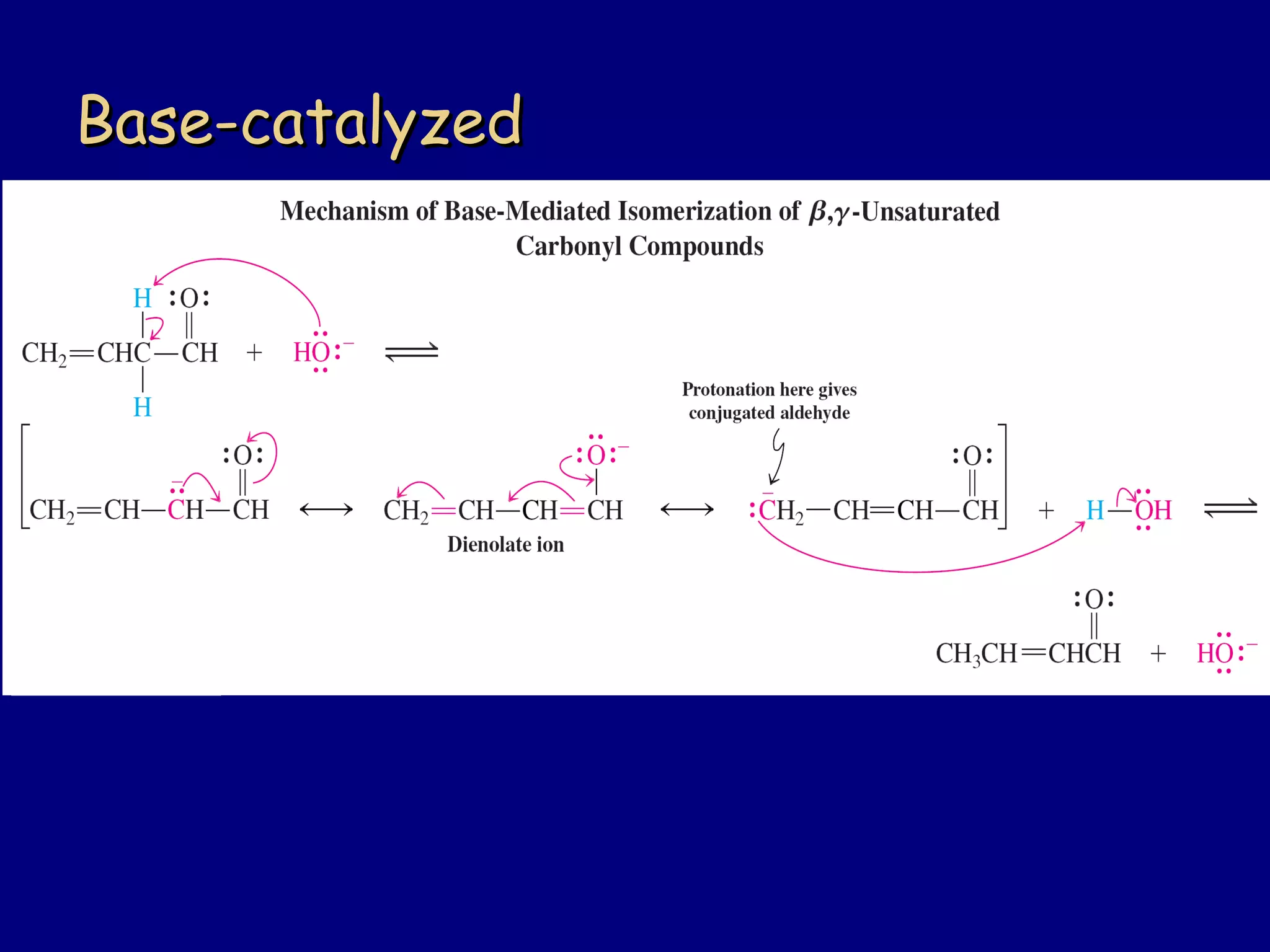
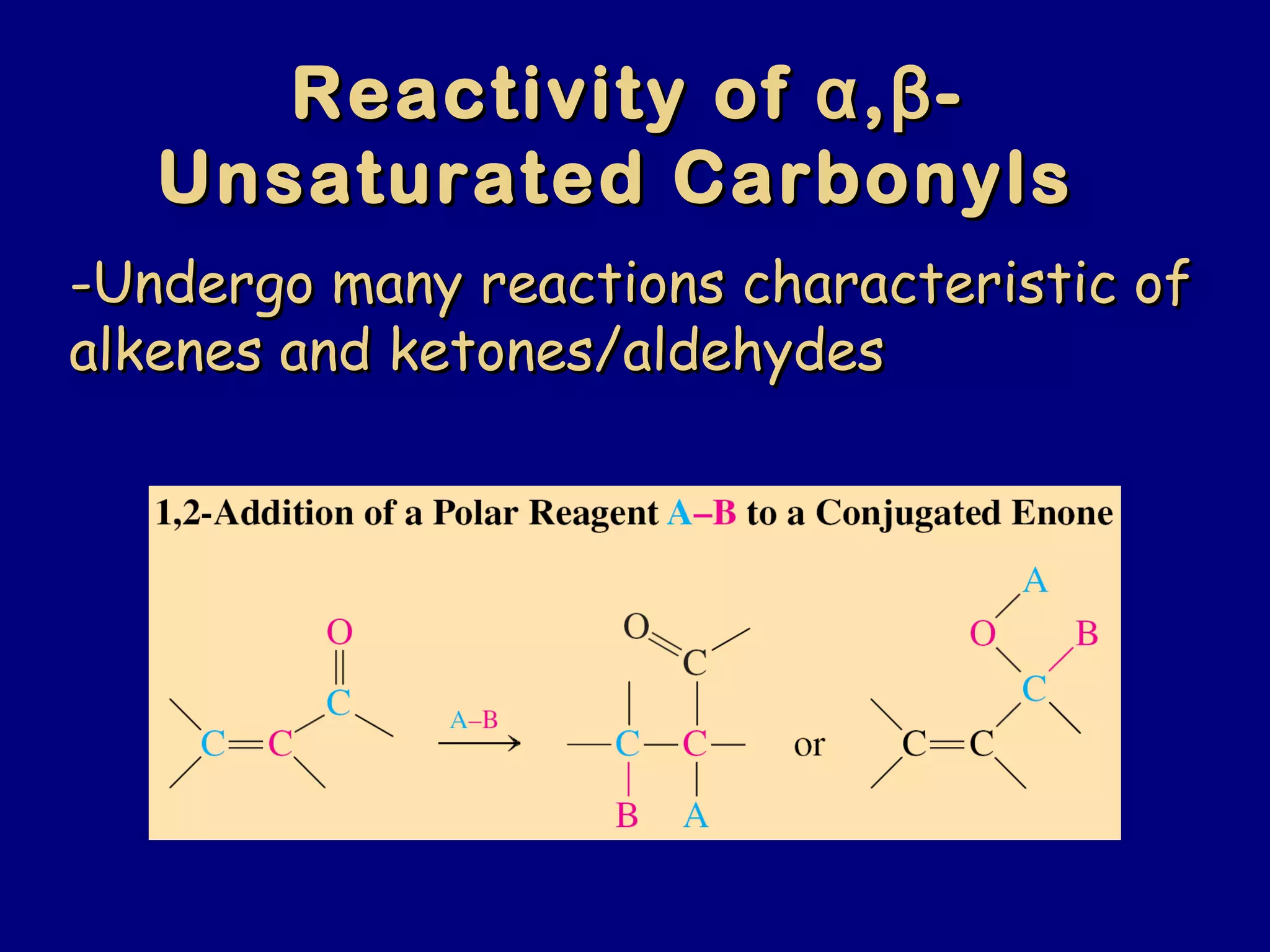
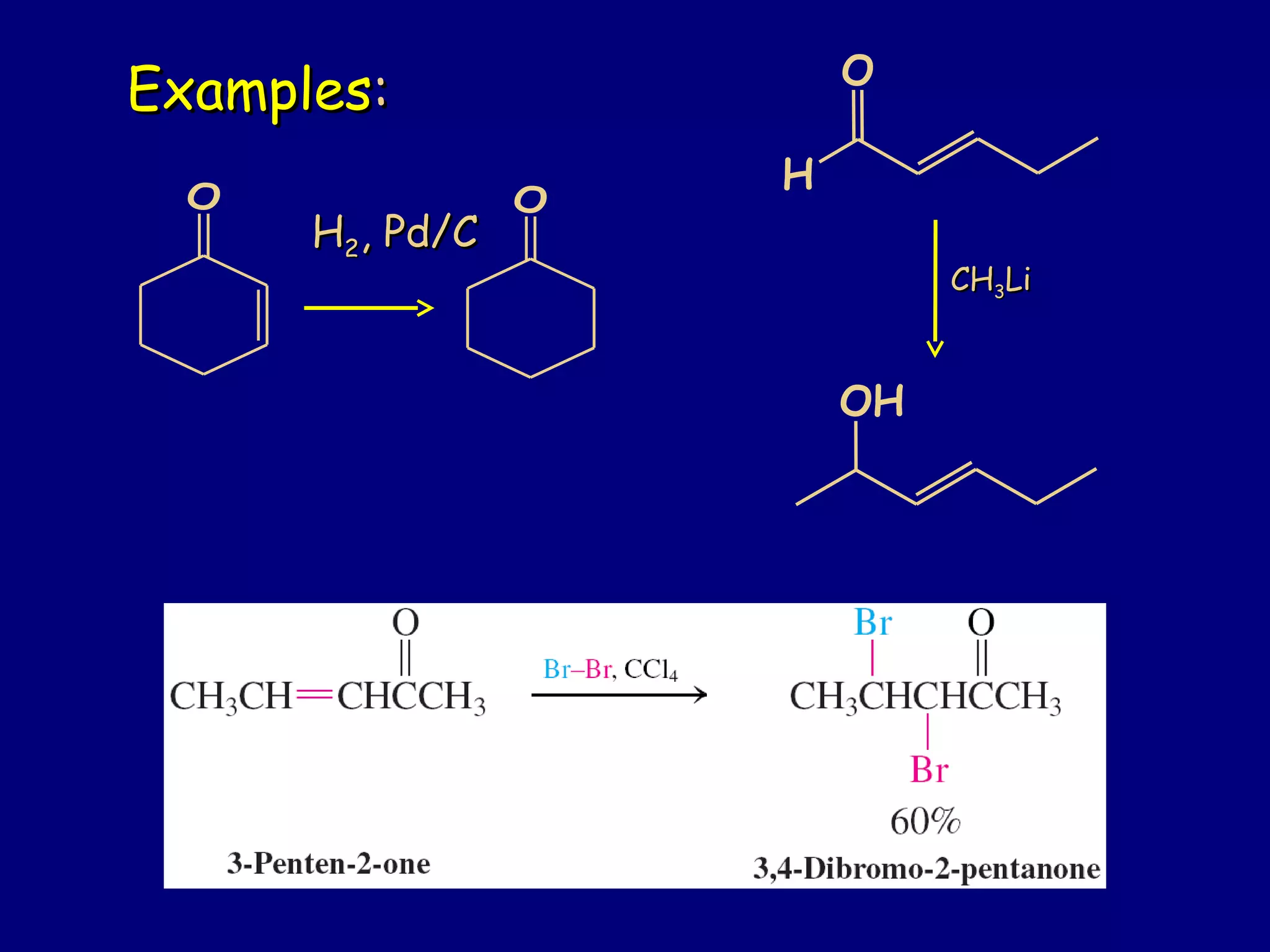
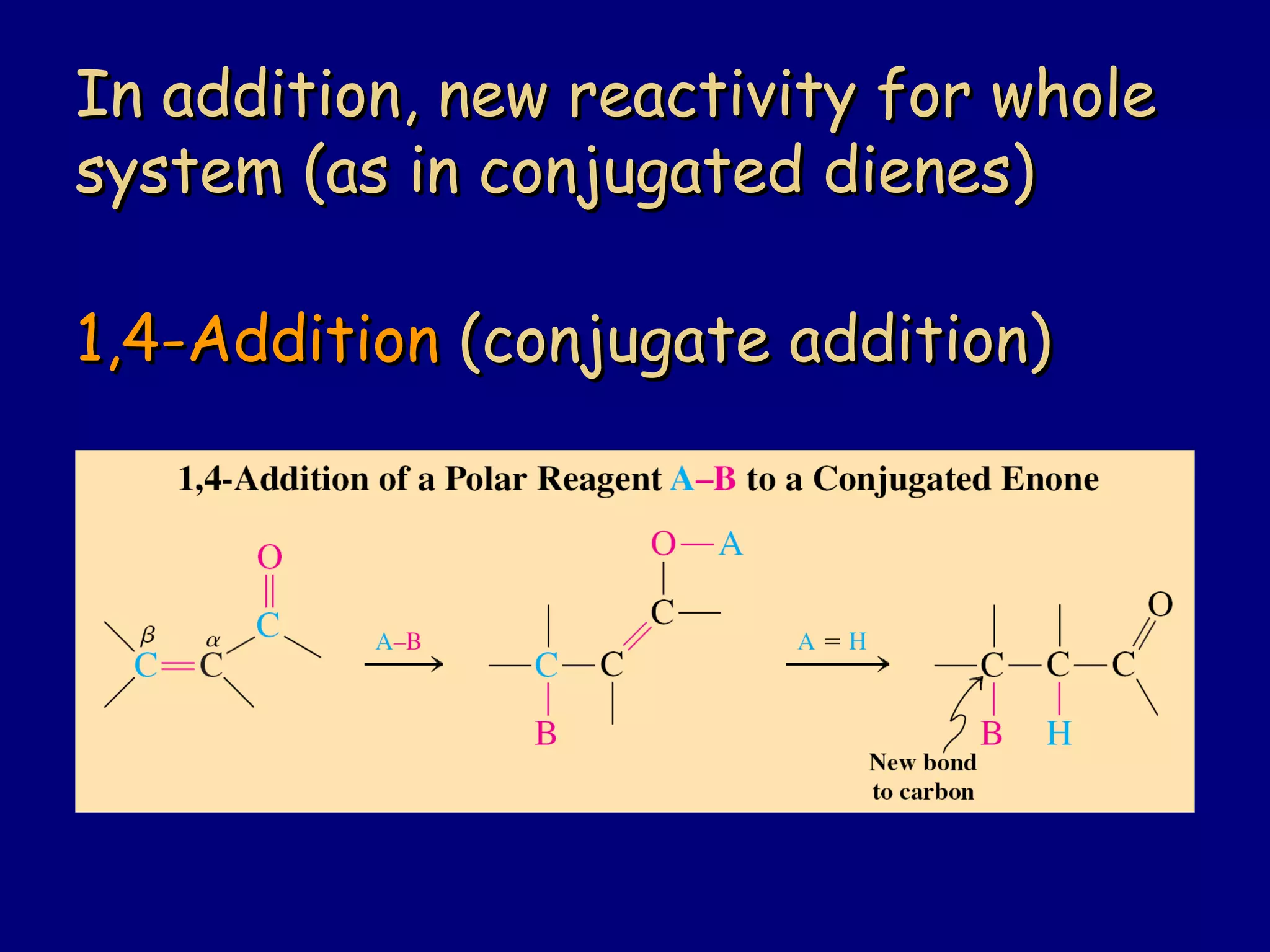
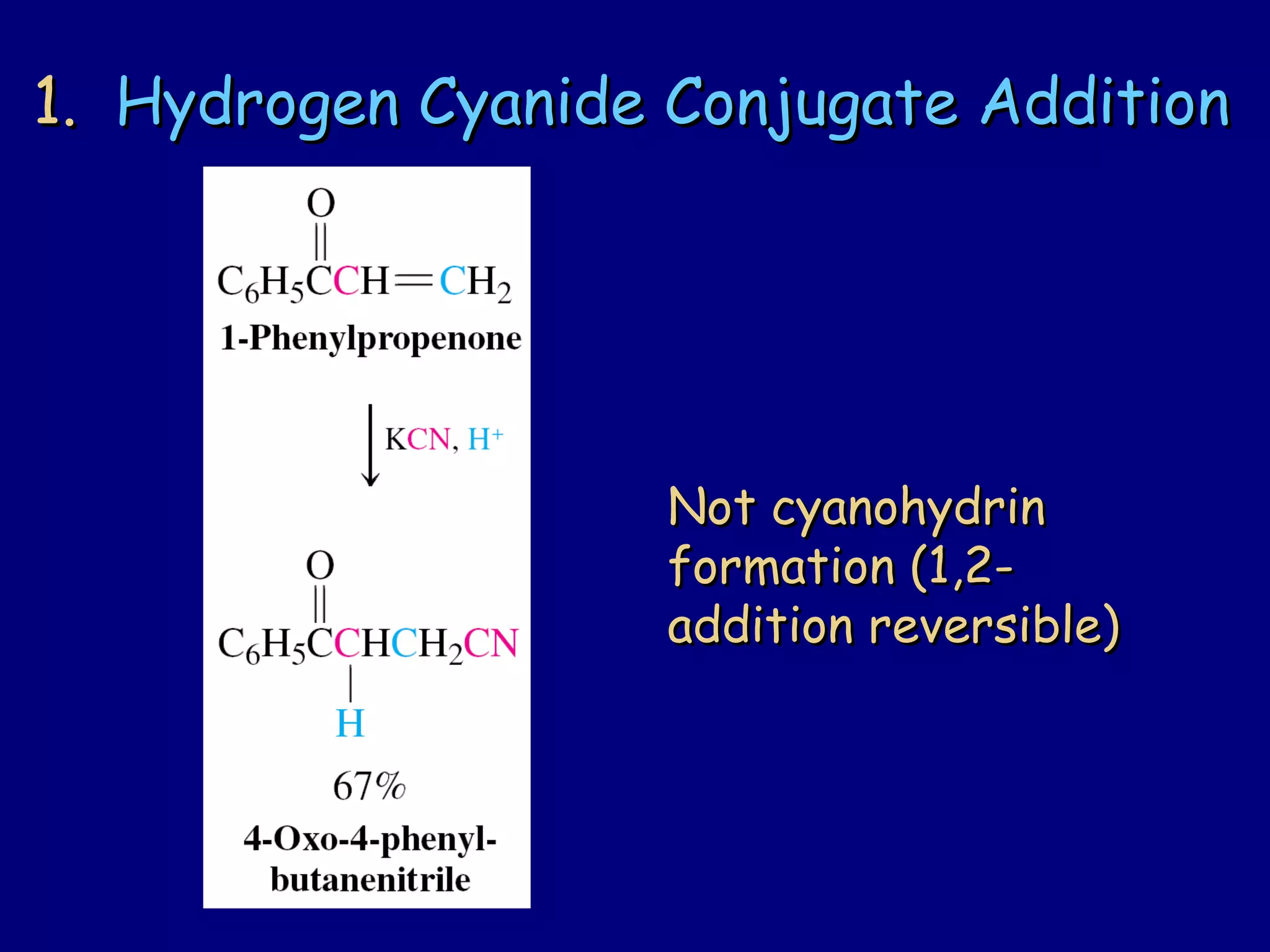
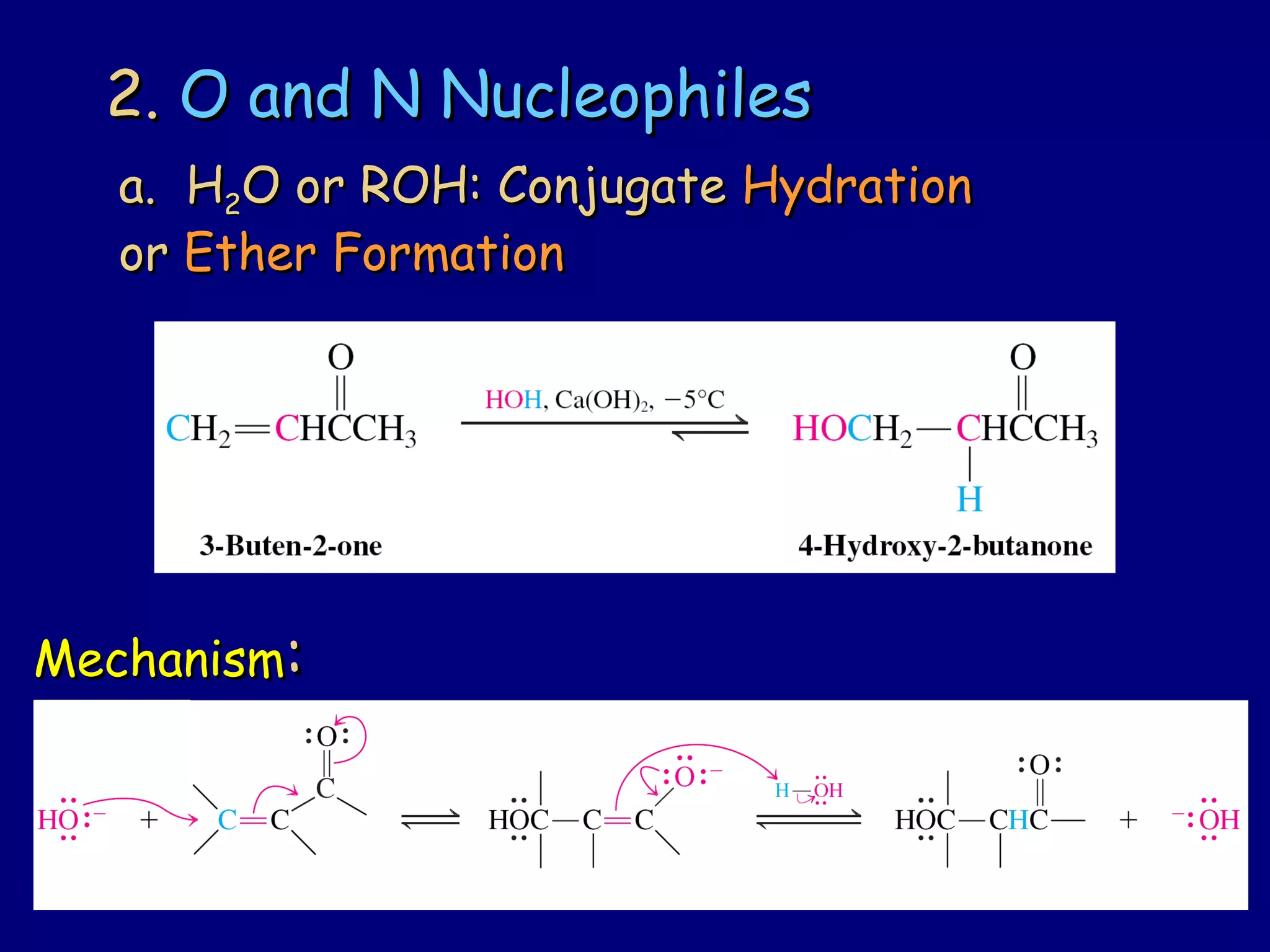
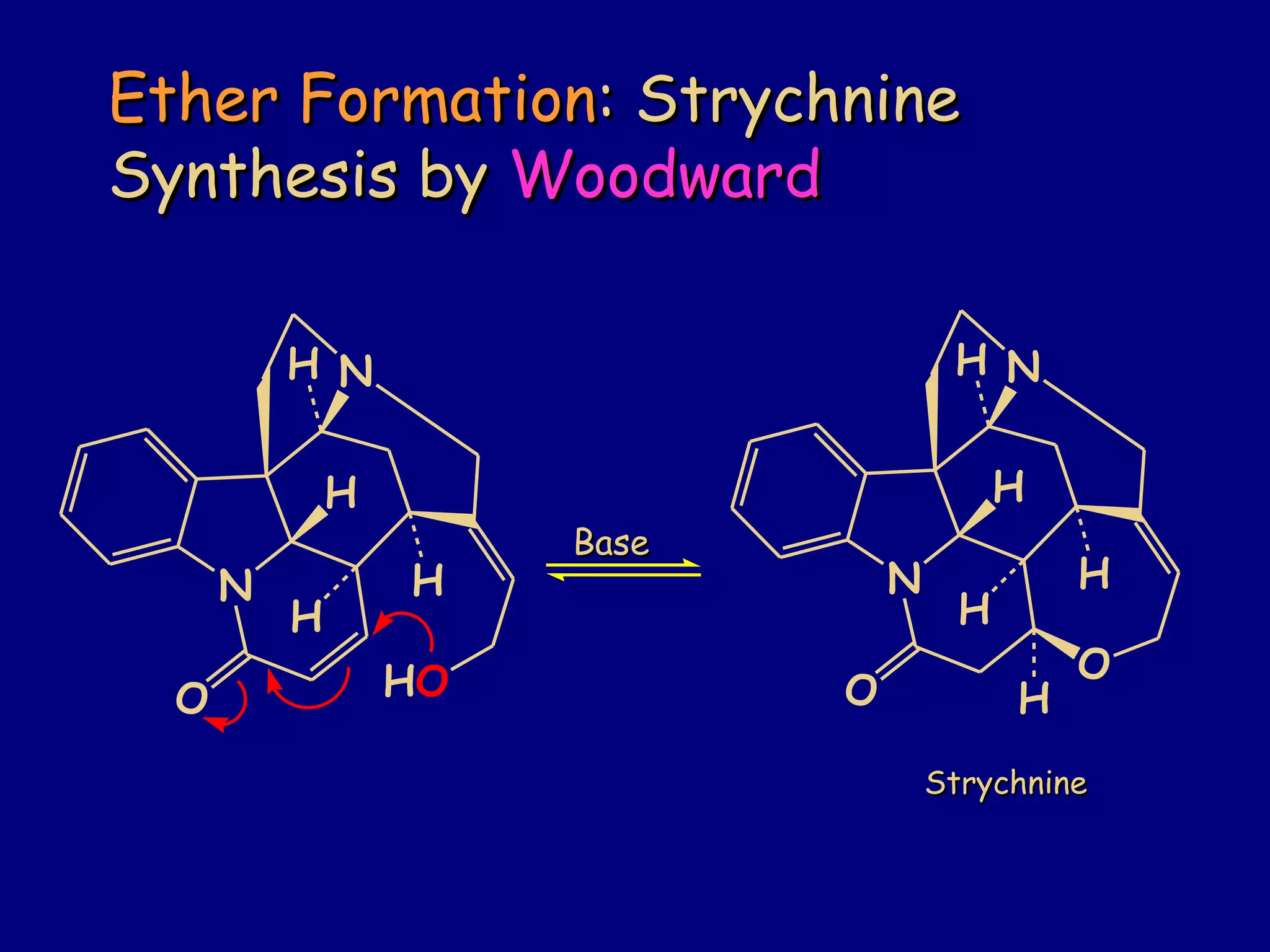
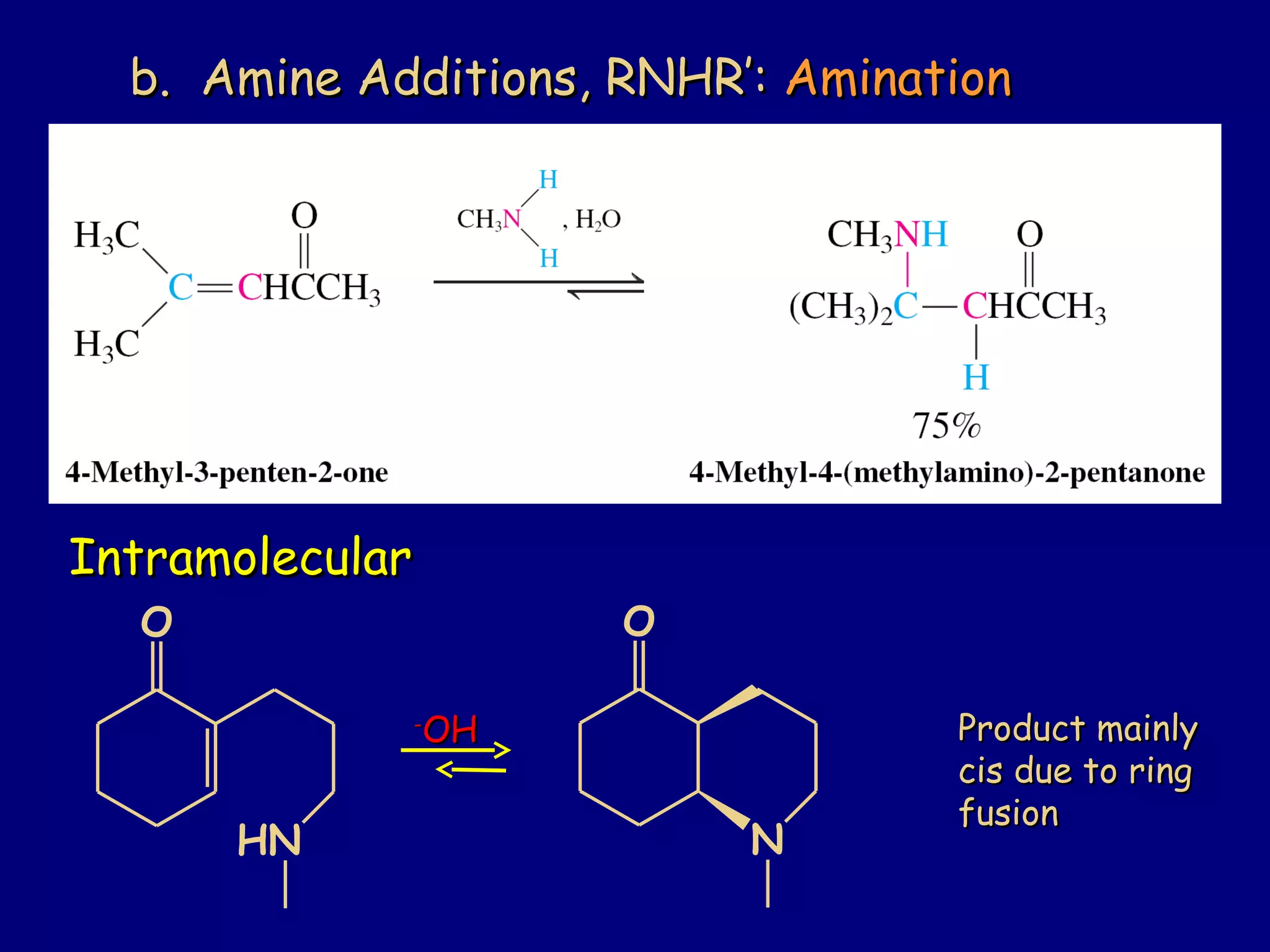
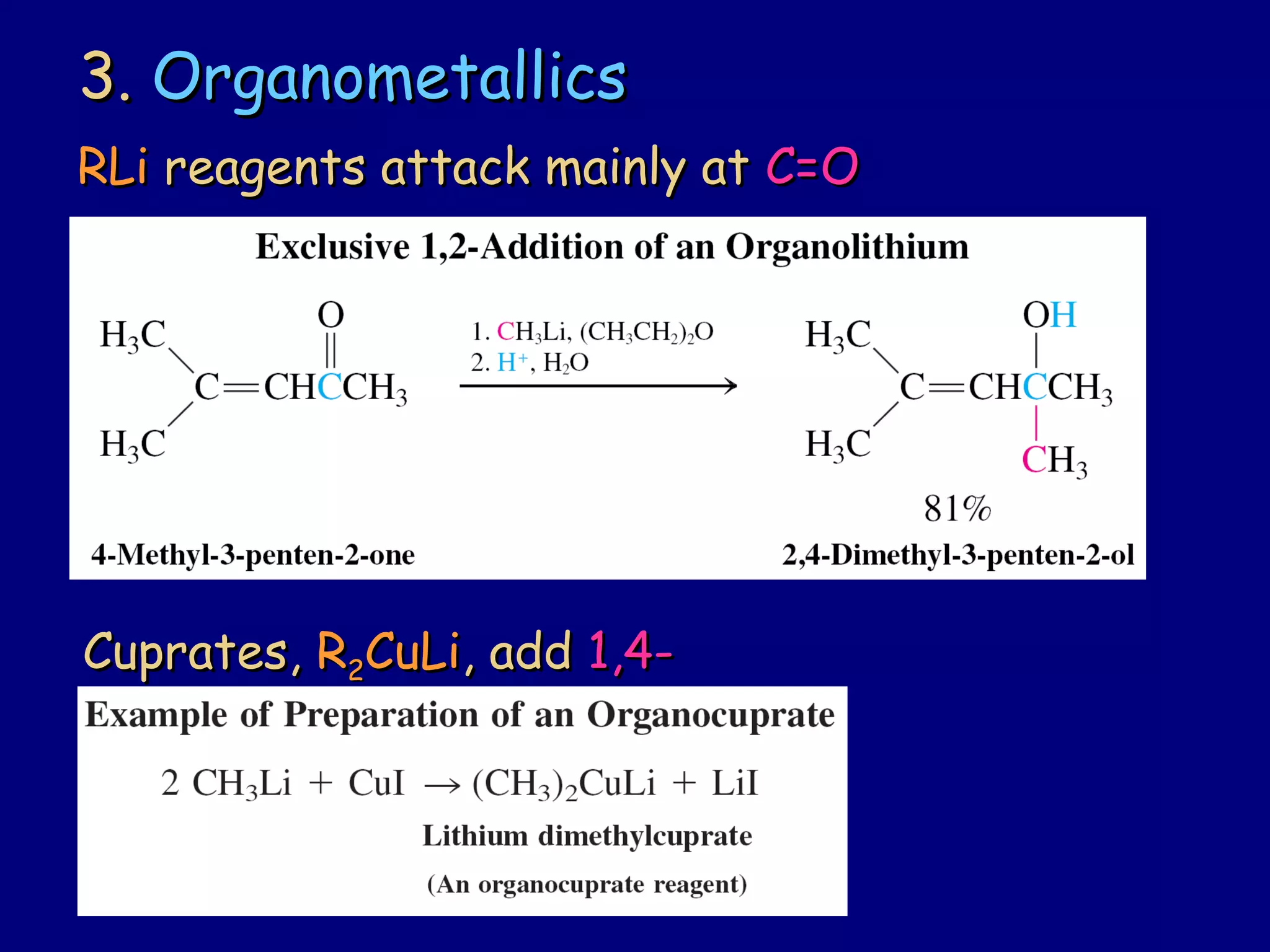
- α,β-Unsaturated carbonyls undergo conjugate additions and other reactions characteristic of alkenes and carbonyl groups. They can rearrange to the thermodynamic enol form.