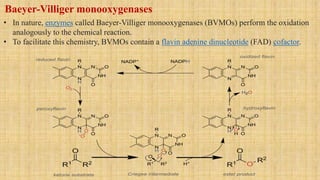
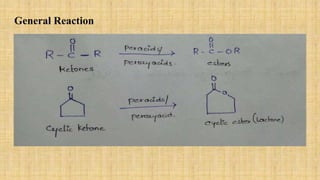
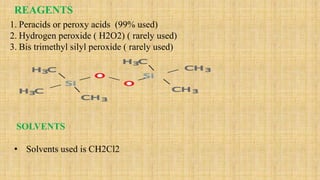
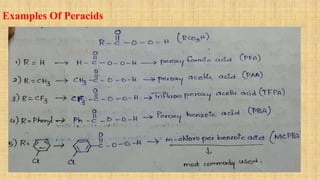
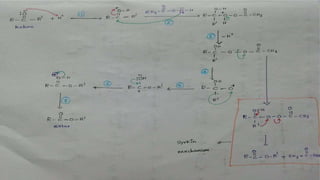
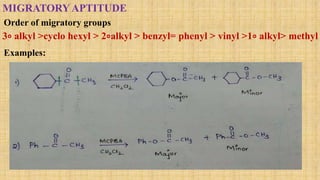
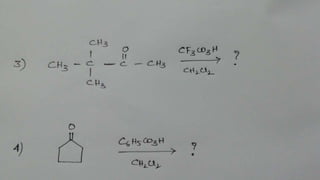
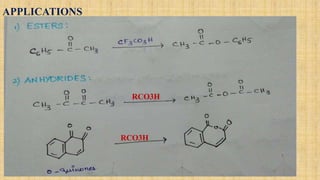
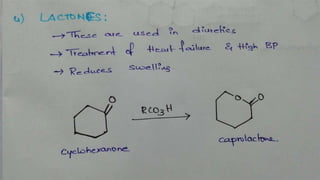
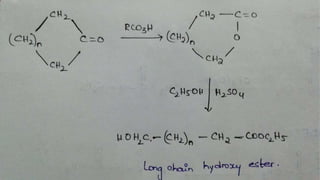
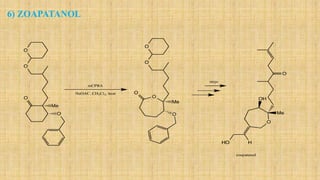
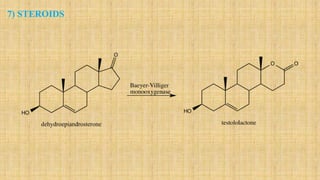
The Baeyer-Villiger oxidation reaction converts cyclic ketones to lactones and acyclic ketones to esters using a peroxy acid as the oxidizing agent. Adolf Baeyer and Victor Villiger first reported this reaction in 1899 using menthone and tetrahydrocarvone. The reaction involves the nucleophilic attack of the peroxy acid on the carbonyl carbon, followed by migration of an alkyl group to the oxygen and formation of the ester or lactone product. This reaction has been modified using hydrogen peroxide as the oxidant and various catalysts. It has applications in synthesizing pharmaceuticals, pheromones, and other fine chemicals.








![• Synthesis of 3-hydroxyindole-2-carboxylates.
• Conversion of non-activated [18F]fluorobenzaldehydes to [18F]fluorophenols with
high radiochemical yield.
• Synthesis of dibenzo-18-crown-6, dibenzo-21-crown-7, and dihydroxydibenzo-18-
crown-6.
• One-pot chemoenzymatic synthesis of g-butyrolactones.
• Metal-free synthesis of vinyl acetates.
• Silica-supported tricobalt tetraoxide (Co3O4/SiO2) catalysts have been employed for
the Baeyer–Villiger oxidation of cyclohexanone under Mukaiyama conditions
• Chemoenzymatic Baeyer–Villiger oxidation of cyclic ketones catalyzed
by Candida antarctica lipase B or Novozyme-435 suspended in an ionic liquid has
been studied.
• Kinetic resolution of racemic 2-substituted cyclopentanones has been achieved via
highly regio- and enantioselective Baeyer–Villiger oxidation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/baeyervilligeroxidation-210710061418/85/Baeyer-villiger-oxidation-20-320.jpg)