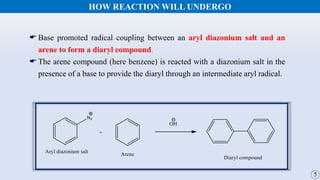
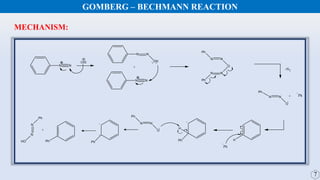
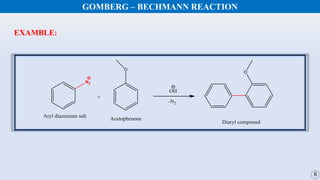
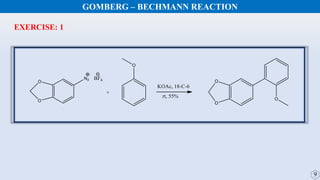
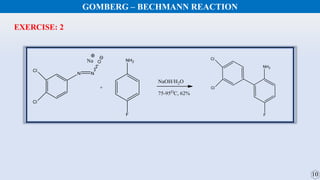
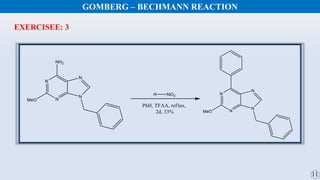
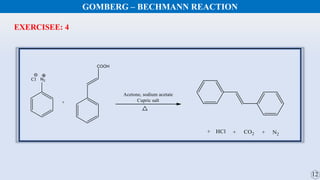
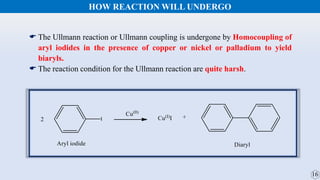
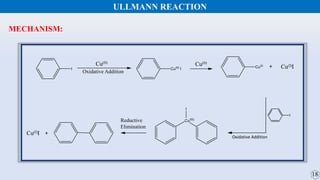
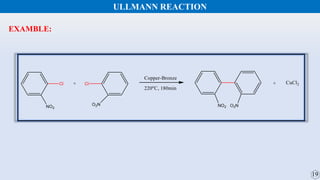
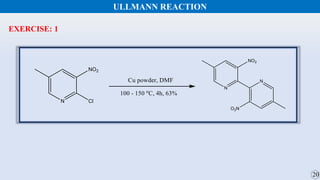
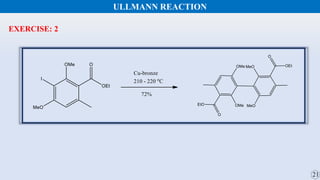
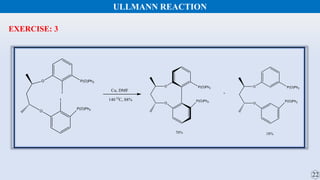
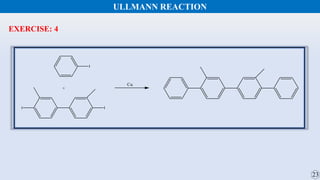
The document discusses the Gomberg-Bachmann reaction and the Ullmann reaction. The Gomberg-Bachmann reaction involves the base-promoted radical coupling of an aryl diazonium salt and an arene to form a diaryl compound. The mechanism proceeds through an aryl radical intermediate. The Ullmann reaction involves the copper-catalyzed coupling of two aryl halides to form a biaryl product. It proceeds through oxidative addition and reductive elimination steps involving a copper intermediate. Several examples and applications are provided for both reactions.